Historic Battles of the World
Battles are decided by various factors. The number and quality of combatants and equipment, the skill of the commanders of each army, and the terrain advantages are among the most prominent factors. A unit may charge with high morale but less discipline and still emerge victorious. This tactic was effectively used by the early French Revolutionary Armies.
Hypothetical World War III

Since the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki during the Second World War, there has been a widespread and prolonged fear of an upcoming Third World War between nuclear-armed powers. World War 3 is generally considered a hypothetical successor to World War 2 and is often suggested to become a nuclear war, devastating in nature and likely much more violent than World War I and World War II combined.
Russian Invasion of Ukraine (2022–)
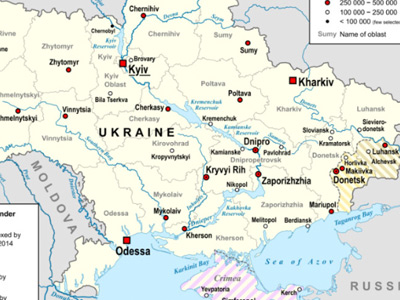
On 24 February 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War that began in 2014. The invasion caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II, with around 7.3 million Ukrainians fleeing the country and a third of the population displaced. It has also caused global food shortages. View Historic Battles »
Persian Gulf Crisis (2019–2021)

The 2019–2021 Persian Gulf Crisis is an ongoing state of heightened military tensions between the Islamic Republic of Iran and the United States of America, along with their respective allies, in the Persian Gulf region. Starting in early May 2019, the U.S. began a buildup of its military presence in the region.
Iraqi Civil War (2014–2017)

The War in Iraq was an armed conflict between Iraq and its allies and the Islamic State which began in 2013 and ended in December 2017. Following December 2013, the insurgency escalated into a full-scale war following the conquest of Ramadi, Fallujah, Tikrit and other towns in the major areas of northern Iraq by the Islamic State.
Iraq War (2003–2011)

The Iraq War was a protracted armed conflict in Iraq that began with the invasion of Iraq by the United States–led coalition that overthrew the Iraqi government of Saddam Hussein. The conflict continued for much of the next decade as an insurgency emerged to oppose the coalition forces and the post-invasion Iraqi government. View Historic Battles »
War in Darfur (2003–2020)
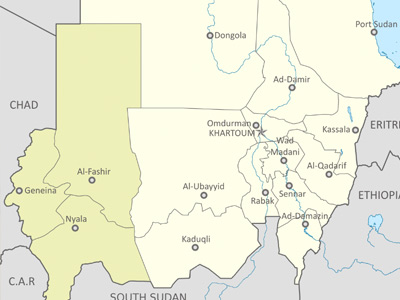
The War in Darfur, also nicknamed the Land Cruiser War, is a major armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan that began in February 2003 when the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) rebel groups began fighting against the government of Sudan. View Historic Battles »
Second Congo War (1998-2003)

The Second Congo War, also known as the Great War of Africa or the Great African War and sometimes referred to as the African World War, began in the Democratic Republic of the Congo in August 1998, little more than a year after the First Congo War, and involved some of the same issues.
Russian Constitutional Crisis (1993)

The 1993 Russian Constitutional Crisis, also known as the 1993 October Coup, Black October, the Shooting of the White House or Ukaz 1400, was a political stand-off and a constitutional crisis between the Russian president Boris Yeltsin and the Russian parliament that was resolved by Yeltsin using military force.
Gulf War (1990–1991)

The Gulf War was an armed campaign waged by a United States-led coalition of 35 countries against Iraq in response to the Iraqi invasion and annexation of Kuwait. The Iraqi military invaded the neighbouring State of Kuwait on 2 August 1990 and fully occupied the country within two days.
Vietnam War (1955–1975)
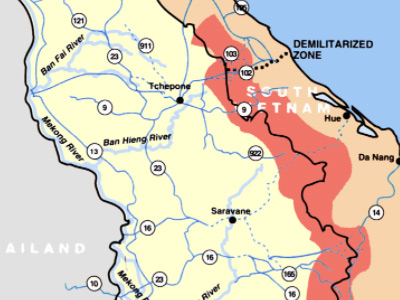
The North Vietnamese army was supported by the Soviet Union, China and other communist allies and the South Vietnamese army was supported by the United States, South Korea, Australia, Thailand and other anti-communist allies. View Historic Battles »
Korean War 한국전쟁 (1950-1953)

The Korean War began when North Korea invaded South Korea on 25 June 1950. The United Nations (UN), with the United States as the principal force, came to the aid of South Korea. China came to the aid of North Korea, and the Soviet Union gave some assistance during the war. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Taegu (1950 August)

The Battle of Taegu was an engagement between UN and North Korean forces early in the Korean War, with fighting continuing from August 5–20, 1950 around the city of Taegu, South Korea. It was a part of the Battle of Pusan Perimeter, and was one of several large engagements fought simultaneously. View Historic Battles »
Cold War (1947–1991)

The Cold War was a state of geopolitical tension after World War II between powers in the Eastern Bloc (the Soviet Union and its satellite states) and powers in the Western Bloc (the United States, its NATO allies and others). The first phase of the Cold War began in the first two years after the end of the Second World War in 1945. View Historic Battles »
World War II (1939-1945)

World War II (WWII or WW2), was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's nations-eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. It was the most widespread war in history, and directly involved more than 100 million people from over 30 countries. View Historic Battles »
Spanish Civil War (1936-1939)

Was fought between the Republicans versus the Nationalists, a falangist, Carlist and a largely aristocratic conservative group led by General Francisco Franco. Although the war is often portrayed as a struggle between democracy and fascism, some historians consider it more accurately described as a struggle between leftist revolution and rightist counterrevolution. View Historic Battles »
Russian Civil War (1917-1922)
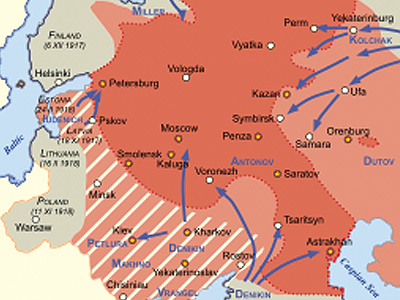
The Russian Civil War was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the overthrowing of the monarchy and the new republican government's failure to maintain stability, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future.
World War I (1914-1918)

World War I (WWI or WW1), also known as the First World War, or the Great War, was a global war originating in Europe that lasted from 28 July 1914 to 11 November 1918. More than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, were mobilized in one of the largest wars in history. Over 9 million combatants and 7 million civilians died as a result of the war. View Historic Battles »
World War
A world war is a war involving many or most of the world's most powerful and populous countries. World wars span multiple countries on multiple continents, with battles fought in multiple theatres. The term is applied to the two major international conflicts that occurred during the twentieth century: the First World War (1914 — 1918) and the Second World War (1939 — 1945). View Historic Battles »
Second Balkan War (1913 June)
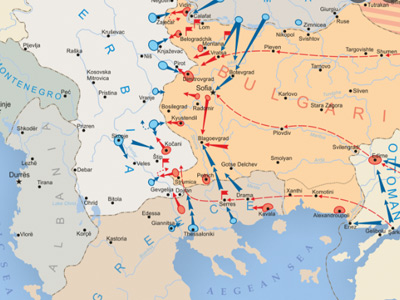
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 29 June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies repulsed the Bulgarian offensive and counter-attacked, entering Bulgaria.
First Balkan War (1912-1913)

The First Balkan War lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and involved actions of the Balkan League against the Ottoman Empire. The Balkan states' combined armies overcame the initially numerically inferior and strategically disadvantaged Ottoman armies and achieved rapid success.
Mexican Revolution (1910-1920)

The Mexican Revolution was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction of the Federal Army and its replacement with a revolutionary army, as well as the transformation of Mexican culture.
1905 Russian Revolution (1905-1907)

The Russian Revolution of 1905, also known as the First Russian Revolution, occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed against the Tsar, nobility and ruling class.
Russo-Japanese War 日露戦争 (1904–1905)

The Russo-Japanese War was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and Korea. Japan had become the rising Asian power and had proven that its military could combat the major powers in Europe with success. View Historic Battles »
British Expedition to Tibet (1903-1904)

The British expedition to Tibet, also known as the Younghusband expedition, began in December 1903 and lasted until September 1904. The expedition was effectively a temporary invasion by British Indian Armed Forces under the auspices of the Tibet Frontier Commission, whose purported mission was to establish diplomatic relations.
Russian Invasion of Manchuria (1900)

