American football

American Football
American football, referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada and also known as gridiron football, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end.

The offense, the team with possession of the oval-shaped football, attempts to advance down the field by running with the ball or throwing it, while the defense, the team without possession of the ball, aims to stop the offense's advance and to take control of the ball for themselves.

The offense must advance the ball at least ten yards in four downs or plays; if they fail, they turn over the football to the defense, but if they succeed, they are given a new set of four downs to continue the drive.

Points are scored primarily by advancing the ball into the opposing team's end zone for a touchdown or kicking the ball through the opponent's goalposts for a field goal. The team with the most points at the end of the game wins.

American football evolved in the United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City., originating from the sports of soccer and rugby. The first American football game was played on November 6, 1869, between two college teams, Rutgers and Princeton, using rules based on the rules of soccer at the time. A set of rule changes drawn up from 1880 onward by Walter Camp, the "Father of American Football", established the snap, the line of scrimmage, eleven-player teams, and the concept of downs.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City., originating from the sports of soccer and rugby. The first American football game was played on November 6, 1869, between two college teams, Rutgers and Princeton, using rules based on the rules of soccer at the time. A set of rule changes drawn up from 1880 onward by Walter Camp, the "Father of American Football", established the snap, the line of scrimmage, eleven-player teams, and the concept of downs.

Later rule changes legalized the forward pass, created the neutral zone, and specified the size and shape of the football. The sport is closely related to Canadian football, which evolved in parallel with and at the same time as the American game, although its rules were developed independently from those of Camp.

Most of the features that distinguish American football from rugby and soccer are also present in Canadian football. The two sports are considered the primary variants of gridiron football.

American football is the most popular sport in the United States in terms of broadcast viewership audience. The most popular forms of the game are professional and college football, with the other major levels being high school and youth football.

As of 2022, nearly 1.04 million high-school athletes play the sport in the U.S., with another 81,000 college athletes in the NCAA and the NAIA. The National Football League (NFL) has one of the highest average attendance of any professional sports league in the world.

Its championship game, the Super Bowl, ranks among the most-watched club sporting events globally. In 2022, the league had an annual revenue of around $18.6 billion, making it the most valuable sports league in the world.

Other professional and amateur leagues exist worldwide, but the sport does not have the international popularity of other American sports like baseball or basketball; the sport maintains a growing following in the rest of North America, Europe, Brazil, and Japan.

Unlike most other ball sports, like basketball, baseball, and soccer, players of American football are not expected to play both offense and defense- usually, each player is assigned to either offense or defense, not both.

Soccer is a sport played between two teams of eleven players with a spherical ball. It is played by 250 million players in over 200 nations, making it the world's most popular sport. The game is played on a rectangular field with a goal at each end. The object of the game is to score by getting the ball into the opposing goal.

As such, each individual player usually only plays for, at most, about half of the game. In modern professional American football, it is very rare, although not unheard of, for players to play both offense and defense. Players who play on both sides of the ball are more common in high school and college football.

Etymology and Names
In the United States, American football is referred to as "football." The term "football" was officially established in the rulebook for the 1876 college football season, when the sport first shifted from soccer-style rules to rugby-style rules; although it could easily have been called "rugby" at this point, Harvard, one of the primary proponents of the rugby-style game, compromised and did not request the name of the sport be changed to "rugby".
In English-speaking countries where other codes of football are popular, such as the United Kingdom, Ireland, Canada, New Zealand, and Australia, the terms "gridiron" or "American football" are favored instead.

Early History
American football evolved from the sports of association football (soccer) and rugby football. Rugby football, like American football, is a sport where two competing teams vie for control of a ball, which can be kicked through a set of goalposts or run into the opponent's goal area to score points.