The Russian Invasion of Manchuria occurred in the aftermath of the First Sino-Japanese War when concerns regarding Qing China's defeat by the Empire of Japan, and Japan's brief occupation of Liaodong, caused the Russian Empire to speed up their long held designs for imperial expansion across Eurasia.
Battle of Manila Bay (1898 May)

The American Asiatic Squadron under Commodore George Dewey engaged and destroyed the Spanish Pacific Squadron. The battle took place in Manila Bay in the Philippines, and was the first major engagement of the Spanish–American War. The battle was one of the most decisive naval battles in history and marked the end of the Spanish colonial period in Philippine history.
Battle of Shiroyama 城山の戦い (1877 September)

The final battle of the Satsuma Rebellion, where the heavily outnumbered samurai under Saigō Takamori made their last stand against Imperial Japanese Army troops under the command of Generals Yamagata Aritomo and Kawamura Sumiyoshi. The battle culminated in the annihilation of Saigō's army as well as his death, marking the end of the Satsuma Rebellion. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Tabaruzaka (1877 March)

Battle of Tabaruzaka was a major battle of the Satsuma Rebellion. It took place in March 1877, on the island of Kyushu, Japan, concurrently to the Siege of Kumamoto Castle. The battle began when troops loyal to the Imperial Meiji government seeking to break the Siege of Kumamoto Castle met rebel Satsuma samurai forces seeking to capture the main road out of Kumamoto. View Historic Battles »
Franco-Prussian War (1870-1871)

Often referred to in France as the War of 1870, was a conflict between the Second French Empire of Napoleon III and the German states of the North German Confederation led by the Kingdom of Prussia. The conflict was caused by Prussian ambitions to extend German unification and French fears of the shift in the European balance of power that would result if the Prussians succeeded. View Historic Battles »
Boshin War 戊辰戦争 (1868-1869)

Boshin War sometimes known as the Japanese Revolution, was a civil war in Japan, fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and those seeking to return political power to the Imperial Court. When the Boshin War began, Japan was already modernizing, following the same course of advancement as that of the industrialized Western nations. View Historic Battles »
French Campaign against Korea 병인양요 (1866)

The French campaign against Korea was an 1866 punitive expedition undertaken by the Second French Empire in retaliation for the earlier Korean execution of several French Catholic missionaries. The encounter over Ganghwa Island lasted nearly six weeks. The result was a French retreat and a check on French influence in the region. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Lissa (1866 July)

The battle in the Adriatic Sea was a significant victory for an Austrian Empire force over a numerically superior Italian force. It was the first major sea battle between ironclads and one of the last to involve deliberate ramming. The Italian navy fired roughly 1450 shots during the engagement, but failed to sink any Austrian ship while losing two ironclads.
Battle of Königgrätz (1866 July)

The Battle of Königgrätz was the decisive battle of the Austro-Prussian War in which the Kingdom of Prussia defeated the Austrian Empire. Prussian forces, totaling around 285,000 troops, used their superior training and tactical doctrine and the Dreyse needle gun to win the battle and the entire war at Königgrätz on their own.
Battle of Langensalza (1866 June)

The Hanoverians won the battle but were then surrounded by a larger and reinforced Prussian army. Unable to link up with their Bavarian allies to the south, the Hanoverians surrendered. That marked the demise of the Hanoverian army and the annexation of Hanover into the burgeoning Prussia, which systematically unified Germany into the modern nation state.
Battle of Gettysburg (1863 July)

The battle was fought by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. The battle involved the largest number of casualties of the entire war and is often described as the war's turning point due to the Union's decisive victory. President Lincoln used the dedication ceremony for the Gettysburg National Cemetery to honor the fallen Union soldiers and redefine the purpose of the war in his historic Gettysburg Address.
Siege of Vicksburg (1863 May-July)

The siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate Army of Mississippi, led by Lt. Gen. John C. Pemberton, into the defensive lines surrounding the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi.
Battle of Antietam (1862 September)

The Battle of Antietam was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862. Part of the Maryland Campaign, it was the first field army–level engagement in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War to take place on Union soil. It remains the bloodiest day in American history, with a combined tally of 22,717 dead, wounded, or missing. Although the Union army suffered heavier casualties than the Confederates, the battle was a major turning point in the Union's favor.
American Civil War (1861-1865)

The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.
Battle of Tetuán (1860 February)

The Battle of Tetuán was fought on 4 to 6 February 1860, near Tetuán, Morocco, between a Spanish army sent to North Africa and the tribal levies which at the time made up the Moroccan Army. The battle was part of the Spanish-Moroccan War of 1859–1860. Spanish artillery inflicted heavy losses on the Moroccan ranks; the Moroccan forces that remained took refuge in Tetuán. The city fell on 6 February 1860. A week of further fighting followed before hostilities ceased.
Battle of Solferino (1859 June)

Battle of Solferino resulted in the victory of the allied French Army under Napoleon III and Sardinian Army under Victor Emmanuel II against the Austrian Army under Emperor Franz Joseph I. It was the last major battle in world history where all the armies were under the personal command of their monarchs. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Magenta (1859 June)

The Battle of Magenta was fought on 4 June 1859 during the Second Italian War of Independence, resulting in a French-Sardinian victory under Napoleon III against the Austrians under Marshal Ferencz Gyulai. The battle of Magenta was not particularly large, but it was a decisive victory for the French-Sardinian forces. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Malakoff (1855 September)

Battle of Malakoff was a major battle during the Crimean War, fought between French-British forces against Russia on 8 September 1855 as a part of the Siege of Sevastopol. The French army under General MacMahon successfully stormed the Malakoff redoubt, whereas a simultaneous British attack on the Redan to the south of the Malakoff was repulsed. View Historic Battles »
Battle of the Chernaya (1855 August)

Battle of the Chernaya was a battle by the Chornaya River fought during the Crimean War on August 16, 1855. The battle was fought between Russian troops and a coalition of French, Sardinian and Ottoman troops. The Chornaya River is on the outskirts of Sevastopol. The battle ended in a Russian retreat and a victory for the French, Sardinians and Turks. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Balaclava (1854 October)

The Battle of Balaclava was part of the Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55), an Allied attempt to capture the port and fortress of Sevastopol, Russia's principal naval base on the Black Sea. The engagement followed the earlier Allied victory in September at the Battle of the Alma, where the Russian General Menshikov had positioned his army in an attempt to stop the Allies progressing south towards their strategic goal.
Battle of the Alma (1854 September)

Battle of the Alma was a battle in the Crimean War between an allied expeditionary force made up of French, British, and Turkish forces against Russian forces defending the Crimean Peninsula on 20 September 1854. The allies had made a surprise landing in Crimea on 14 September. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Cetate (1853-1854)

The Battle of Cetate was fought during the Crimean War. In this battle a large Ottoman force under Ahmed Pasha attempted to capture the village of Cetate in Wallachia, controlled by the troops of Colonel Alexander Baumgarten, but were unsuccessful. The battle at Cetate was ultimately indecisive. After heavy casualties on both sides, both armies were back at their start positions. View Historic Battles »
Second Battle of Komárom (1849 July)

The Second Battle of Komárom, also known as the Battle of Ács, took place between the Hungarian Revolutionary Army and the Imperial Austrian Army of the Austrian Empire; a contingent of almost 12,000 Russian Empire troops. The Austrian army outnumbered the Hungarian troops two to one, and had a multitude of infantry, light infantry, heavy cavalry, and better weapons.
Battle of Mazagran (1840 February)

The Battle of Mazagran was a combat between Arab and Berber forces against French troops during the French conquest of Algeria. The small French contingent, holed up in a fortification at Mazagran, near the port city of Mostaganem, withstood several days of assault by `Abd al-Qādir 's troops.
First Carlist War (1833-1839)

The First Carlist War was a civil war in Spain from 1833 to 1839, fought between factions over the succession to the throne and the nature of the Spanish monarchy. It was fought between supporters of the regent, Maria Christina, acting for Isabella II of Spain, and those of the late king's brother, Carlos de Borbón (or Carlos V). The Carlists supported return to an absolute monarchy. View Historic Battles »
Belgian Revolution (1830-1831)

The Belgian Revolution was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium. The Dutch accepted the decision of the London conference and Belgian independence in 1839 by signing the Treaty of London.
July Revolution (1830 July)

The French Revolution of 1830 was a second French Revolution after the first in 1789. It led to the overthrow of King Charles X, the French Bourbon monarch, and the ascent of his cousin Louis Philippe, Duke of Orléans. After 18 precarious years on the throne, Louis-Philippe was overthrown in the French Revolution of 1848.
French Conquest of Algeria (1830-1903)

In 1827, an argument between ruler of the Deylik of Algiers and the French consul escalated into a blockade, following which the July Monarchy of France invaded and quickly seized Algiers in 1830, and seized other coastal communities. Amid internal political strife in France, decisions were repeatedly taken to retain control of the territory.
Portuguese Civil War (1828-1834)

The Portuguese Civil War was a war between progressive constitutionalists and authoritarian absolutists in Portugal over royal succession that lasted from 1828 to 1834. Embroiled parties included the Kingdom of Portugal, Portuguese rebels, the United Kingdom, France, the Church of Rome, and Spain. View Historic Battles »
Burning of Washington (1814 August)

The Burning of Washington was a British invasion of Washington City, the capital of the United States. It is the only time since the American Revolutionary War that a foreign power has captured and occupied the capital of the United States. That night, British forces set fire to multiple government and military buildings, including the Presidential Mansion, the Capitol building, as well as other facilities of the U.S. government.
Battle of Leipzig (1813 October)

Also known as the Battle of the Nations, was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813 at Leipzig, Saxony. The Coalition armies of Austria, Prussia, Sweden, and Russia decisively defeated the Grande Armée of French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. Decisively defeated again, Napoleon was compelled to return to France while the Sixth Coalition kept up its momentum, dissolving the Confederation of the Rhine and invading France early the next year.
French Invasion of Russia (1812 June-December)

The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental blockade of the United Kingdom. Napoleon's invasion of Russia is one of the best studied military campaigns in history and is listed among the most lethal military operations in world history.
Battle of Raszyn (1809 April)

The first Battle of Raszyn was fought on 19 April 1809 between armies of the Austrian Empire under Archduke Ferdinand Karl Joseph of Austria-Este and the Duchy of Warsaw under Józef Antoni Poniatowski, as part of the War of the Fifth Coalition in the Napoleonic Wars. The battle was not decisive, but it did result in the Austrians obtaining their goal by capturing the Polish capital Warsaw.
Peninsular War (1807–1814)

The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. The war on the peninsula lasted until the Sixth Coalition defeated Napoleon in 1814, and is regarded as one of the first wars of national liberation. It is also significant for the emergence of large-scale guerrilla warfare.
Battle of Friedland (1807 June)

Major engagement of the Napoleonic Wars between the armies of the French Empire commanded by Napoleon I and the armies of the Russian Empire led by Count von Bennigsen. Napoleon and the French obtained a decisive victory that routed much of the Russian army, which retreated chaotically over the Alle River by the end of the fighting.
Battle of Eylau (1807 February)

The Battle of Eylau was a bloody and strategically inconclusive battle on 7 and 8 February 1807 between Napoléon's Grande Armée and the Imperial Russian Army under the command of Levin August von Bennigsen near the town of Preussisch Eylau in East Prussia. Late in the battle, the Russians received timely reinforcements from a Prussian division of von L'Estocq.
Battle of Jena–Auerstedt (1806 October)

The twin battles of Jena and Auerstedt were fought on the plateau west of the river Saale in today's Germany, between the forces of Napoleon I of France and Frederick William III of Prussia. The defeat suffered by the Prussian Army subjugated the Kingdom of Prussia to the French Empire until the Sixth Coalition was formed in 1813. The Prussians were not organized well enough and lacked the speed as well as the efficient information flow of the French army.
Battle of San Domingo (1806 February)

The Battle of San Domingo was a naval battle of the Napoleonic Wars fought on 6 February 1806 between squadrons of French and British ships of the line off the southern coast of the French-occupied Spanish colonial Captaincy General of Santo Domingo in the Caribbean. The battle of San Domingo was the last fleet engagement of the war between French and British capital ships in open water.
Battle of Austerlitz (1805 December)

Also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz in the Austrian Empire. The decisive victory of Napoleon's Grande Armée brought the War of the Third Coalition to a rapid end, with the Treaty of Pressburg signed by the Austrians later in the month. The battle is often cited as a tactical masterpiece.
Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815)

The Napoleonic Wars were a series of major conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European powers formed into various coalitions. The wars resulted from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the Revolutionary Wars, which had raged on for years before concluding with the Treaty of Amiens in 1802. View Historic Battles »
War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802)

The second war on revolutionary France by the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal and Naples. Their goal was to contain the spread of chaos from France, which was bankrupt after its expenditures in support of the American War of Independence. View Historic Battles »
War of the First Coalition (1792–1797)

Was the first attempt by the European monarchies to defeat the French First Republic. France declared war on the Habsburg Monarchy of Austria on 20 April 1792. In July 1792, an army under the Duke of Brunswick and composed mostly of Prussians joined the Austrian side and invaded France. View Historic Battles »
Storming of the Bastille (1789 July)

The medieval fortress, armory, and political prison in Paris known as the Bastille represented royal authority in the centre of Paris. The prison contained just seven inmates at the time of its storming, but was seen by the revolutionaries as a symbol of the monarchy's abuses of power; its fall was the flashpoint of the French Revolution. View Historic Battles »
Battles of Saratoga (1777 September)

Battles of Saratoga marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led a large invasion army southward from Canada in the Champlain Valley, hoping to meet a similar British force marching northward from New York City and another British force marching eastward from Lake Ontario. View Historic Battles »
American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)

The American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), also known as the American War of Independence, was a global war that began as a conflict between Great Britain and her Thirteen Colonies, which declared independence as the United States of America. The last British troops departed New York City on November 25, 1783, marking the end of British rule in the new United States. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Leuthen (1757 December)

The Battle of Leuthen was fought on 5 December 1757 and involved Frederick the Great's Prussian Army using maneuver warfare and terrain to rout a larger Austrian force completely, which was commanded by Prince Charles of Lorraine and Count Leopold Joseph von Daun. The victory ensured Prussian control of Silesia during the Third Silesian War, which was part of the Seven Years' War.
Battle of Plassey (1757 June)

Decisive victory of the British East India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23 June 1757. Over the next hundred years, they seized control of most of the rest of the Indian subcontinent, including Burma. The British further used this revenue to increase their military might and push the other European colonial powers such as the Dutch and the French out of South Asia, thus expanding the British Empire.
Seven Years' War (1756-1763)

The Seven Years' War was a war fought between 1754 and 1763, the main conflict occurring in the seven-year period from 1756 to 1763. It involved every European great power of the time except the Ottoman Empire and spanned five continents, affecting Europe, the Americas, West Africa, India, and the Philippines. View Historic Battles »
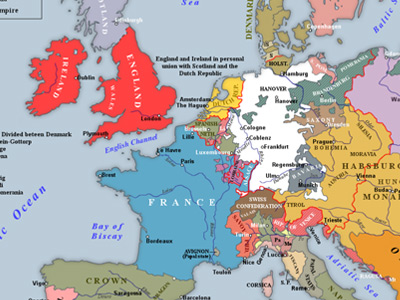
French and Indian War (1754–1763)
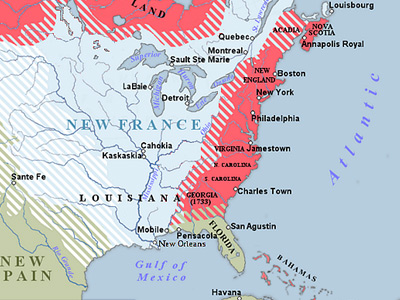
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) comprised the North American theater of the worldwide Seven Years' War of 1754–1763. The war pitted the colonies of British America against those of New France, with both sides supported by military units from their parent countries of Great Britain and France, as well as by Native American allies. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Hohenfriedberg (1745 June)

The Battle of Hohenfriedberg was one of Frederick the Great's most admired victories. Frederick's Prussian army decisively defeated an Austrian army during the Second Silesian War. Hohenfriedberg was a great victory for Frederick, and soon, he was being called "Frederick the Great" by his contemporaries.
War of the Polish Succession (1733–1738)

A major European war sparked by a Polish civil war over the succession to Augustus II, which the other European powers widened in pursuit of their own national interests. The slight amount of fighting in Poland resulted in the accession of Augustus III, who in addition to Russia and Saxony, was politically supported by the Habsburgs. View Historic Battles »
War of the Quadruple Alliance (1717–1720)

The War of the Quadruple Alliance was fought from 1717 to 1720 by Spain and the Habsburg Monarchy, with the latter being joined in 1718 by Great Britain, France, and Savoy, and in 1719 by the Dutch Republic. Caused by Spanish attempts to recover territories in Italy ceded in the 1713 Peace of Utrecht, most of the fighting took place in Sicily and Spain, with minor engagements in North America. View Historic Battles »
Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–1718)