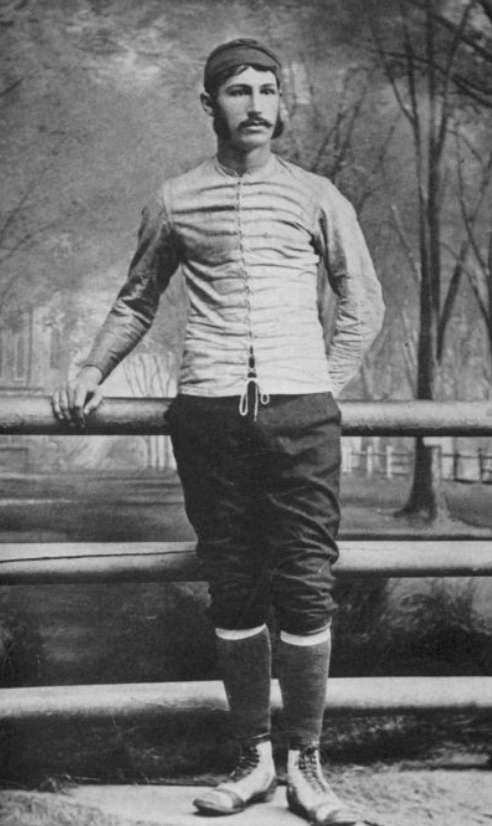
What is considered to be the first American football game was played on November 6, 1869 between Rutgers and Princeton, two college teams. The game was played between two teams of 25 players each and used a round ball that could not be picked up or carried. It could, however, be kicked or batted with the feet, hands, head or sides, with the ultimate goal being to advance it into the opponent's goal. Rutgers won the game 6 goals to 4. Collegiate play continued for several years in which matches were played using the rules of the host school. Representatives of Yale, Columbia, Princeton and Rutgers met on October 19, 1873 to create a standard set of rules for all schools to adhere to. Teams were set at 20 players each, and fields of 400 by 250 feet (122 m × 76 m) were specified. Harvard abstained from the conference, as they favored a rugby-style game that allowed running with the ball.

An 1875 Harvard-Yale game played under rugby-style rules was observed by two impressed Princeton athletes. These players introduced the sport to Princeton, a feat the Professional Football Researchers Association compared to "selling refrigerators to Eskimos." Princeton, Harvard, Yale and Columbia then agreed to intercollegiate play using a form of rugby union rules with a modified scoring system. These schools formed the Intercollegiate Football Association, although Yale did not join until 1879. Yale player Walter Camp, now regarded as the "Father of American Football," secured rule changes in 1880 that reduced the size of each team from 15 to 11 players and instituted the snap to replace the chaotic and inconsistent scrum.

Evolution of the Game
The introduction of the snap resulted in unexpected consequences. Prior to the snap, the strategy had been to punt if a scrum resulted in bad field position. However, a group of Princeton players realized that, as the snap was uncontested, they now could hold the ball indefinitely to prevent their opponent from scoring. In 1881, both teams in a game between Yale-Princeton used this strategy to maintain their undefeated records. Each team held the ball, gaining no ground, for an entire half, resulting in a 0-0 tie. This "block game" proved extremely unpopular with the spectators and fans of both teams.

A rule change was necessary to prevent this strategy from taking hold, and a reversion to the scrum was considered. However, Camp successfully proposed a rule in 1882 that limited each team to three downs, or tackles, to advance the ball five yards. Failure to advance the ball the required distance within those three downs would result in control of the ball being forfeited to the other team. This change effectively made American football a separate sport from rugby, and the resulting five-yard lines added to the field to measure distances made it resemble a gridiron in appearance.

Other major rule changes included a reduction of the field size to 110 by 53.333 yards (100.584 m × 48.768 m), and the adoption of a scoring system that awarded four points for a touchdown, two for a safety and a goal following a touchdown, and five for a goal from field; additionally, tackling below the waist was legalized. The last, and arguably most important innovation, which would at last make American football uniquely "American", was the legalization of interference, or blocking, a tactic which was highly illegal under the rugby-style rules.

Despite these new rules, football remained a violent sport. Dangerous mass-formations, which involved interlocking interference, like the flying wedge resulted in serious injuries and deaths. A 1905 peak of 19 fatalities nationwide resulted in a threat by President Theodore Roosevelt to abolish the game unless major changes were made.

26th president of the United States Theodore Roosevelt
In response, sixty-two colleges and universities met in New York City to discuss rule changes on December 28, 1905, and these proceedings resulted in the formation of the Intercollegiate Athletic Association of the United States, later named the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA).