The Seventh Ottoman–Venetian War was fought between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire between 1714 and 1718. It was the last conflict between the two powers, and ended with an Ottoman victory and the loss of Venice's major possession in the Greek peninsula, the Peloponnese. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Blenheim (1704 August)

The Battle of Blenheim fought on 13 August 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied victory ensured the safety of Vienna from the Franco-Bavarian army, thus preventing the collapse of the reconstituted Grand Alliance.
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713)

The second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Great Britain. In Europe, it is generally viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession; in the Americas, it is more commonly viewed as a standalone conflict. View Historic Battles »
War of the Spanish Succession (1702-1715)

The War of the Spanish Succession (1702–1715) was a major European conflict of the early 18th century, triggered by the death in 1700 of the last Habsburg King of Spain, the infirm and childless Charles II. Charles II had ruled over a large active empire which spanned the globe, and the question of who would succeed him had long troubled ministers in capitals throughout Europe. View Historic Battles »
47 Ronin 四十七士 (1701-1703)

47 Ronin, also known as the Akō vendetta or the Genroku Akō incident, is an 18th-century historical event and a legend in Japan in which a band of ronin (leaderless samurai) avenged the death of their master. One noted Japanese scholar described the tale as the best known example of the samurai code of honor, bushidō, and as the country's "national legend". View Historic Battles »
Battle of Zenta (1697 September)

The Battle of Zenta was fought between Ottoman and Holy League armies during the Great Turkish War. The scale of the defeat forced the Ottoman Empire into the Treaty of Karlowitz (1699) ceding Croatia, Hungary, Transylvania and Slavonia to Austria. Zenta was one of the Ottoman Empire's greatest defeats and ultimately signalled the end of Ottoman dominance in Europe.
Nine Years' War (1688–1697)

The Nine Years' War (1688–97) – often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg – was a major conflict between Louis XIV of France and a European-wide coalition of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, Spain, Britain, and Savoy. It was fought on the European continent and the surrounding seas, Ireland, and in North America. View Historic Battles »
Second Battle of Mohács (1687 August)

The Second Battle of Mohács was fought on 12 August 1687 between the forces of Ottoman Sultan Mehmed IV and the forces of Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I. The result was a decisive victory for the Austrians. After the battle, the Ottoman Empire fell into deep crisis. The disintegration of the Ottoman army allowed Imperial Habsburg armies to conquer large areas.
Battle of Vienna (1683 September)

The Battle of Vienna took place at Kahlenberg Mountain near Vienna after the imperial city had been besieged by the Ottoman Empire for two months. The battle was fought by the Holy Roman Empire against the Ottomans and their vassal and tributary states. Historians maintain that the battle marked the turning point in the Ottoman–Habsburg wars, a 300-year struggle between the Holy Roman and Ottoman Empires.
Franco-Dutch War (1672-1678)

The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War, was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts.
Second Northern War (1655–1660)

The Second Northern War (1655–60, also First or Little Northern War) was fought between Sweden and its adversaries the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Russia, Brandenburg-Prussia, the Habsburg Monarchy and Denmark–Norway. The Dutch Republic often intervened against Sweden. View Historic Battles »
Anglo–Dutch Wars (1652–1784)

The Anglo–Dutch Wars were a series of conflicts mainly fought between the Dutch Republic and England over trade and overseas colonies. Almost all the battles were naval engagements. The English were successful in the first, while the Dutch were successful in the second and third clashes. However, by the time of the fourth war, the British Royal Navy had become the most powerful maritime force in the world.
Portuguese Restoration War (1640–1668)

The war between Portugal and Spain that began with the Portuguese revolution of 1640 and ended with the Treaty of Lisbon in 1668, bringing a formal end to the Iberian Union. The period from 1640 to 1668 was marked by periodic skirmishes between Portugal and Spain, as well as short episodes of more serious warfare, much of it occasioned by Spanish and Portuguese entanglements with non-Iberian powers.
Invasion of Ryukyu 琉球侵攻 (1609)

The invasion by forces of the Japanese feudal domain of Satsuma was met with stiff resistance from the Ryukyuan military on all but one island during the campaign. Ryukyu would remain a vassal state under Satsuma, alongside its already long-established tributary relationship with China. View Historic Battles »
Dutch–Portuguese War (1602-1663)

The Dutch–Portuguese War was a global armed conflict involving Dutch forces, in the form of the Dutch East India Company and the Dutch West India Company, as well as their allies against the Iberian Union, and after 1640, the Portuguese Empire. Beginning in 1602, the conflict primarily involved the Dutch companies invading Portuguese colonies in the Americas, Africa, and the East Indies.
Battle of Sekigahara 関ヶ原の戦い (1600)

Battle of Sekigahara was a decisive battle that preceded the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate. Tokugawa Ieyasu took three more years to consolidate his position of power over the Toyotomi clan and the daimyōs, but Sekigahara is widely considered to be the unofficial beginning of the Tokugawa bakufu, the last shogunate to control Japan. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Myeongnyang 명량대첩 (1597 October)
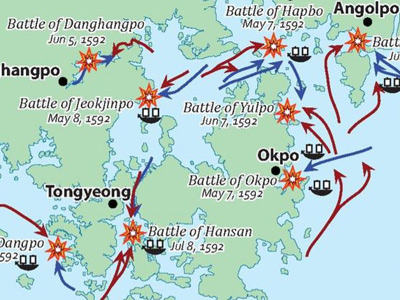
In the Battle of Myeongnyang, on October 26, 1597, the Korean Joseon kingdom's navy, led by Admiral Yi Sun-sin, fought the Japanese navy in the Myeongnyang Strait, near Jindo Island, off the southwest corner of the Korean peninsula. With only 12 ships remaining from Admiral Won Gyun's disastrous defeat at the Battle of Chilchonryang, Admiral Yi held the strait as a "last stand" battle against the Japanese Navy. View Historic Battles »
Long Turkish War (1593-1606)

The Long Turkish War or Thirteen Years' War was an indecisive land war between the Habsburg Monarchy and the Ottoman Empire, primarily over the Principalities of Wallachia, Transylvania, and Moldavia. It was waged from 1593 to 1606 but in Europe it is sometimes called the Fifteen Years War. Overall, the conflict consisted in a large number of costly battles and sieges, but with little gain for either side.
Siege of Busanjin (1592)

The Siege of Busanjin was a battle fought at Busan on April 13–14, 1592, between Japanese and Korean forces. Along with Dadaejin, Busanjin of Dongnae-bu was the site of the first battle in the Imjin War. This battle marked the beginning of a long war on the Korean Peninsula. View Historic Battles »
Spanish Armada (1588)

Spanish Armada was a Spanish fleet of 130 ships that sailed from La Coruña in August 1588, under the command of the Duke of Medina Sidonia with the purpose of escorting an army from Flanders to invade England. The strategic aim was to overthrow Queen Elizabeth I and her establishment of Protestantism in England. View Historic Battles »
Invasion of Shikoku (1585)

Despite the overwhelming size of Hideyoshi's army, and the suggestions of his advisors, Chōsokabe chose to fight to defend his territories. The battles culminated in the siege of Ichinomiya Castle, which lasted for 26 days. Chōsokabe made a half-hearted attempt to relieve his castle from the siege, but surrendered in the end. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Takamatsu 備中高松城の戦い (1582)

Toyotomi Hideyoshi laid siege to Takamatsu Castle, which was controlled by the Mōri clan. He diverted a nearby river with dikes to surround and flood the castle, leading to a relatively speedy surrender. He also constructed towers on barges from which his arquebusiers could keep up a constant rate of fire and be unhindered themselves by the flooding. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Nagashino 長篠の戦い (1575)

Battle of Nagashino took place in 1575 near Nagashino Castle on the plain of Shitarabara in the Mikawa Province of Japan. Takeda Katsuyori attacked the castle when Okudaira Sadamasa rejoined the Tokugawa, and when his original plot with Oga Yashiro for taking Okazaki Castle, the capital of Mikawa, was discovered. View Historic Battles »
Eighty Years' War (1568–1648)

Eighty Years' War was a revolt of the Seventeen Provinces of what are today the Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg, as well as the French region of Hauts-de-France against the political and religious hegemony of Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Habsburg Netherlands. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Inabayama Castle 稲葉山城の戦い (1567)

Siege of Inabayama Castle was the final battle in Oda Nobunaga's campaign to defeat the Saitō clan in their mountaintop castle and conquer Mino Province, Japan. The siege ended in a decisive battle and victory of Nobunaga's combined forces, and resulted in the subjugation of the Saitō clan, their vassals, and allies. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Szigeth (1566 August-September)

The Battle of Szigeth was a siege of the fortress of Szigetvár, Kingdom of Hungary, that blocked Sultan Suleiman's line of advance towards Vienna in 1566. The battle was fought between the defending forces of the Habsburg monarchy under the leadership of Nikola IV Zrinski, former Ban of Croatia, and the invading Ottoman army under the nominal command of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent.
Battle of Okehazama 桶狭間の戦い (1560)

Battle of Okehazama took place in June 1560. Imagawa Yoshimoto, with an army of about 25,000 men, set forth on a march to Kyoto. In this battle, Oda Nobunaga defeated Imagawa Yoshimoto and established himself as one of the front-running warlords in the Sengoku period. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Calais (1558 January)

The French Siege of Calais was part of the Italian War of 1551–1559 between France and England and their respective allies. It resulted in the seizure of the town by France. The Pale of Calais had been ruled by England since 1347, during the Hundred Years' War. Following the failure in mid-1557, a renewed attack captured the outlying forts of Nieullay and Rysbank and Calais was besieged.
Battles of Kawanakajima 川中島の戦い (1553-1564)

The battles were fought after Shingen conquered Shinano, expelling Ogasawara Nagatoki and Murakami Yoshikiyo, who subsequently turned to Kenshin for help. The battles became one of the most cherished tales in Japanese military history, the epitome of Japanese chivalry and romance, mentioned in epic literature, woodblock printing and movies. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Ceresole (1544 April)

The Battle of Ceresole took place during the Italian War of 1542–1546, outside the village of Ceresole d'Alba in the Piedmont region of Italy. A French army defeated the combined forces of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. Despite having inflicted substantial casualties on the Imperial troops, the French subsequently failed to exploit their victory by taking Milan.
Battle of Mohács (1526 August)

The Battle of Mohács was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and those of the Ottoman Empire, led by Suleiman the Magnificent. The Ottoman victory led to the partition of Hungary for several centuries between the Ottoman Empire, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Principality of Transylvania.
Battle of Pavia (1525 February)

The battle was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521–1526 between the Kingdom of France and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor as well as ruler of Spain, Austria, the Low Countries, and the Two Sicilies. In the battle, the French army was split and defeated in detail. The outcome of the battle cemented Habsburg ascendancy in Italy and Europe, but Francis denounced the treaty after his liberation and soon re-opened hostilities over Burgundy and Milan.
Battle of Marignano (1515)

The Battle of Marignano was the last major engagement of the War of the League of Cambrai and took place on 13–14 September 1515, near the town now called Melegnano, 16 km southeast of Milan. It pitted the French army, composed of the best heavy cavalry and artillery in Europe, led by Francis I, newly crowned King of France, against the Old Swiss Confederacy, whose mercenaries until that point were regarded as the best medieval infantry force in Europe.
Battle of Ravenna (1512 April)

The Battle of Ravenna was a major battle of the War of the League of Cambrai. It pitted forces of the Holy League against France and their Ferrarese allies. Although the French and Ferrarese eliminated the Papal-Spanish forces as a serious threat, their triumph was overshadowed by the loss of their young general Gaston of Foix. The battle went on for eight hours and left, by contemporary accounts, more than 10,000 dead between both sides.
Battle of Garigliano (1503 December)

The Battle of Garigliano was fought on 29 December 1503 between a Spanish army under Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba and a French army commanded by Ludovico II, Marquis of Saluzzo. The Spanish victory was decisive, as the offensive capacity of the French army was destroyed. After some days of siege in Gaeta, the French surrendered. With the Treaty of Blois in 1504, France recognized Spain's authority over Naples.
Battle of Cerignola (1503 April)

The Battle of Cerignola was fought on 28 April 1503 between Spanish and French armies outside the town of Cerignola, Apulia, Kingdom of Naples. The Spanish force comprising 6,300 men defeated the French force of 9,000 men. It was one of the first European battles won by gunpowder weapons, as the attacks by the French cavalry and Swiss pikemen were shattered by the fire of Spanish arquebusiers behind a defensive ditch.
Battle of Bosworth (1485 August)

The Battle of Bosworth was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of Lancaster and York that extended across England in the latter half of the 15th century. The battle was won by an alliance of Lancastrians and disaffected Yorkists. His opponent Richard III, the last king of the House of York, was killed during the battle, the last English monarch to die in combat.
Battle of Tewkesbury (1471 May)

The Battle of Tewkesbury was one of the most decisive battles of the Wars of the Roses in England. King Edward IV and his forces loyal to the House of York completely defeated those of the rival House of Lancaster. The Lancastrian king, Henry VI, who was a prisoner in the Tower of London, died shortly after the battle, perhaps murdered. Tewkesbury restored political stability to England until the death of Edward IV in 1483.
Battle of Barnet (1471 April)

The Battle of Barnet was a decisive engagement in the Wars of the Roses, a dynastic conflict of 15th-century England. The military action, along with the subsequent Battle of Tewkesbury, secured the throne for Edward IV. Historians regard the battle as one of the most important clashes in the Wars of the Roses, since it brought about a decisive turn in the fortunes of the two houses.
Battle of Towton (1461 March)

The Battle of Towton took place during the Wars of the Roses and "has the dubious distinction of being probably the largest and bloodiest battle on English soil". Fought for ten hours between an estimated 50,000 soldiers in a snowstorm on Palm Sunday, the Yorkist army achieved a decisive victory over their Lancastrian opponents. As a result, Edward IV deposed the Lancastrian Henry VI and secured the English throne.
Wars of the Roses (1455–1487)

Series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. Following the war, the Houses of Lancaster and York were united, creating a new royal dynasty and thereby resolving their rival claims. For over thirty years, there were greater and lesser levels of violent conflict between various rival contenders for control of the English monarchy.
Battle of Formigny (1450)

Battle of Formigny was a major battle of the Hundred Years' War between England and France. The destruction of England's last army in Normandy in the battle and the decisive French victory paved the way for the capture of the remaining English strongholds in Normandy. View Historic Battles »
Second Battle of Kosovo (1448)

Land battle between a Hungarian-led Crusader army and the Ottoman Empire at Kosovo Polje. It was the culmination of a Hungarian offensive to avenge the defeat at Varna four years earlier. The battle ended any hopes of saving Constantinople from the Ottoman Empire. The Hungarian kingdom no longer had the military and financial resources to mount an offensive against the Ottomans. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Varna (1444)

The Battle of Varna took place on 10 November 1444 near Varna in eastern Bulgaria. The Ottoman Army under Sultan Murad II defeated the Hungarian–Polish and Wallachian armies commanded by Władysław III of Poland, John Hunyadi and Mircea II of Wallachia. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Orléans (1428–1429)

The Siege of Orléans (1428–1429) was the watershed of the Hundred Years' War between France and England. It was the French Royal army's first major military victory while Joan of Arc was with the army and the first to follow the crushing defeat at Agincourt in 1415. The siege took place at the pinnacle of English power during the later stages of the war. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Arbedo (1422 June)

The Battle of Arbedo was fought between the Duchy of Milan and the Swiss Confederation, and ended with a Milanese victory. The Swiss were mainly equipped with halberds and were initially successful in repelling two Milanese cavalry charges. Carmagnola then brought up his crossbowmen on the Swiss flanks and ordered his men-at-arms to dismount and fight on foot with their lances, which outreached the halberds.
Battle of Grunwald (1410)

Fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respectively by King Władysław II Jagiełło (Jogaila) and Grand Duke Vytautas, decisively defeated the German–Prussian Teutonic Knights, led by Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Shrewsbury (1403 July)

The Battle of Shrewsbury waged between an army led by the Lancastrian King Henry IV and a rebel army led by Henry "Harry Hotspur" Percy from Northumberland. The battle, the first in which English archers fought each other on English soil, reaffirmed the effectiveness of the longbow and ended the Percy challenge to King Henry IV of England.
Battle of Nicopolis (1396)

The Battle of Nicopolis took place on 25 September 1396 and resulted in the rout of an allied crusader army of Hungarian, Croatian, Bulgarian, Wallachian, French, English, Burgundian, German and assorted troops at the hands of an Ottoman force, raising of the siege of the Danubian fortress of Nicopolis and leading to the end of the Second Bulgarian Empire. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Aljubarrota (1385 August)