The legal forward pass was introduced in 1906, although its impact was initially limited due to the restrictions placed on its use. Other rule changes introduced that year included the reduction of the time of play from 70 to 60 minutes and the increase of the distance required for a first down from 5–10 yards (4.6–9.1 m). To reduce infighting and dirty play between teams, the neutral zone was created along the width of the football. Scoring was also adjusted: field goals were lowered to three points in 1909 and touchdowns were raised to six points in 1912.

The field was also reduced to 100 yards (91 m) long, but two 10-yard-long end zones were created, and teams were given four downs instead of three to advance the ball 10 yards (9.1 m). The roughing-the-passer penalty was implemented in 1914, and eligible players were first allowed to catch the ball anywhere on the field in 1918.

The Professional Era
On November 12, 1892, when William "Pudge" Heffelfinger was paid $500 to play a game for the Allegheny Athletic Association in a match against the Pittsburgh Athletic Club. This is the first recorded instance of a player being paid to participate in a game of American football, although many athletic clubs in the 1880s offered indirect benefits, such as helping players attain employment, giving out trophies or watches that players could pawn for money, or paying double in expense money. Despite these extra benefits, the game had a strict sense of amateurism at the time, and direct payment to players was frowned upon, if not outright prohibited.

Over time, professional play became increasingly common, and with it came rising salaries and unpredictable player movement, as well as the illegal payment of college players who were still in school. The National Football League (NFL), a group of professional teams that was originally established in 1920 as the American Professional Football Association, aimed to solve these problems.

This new league's stated goals included an end to bidding wars over players, prevention of the use of college players, and abolition of the practice of paying players to leave another team. By 1922, the NFL had established itself as the premier professional football league.

The dominant form of football at the time was played at the collegiate level, but the upstart NFL received a boost to its legitimacy in 1925 when an NFL team, the Pottsville Maroons, defeated a team of Notre Dame all-stars in an exhibition game. A greater emphasis on the passing game helped professional football to further distinguish itself from the college game during the late 1930s.

Football in general became increasingly popular following the 1958 NFL Championship game, a match between the Baltimore Colts and the New York Giants that is still referred to as the "Greatest Game Ever Played". The game, a 23–17 overtime victory by the Colts, was seen by millions of television viewers and had a major impact on the popularity of the sport. This, along with the innovations introduced by the new American Football League (AFL) in the early 1960s, helped football to become the most popular sport in the United States by the mid-1960s.

The rival American Football League arose in 1960 and challenged the NFL's dominance. The AFL began in relative obscurity but eventually thrived, with an initial television contract with the ABC network. The AFL's existence forced the conservative NFL to expand to Dallas and Minnesota in an attempt to destroy the new league.
Meanwhile, the AFL introduced many new features to Professional Football in the United States: official time on the scoreboard clock, rather than on a watch in the referee's pocket, as the NFL did; optional two-point conversions by pass or run after touchdowns; names on the jerseys of players; and several others, including expansion of the role of minority players, actively recruited by the league in contrast to the NFL. The AFL also signed several star college players that had also been drafted by NFL teams.

Competition for players heated up in 1965, when the AFL New York Jets signed rookie Joe Namath to a then-record US $437,000 contract. A five-year, $40 million NBC television contract followed, which helped to sustain the young league. The bidding war for players ended in 1966, when NFL owners approached the AFL regarding a merger, and the two leagues agreed on one that would take full effect in 1970.

This agreement provided for a common draft that would take place each year, and it instituted an annual World Championship game to be played between the champions of each league. That game began play at the end of the 1966 season. Once the merger was completed, it was no longer a championship game between two leagues, and reverted to the NFL championship game, which came to be known as the Super Bowl.

College football maintained a tradition of postseason bowl games. Each bowl game would be associated with a particular conference, and earning a spot in a bowl game was the reward for winning a conference. This arrangement was profitable, but it tended to prevent the two top-ranked teams from meeting in a true national championship game, as they would normally be committed to the bowl games of their respective conferences.

Several systems have been used since 1992 to determine a national champion of college football. The first was the Bowl Coalition, in place from 1992 to 1994. This was replaced in 1995 by the Bowl Alliance, which gave way in 1997 to the Bowl Championship Series (BCS). The BCS arrangement proved to be controversial, and was replaced in 2014 by the College Football Playoff (CFP).