The Battle of Aljubarrota was fought between the Kingdom of Portugal and the Crown of Castile. The result was a decisive victory for the Portuguese, ruling out Castilian ambitions to the Portuguese throne, ending the 1383–85 Crisis and assuring John as King of Portugal. Portuguese independence was confirmed and a new dynasty, the House of Aviz, was established.
Battle of Shijōnawate 四條畷の戦い (1348)

Battle of Shijōnawate was a battle of the Nanboku-chō period of Japanese history, and took place in Yoshino, Nara. It was fought between the armies of the Northern and Southern Emperors of Japan. The Southern army, led by Kusunoki Masatsura was attacked at Yoshino, the temporary palace of the Imperial residence. View Historic Battles »
Genkō War 元弘の乱 (1331-1333)

Genkō War was a civil war in Japan which marked the fall of the Kamakura shogunate and end of the power of the Hōjō clan. The war thus preceded the Nanboku-chō period and the rise of the Ashikaga shogunate. Genkō is the name of the Japanese era corresponding to the period 1331-1334. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Worringen (1288)
Fought near the town of Worringen, which is now the northernmost borough of Cologne. It was the decisive battle of the War of the Limburg Succession, fought for the possession of the Duchy of Limburg between Archbishop Siegfried II of Cologne and Duke John I of Brabant, and one of the largest battles in Europe in the Middle Ages. View Historic Battles »
Battle on the Marchfeld (1278)

The opponents were a Bohemian (Czech) army led by the Přemyslid king Ottokar II of Bohemia and the German army under the German king Rudolph I of Habsburg in alliance with King Ladislaus IV of Hungary. Although both sides also had infantry in their armies, the battle itself was primarily a great collision of heavy knights. View Historic Battles »
Ninth Crusade (1271–1272)

Commonly considered to be the last major medieval Crusade to the Holy Land. It is arguable that the Crusading spirit was nearly "extinct" by this period as well. It also foreshadowed the imminent collapse of the last remaining crusader strongholds along the Mediterranean coast. View Historic Battles »
Eighth Crusade (1270)

The Eighth Crusade was a crusade launched by Louis IX of France against the city of Tunis in 1270. The crusade is considered a failure after Louis died shortly after arriving on the shores of Tunisia, with his disease-ridden army dispersing back to Europe shortly afterwards. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Kressenbrunn (1260 July)

The Battle of Kressenbrunn was fought between the Kingdom of Bohemia and the Kingdom of Hungary for the possession of the duchies of Austria and Styria. The fight is considered one of the biggest battles in Central Europe in the Middle Ages, though scholars doubt the possibility of supplying such a vast number of mercenaries.
Seventh Crusade (1248–1254)

A crusade led by Louis IX of France. His troops were defeated by the Egyptian army led by the Ayyubid Sultan Turanshah and Louis was captured. Approximately 800,000 bezants were paid in ransom for his return. His crusade was a failure, but he was considered a saint by many, and his fame gave him an even greater authority in Europe than the Holy Roman Emperor. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Taillebourg (1242)

The Battle of Taillebourg was a 1242 battle between the Capetian troops of Louis IX and his brother Alphonse of Poitiers, against the rebel followers of Hugh X of Lusignan and Henry III of England. It was fought over the bridge built over the Charente River, a point of strategic importance on the route between northern and southern France. View Historic Battles »
Battle of the Puig (1237 August)

The Battle of the Puig of 1237 was a battle of the Iberian Reconquista and of the Aragonese Conquest of Valencia. The battle took place in August 1237, pitting the forces of the Crown of Aragon against the forces of the Taifa of Valencia. The battle resulted in a decisive Aragonese victory and the conquest of Valencia by the crown of Aragon.
Sixth Crusade (1228–1229)

The Sixth Crusade started in 1228 as an attempt to regain Jerusalem. It began seven years after the failure of the Fifth Crusade and involved very little actual fighting. The diplomatic maneuvering of the Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II, resulted in the Kingdom of Jerusalem regaining some control over Jerusalem for much of the ensuing fifteen years as well as over other areas of the Holy Land. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Muret (1213)
At the Battle of Muret on 12 September 1213 the Crusader army of Simon IV de Montfort defeated the Catharist, Aragonese and Catalan forces of Peter II of Aragon, at Muret near Toulouse. This would be the last major battle of the Albigensian crusade. During the battle, Saint Dominic prayed the rosary. The victors credited their success to divine intervention. View Historic Battles »
Fifth Crusade (1213–1221)

The Fifth Crusade (1213–1221) was an attempt by Western Europeans to reacquire Jerusalem and the rest of the Holy Land by first conquering the powerful Ayyubid state in Egypt. After occupying the port of Damietta, the Crusaders marched south towards Cairo in July 1221, but were turned back after their dwindling supplies led to a forced retreat. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa (1212)

The Christian forces of King Alfonso VIII of Castile were joined by the armies of his rivals, Sancho VII of Navarre, Peter II of Aragon and Afonso II of Portugal, in battle against the Almohad Muslim rulers of the southern half of the Iberian Peninsula. View Historic Battles »
Fourth Crusade (1202–04)

Originally intended to reconquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. Instead, a sequence of events culminated in the Crusaders sacking the city of Constantinople, the capital of the Christian-controlled Byzantine Empire. View Historic Battles »
Third Crusade (1189–1192)

Also known as The Kings' Crusade, was an attempt by European leaders to reconquer the Holy Land from Saladin. The campaign was largely successful in capturing the important cities of Acre and Jaffa, and reversing most of Saladin's conquests, but it failed to capture Jerusalem, the emotional and spiritual motivation of the Crusade. View Historic Battles »
Genpei War 源平合戦 (1180–1185)

Genpei War was a conflict between the Taira and Minamoto clans during the late-Heian period of Japan. It resulted in the fall of the Taira clan and the establishment of the Kamakura shogunate under Minamoto no Yoritomo in 1192. View Historic Battles »
Heiji Rebellion 平治の乱 (1160)

Heiji Rebellion was a short civil war between rival subjects of the cloistered Emperor Go-Shirakawa of Japan in 1159 fought in order to resolve a dispute about political power. It is also seen as a precursor of a broader civil war. View Historic Battles »
Hōgen Rebellion 保元の乱 (1156)

Hōgen Rebellion was a short civil war fought in order to resolve a dispute about Japanese Imperial succession. The dispute was also about the degree of control exercised by the Fujiwara clan who had become hereditary Imperial regents during the Heian period. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Lisbon (1147)

The military action against the Muslim-ruled Taifa of Badajoz that brought the city of Lisbon under the definitive control of the new Christian power, the Kingdom of Portugal. The siege of Lisbon was one of the few Christian victories of the Second Crusade and is seen as a pivotal battle of the wider Reconquista. Most of the crusaders settled in the newly-captured city, but some of the crusaders set sail and continued to the Holy Land.
Second Crusade (1145–1149)

The second major crusade launched from Europe as a Catholic ('Latin') holy war against Islam. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Crusade (1096–1099) by King Baldwin of Boulogne in 1098. While it was the first Crusader state to be founded, it was also the first to fall. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Ourique (1139 July)

The Battle of Ourique took place on 25 July 1139. Despite the fact that the Christian Portuguese forces were strongly outnumbered, the Muslim armies were weakened by internal leadership problems, which led to Afonso Henriques's victory and subsequently his proclamation as King of the Portuguese, as Afonso I, with the support from his troops, vanquishing and slaying, so legend says, five Muslim kings.
Battle of Fraga (1134)

The battle was fought between the forces of the Kingdom of Aragon, commanded by Alfonso the Battler and a variety of Almohad forces that had come to the aid of the town of Fraga which was being besieged by King Alfonso I. The battle resulted in an Almoravid victory. The Aragonese monarch Alfonso I died shortly after the battle. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Tinchebray (1106)

Fought on 28 September in Normandy, between an invading force led by King Henry I of England, and his older brother Robert Curthose, the Duke of Normandy. Henry's knights won a decisive victory, capturing Robert and imprisoning him in England and then Wales until Robert's death. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Ascalon (1099 August)

The battle took place shortly after the capture of Jerusalem, and is often considered the last action of the First Crusade. The crusader army led by Godfrey of Bouillon defeated and drove off a Fatimid army, securing the safety of Jerusalem. At dawn, the Crusader army launched a surprise attack on the Fatimid army still sleeping in its camp outside the defensive walls of Ascalon.
First Crusade (1095–1099)

The first of a number of crusades that attempted to capture the Holy Land, called for by Pope Urban II at the Council of Clermont in 1095. Urban called for a military expedition to aid the Byzantine Empire, which had recently lost most of Anatolia to the Seljuq Turks. The resulting military expedition of primarily Frankish nobles, known as the Princes' Crusade not only re-captured Anatolia but went on to conquer the Holy Land. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Toledo (1085 May)

The Siege of Toledo was Alfonso VI of León and Castile's siege and conquest of Toledo. The Castilian conquest of the former Visigothic capital was achieved through a strategy of attrition warfare developed by Castile in the preceding years. As it represented a shift in power on the Iberian peninsula, the siege of Toledo was the most significant event in the taifa period.
Battle of Manzikert (1071 August)

The Battle of Manzikert was fought between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire on 26 August 1071. The decisive defeat of the Byzantine army and the capture of the Emperor Romanos IV Diogenes played an important role in undermining Byzantine authority in Anatolia and Armenia, and allowed for the gradual Turkification of Anatolia.
Battle of Hastings (1066)

The Battle of Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman conquest of England. It took place approximately 7 miles northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Norman victory. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Stamford Bridge (1066 September)

The Battle of Stamford Bridge took place at the village of Stamford Bridge, East Riding of Yorkshire, in England on 25 September 1066, between an English army under King Harold Godwinson and an invading Norwegian force led by King Harald Hardrada and the English king's brother Tostig Godwinson. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Fulford (1066 September)

The Battle of Fulford was fought on the outskirts of the village of Fulford just south of York in England, when King Harald III of Norway and Tostig Godwinson, his English ally, fought and defeated the Northern Earls Edwin and Morcar. The battle was a victory for the Viking army. The earls of York could have hidden behind the walls of their city but instead they met the Viking army across a river.
Battle at Brůdek (1040 August)

The battle fought between Henry III, King of the Romans, and Břetislav I, Duke of Bohemia. Henry requested a truce, but was answered with the demand for unconditional surrender, so the king planned a second campaign. This turned out to be more successful, Henry succeeded in meeting with the Saxon forces before Prague on 8 September and Břetislav was forced to surrender on 29 September 1041.
Battle of Stiklestad (1030)

Battle of Stiklestad is one of the most famous battles in the history of Norway. In this battle, King Olaf II of Norway was killed. During the pontificate of Roland of Siena, the Roman Catholic Church declared Olaf a saint in 1164. Harald was only fifteen when the battle of Stiklestad took place. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Assandun (1016)
There is disagreement whether Assandun may be Ashdon near Saffron Walden in north Essex or, as long supposed, Ashingdon near Rochford in southeast Essex, England. It ended in victory for the Danes, led by Canute the Great, who triumphed over the English army led by King Edmund Ironside. The battle was the conclusion to the Danish reconquest of England. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Svolder (1000)

Battle of Svolder was a naval battle fought in September 999 or 1000 in the western Baltic Sea between King Olaf Tryggvason of Norway and an alliance of his enemies. The backdrop of the battle was the unification of Norway into a single state, long-standing Danish efforts to gain control of the country, and the spread of Christianity in Scandinavia. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Edington (878 AD)
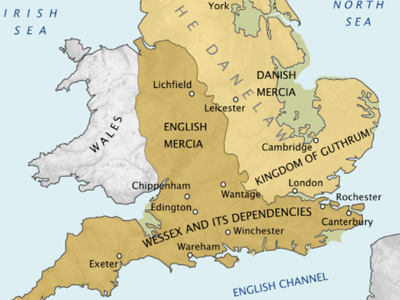
At the Battle of Edington an army of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex under Alfred the Great defeated the Great Heathen Army led by Guthrum on a date between 6 and 12 May AD 878, soon resulting in the Treaty of Wedmore later the same year. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Covadonga (722 AD)

The battle followed the creation in 718 of an independent Christian principality in the mountains of the northwestern region of the Iberian peninsula that grew into the Kingdom of Asturias and became a bastion of Christian resistance to the expansion of Muslim rule. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Guadalete (711 AD)

The Battle of Guadalete was fought in 711 at an unidentified location between the Christian Visigoths of Hispania under their king, Roderic, and the invading forces of the Muslim Umayyad Caliphate, composed of Arabs and Berbers under the commander Ṭāriq ibn Ziyad. View Historic Battles »
Goguryeo–Sui War (598-614 AD)
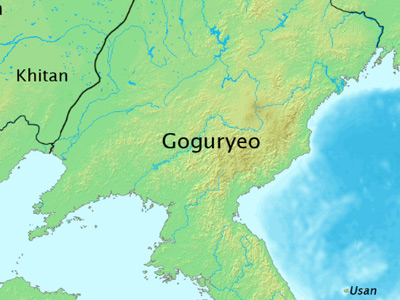
The Goguryeo–Sui War were a series of invasions launched by the Sui dynasty of China against Goguryeo, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. It resulted in the defeat of the Sui and was one of the pivotal factors in the collapse of the dynasty, which led to its overthrow by the Tang dynasty in AD 618. View Historic Battles »
Vandalic War (533-534 AD)

The Vandalic War was a conflict fought in North Africa (largely in modern Tunisia) between the forces of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire and the Vandalic Kingdom of Carthage, in 533–534. It was the first of Justinian I's wars of reconquest of the lost Western Roman Empire. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Châlons (451 AD)

Also called the Battle of Châlons or the Battle of Maurica, took place on June 20, 451 AD between a coalition led by the Roman general Flavius Aetius and the Visigothic king Theodoric I against the Huns and their vassals commanded by their king Attila. View Historic Battles »
Sack of Rome (410 AD)

The Sack of Rome occurred on 24 August 410 where the city was attacked by the Visigoths led by King Alaric. This was the first time in almost 800 years that Rome had fallen to a foreign enemy. The sacking of 410 is seen as a major landmark in the fall of the Western Roman Empire. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Adrianople (378 AD)

The Battle of Adrianople (9 August 378), sometimes known as the Battle of Hadrianopolis, was fought between an Eastern Roman army led by the Eastern Roman Emperor Valens and Gothic rebels led by Fritigern. It ended with an overwhelming victory for the Goths and the death of Emperor Valens. View Historic Battles »
Battle of the Milvian Bridge (312 AD)

The Battle of the Milvian Bridge took place between the Roman Emperors Constantine I and Maxentius on 28 October 312. It takes its name from the Milvian Bridge, an important route over the Tiber. Constantine won the battle and started on the path that led him to end the Tetrarchy and become the sole ruler of the Roman Empire. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Edessa (260 AD)

The battle took place between the armies of the Roman Empire and Sassanid forces. The Roman army was defeated and captured in its entirety by the Persian forces; for the first time in Rome's military history their emperor was taken prisoner. As such, the battle is generally viewed as one of the worst disasters in Roman military history. View Historic Battles »
Roman Invasion of Caledonia (208–210 AD)
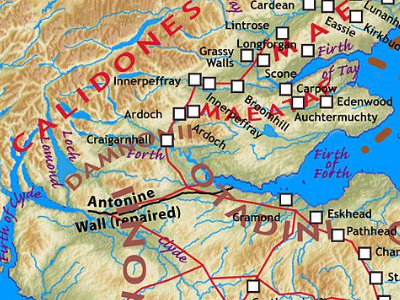
The Roman invasion of Caledonia launched in 208 by the Roman emperor Septimius Severus. The war started well for the Romans with Severus managing to quickly reach the Antonine Wall, but when Severus pushed north into the highlands he became bogged down in a Guerrilla war and he was never able to fully subjugate Caledonia. View Historic Battles »
Roman Civil War (193-197 AD)

The Year of the Five Emperors refers to the year 193 AD, in which there were five claimants for the title of Roman Emperor. The five were Pertinax, Didius Julianus, Pescennius Niger, Clodius Albinus and Septimius Severus. View Historic Battles »
Marcomannic Wars (166-180 AD)

The Marcomannic Wars were a series of wars lasting over a dozen years from about 166 until 180 AD. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against, principally, the Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges. View Historic Battles »
Second Dacian War (105-106 AD)

The Second Roman–Dacian War was fought in 105 to 106 AD because the Dacian King Decebalus had broken his peace terms with the Roman Emperor Trajan from the First Dacian War. View Historic Battles »
First Dacian War (101-102 AD)