The football itself is an oval ball, similar to the balls used in rugby or Australian rules football. At all levels of play, the football is inflated to 12 1⁄2 to 13 1⁄2 pounds per square inch (psi) and weighs 14 to 15 ounces (397 to 425 grams); beyond that, the exact dimensions vary slightly. In professional play the ball has a long axis of 11 to 11 1⁄4 inches, a long circumference of 28 to 28 1⁄2 inches, and a short circumference of 21 to 21 1⁄4 inches, while in college and high school play the ball has a long axis of 10 7⁄8 to 11 7⁄16 inches, a long circumference of 27 3⁄4 to 28 1⁄2 inches, and a short circumference of 20 3⁄4 to 21 1⁄4 inches.

Safety
Football is a full-contact sport, and injuries are relatively common. Most injuries occur during training sessions, particularly ones that involve contact between players.

To try to prevent injuries, players are required to wear a set of equipment. At a minimum players must wear a football helmet and a set of shoulder pads, but individual leagues may require additional padding such as thigh pads and guards, knee pads, chest protectors, and mouth guards.

Most injuries occur in the lower extremities, particularly in the knee, but a significant number also affect the upper extremities.

The most common types of injuries are strains, sprains, bruises, fractures, dislocations, and concussions.
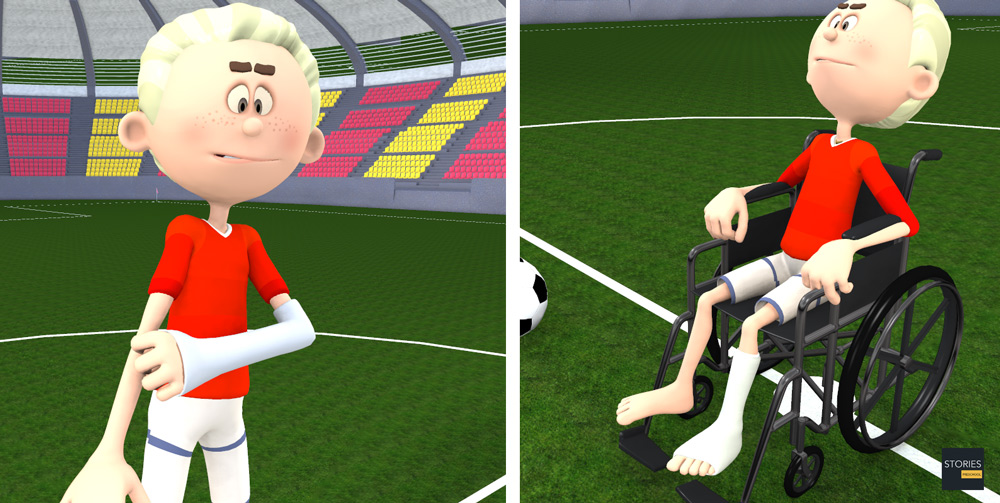

Repeated concussions can increase a person's risk in later life for chronic traumatic encephalopathy and mental health issues such as dementia, Parkinson's disease, and depression.

Concussions are often caused by helmet-to-helmet or upper-body contact between opposing players, although helmets have prevented more serious injuries such as skull fractures.

Various programs are aiming to reduce concussions by reducing the frequency of helmet-to-helmet hits; USA Football's "Heads Up Football" program is aiming to reduce concussions in youth football by teaching coaches and players about the signs of a concussion, the proper way to wear football equipment and ensure it fits, and proper tackling methods that avoid helmet-to-helmet contact.

However, a study in the Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine found that Heads Up Football was ineffective; the same study noted that more extensive reforms implemented by Pop Warner Little Scholars and its member teams were effective in significantly reducing concussion rates.

A 2018 study performed by the VA Boston Healthcare System and the Boston University School of Medicine found that tackle football before age 12 was correlated with earlier onset of symptoms of CTE, but not with symptom severity.

More specifically, each year a player played tackle football under age 12 predicted earlier onset of cognitive, behavioral, and mood problems by an average of two and a half years.

SPORTS

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia articles "American Football" and "American Football Rules", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.