The Kingdom of Dacia, under King Decebalus, had become a threat to the Roman Empire, and defeated several of Rome's armies during Domitian's reign (81-96). The Emperor Trajan was set on ridding this threat to Rome's power and in 101 set out determined to defeat Dacia. View Historic Battles »
Roman Civil War (68-69 AD)
The Year of the Four Emperors was a year in the history of the Roman Empire, AD 69, in which four emperors ruled in succession: Galba, Otho, Vitellius, and Vespasian. The suicide of the emperor Nero in 68 was followed by a brief period of civil war, the first Roman civil war since Mark Antony's death in 30 BC. View Historic Battles »
Roman–Parthian War (58–63 AD)
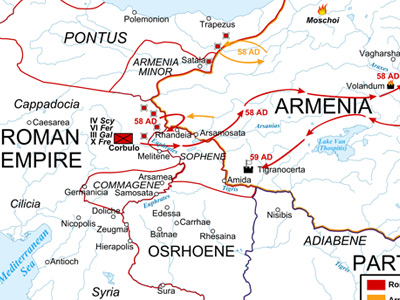
The Roman–Parthian War of 58–63 or the War of the Armenian Succession was fought between the Roman Empire and the Parthian Empire over control of Armenia, a vital buffer state between the two realms. View Historic Battles »
Roman Conquest of Britain (43-96 AD)
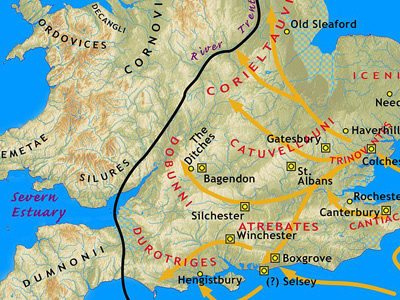
The Roman conquest of Britain was a gradual process, beginning effectively in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, whose general Aulus Plautius served as first governor of Roman Britain. Great Britain had already frequently been the target of invasions, planned and actual, by forces of the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Baduhenna Wood (28 AD)

Battle of Baduhenna Wood was a battle, possibly fought near Heiloo, Netherlands in 28 AD between the Frisii and a Roman army led by Roman General Lucius Apronius. The Romans did not attack them after devastating the lands of the Rhine Germans, but merely passed through their territory and along their coast in order to attack the Chauci. View Historic Battles »
Battle of the Teutoburg Forest (9 AD)

An alliance of Germanic tribes ambushed and decisively destroyed three Roman legions and their auxiliaries. Arminius had acquired Roman citizenship and had received a Roman military education, which enabled him to deceive the Roman commander methodically and anticipate the Roman army's tactical responses. View Historic Battles »
Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC)
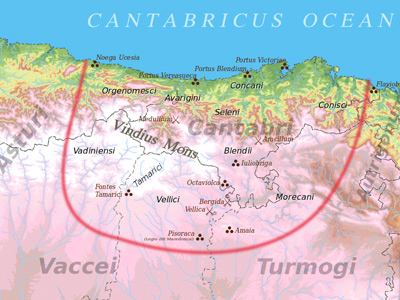
Also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars, were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what today are the provinces of Cantabria, Asturias and León, in northwestern Spain. View Historic Battles »
Final War of the Roman Republic (32-30 BC)

The Final War of the Roman Republic, also known as Antony's Civil War or The War between Antony and Octavian, was the last of the Roman civil wars of the republic, fought between Cleopatra (assisted by Mark Antony) and Octavian. View Historic Battles »
Great Roman Civil War (49–45 BC)
Also known as Caesar's Civil War, was one of the last politico-military conflicts in the Roman Republic before the establishment of the Roman Empire. Caesar was later proclaimed dictator first for ten years and then in perpetuity. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Uxellodunum (51 BC)
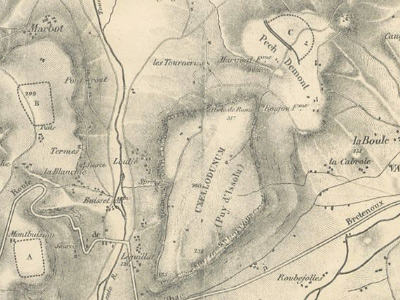
The Siege of Uxellodunum was one of the last battles of the Gallic Wars. It took place in 51 BC at Uxellodunum. It was the last major military confrontation of the Gallic Wars and marked the pacification of Gaul under Roman rule. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman victory. View Historic Battles »
Ambiorix's Revolt (54-53 BC)

Ambiorix's revolt was an episode during the Gallic Wars between 54 and 53 BC in which the Eburones tribe, under its leader, Ambiorix, rebelled against the Roman Republic. Discontent among the subjugated Gauls prompted a major uprising amongst the Belgae against Julius Caesar in the winter of 54–53 BC. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Bibracte (58 BC)

Battle of Bibracte was fought between the Helvetii and six Roman legions, under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar. After following the migration of the Helvetii and defeating them, Caesar moved towards Bibracte to obtain the supplies promised by his allies. View Historic Battles »
Gallic Wars (58–50 BC)

The Gallic Wars were a series of military campaigns waged by the Roman proconsul Julius Caesar against several Gallic tribes. Rome's war against the Gallic tribes lasted from 58 BC to 50 BC and culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the Roman Republic over the whole of Gaul. View Historic Battles »
Third Mithridatic War (73-63 BC)
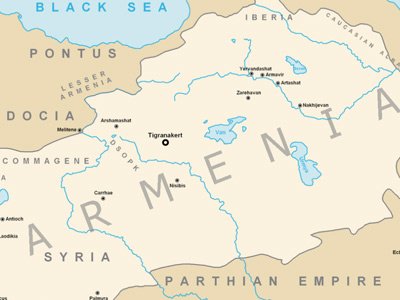
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC) was the last and longest of three Mithridatic Wars and was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus, who was joined by his allies, and the Roman Republic. The war ended in defeat for Mithridates, ending the Pontic Kingdom, and resulted in the Kingdom of Armenia becoming an allied client state of Rome. View Historic Battles »
Third Servile War (73-71 BC)

Also called the Gladiator War and The War of Spartacus, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic, known collectively as the Servile Wars. The Third was the only one directly to threaten the Roman heartland of Italia. It was particularly alarming to Rome because its military seemed powerless to suppress it. View Historic Battles »
Second Mithridatic War (83-81 BC)
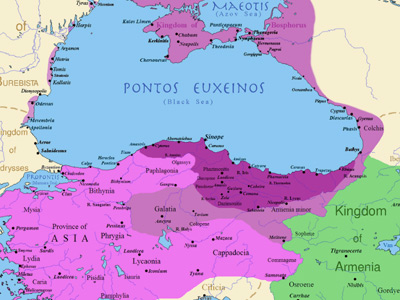
Second Mithridatic War was one of three wars fought between Pontus and the Roman Republic. This war was fought between King Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman general Lucius Licinius Murena. Murena invaded Mithridates’ territory. The latter thought that this was done under the orders of Rome and sent Gordius, his commander, to retaliate on Roman villages. View Historic Battles »
First Mithridatic War (89-85 BC)
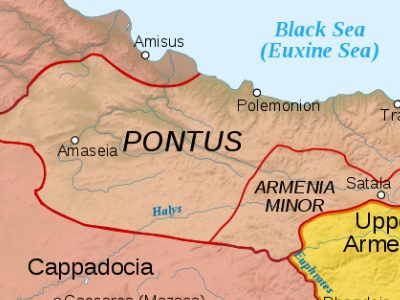
In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Rome were led by Mithridates VI of Pontus against the Roman Republic and the Kingdom of Bithynia. The war lasted five years and ended in a Roman victory which forced Mithridates to abandon all his conquests and return to Pontus. View Historic Battles »
Social War (91–88 BC)
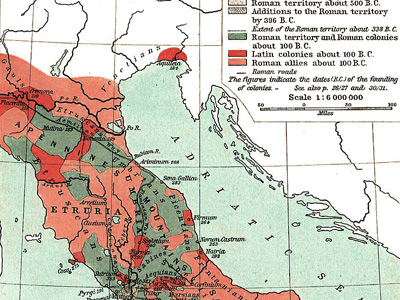
The War of the Allies or the Marsic War, was a war waged from 91 to 88 BC between the Roman Republic and several of the other cities in Italy, which prior to the war had been Roman allies for centuries. The Social War began in 91 BC when the Italian allies revolted. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Vercellae (101 BC)

Battle of Vercellae or Battle of the Raudine Plain, in 101 BC was the Roman victory of Consul Gaius Marius over the invading Celto-Germanic tribe of the Cimbri near the settlement of Vercellae in Cisalpine Gaul. The two armies met on the Raudian plain and the Romans won a total victory over the invaders. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC)

After a string of Roman defeats, the Romans under Gaius Marius finally defeated the Teutones and Ambrones. The Teutones and the Ambrones were virtually wiped out, with the Romans claiming to have killed 90,000 and captured 20,000, including large numbers of women and children who were later sold into slavery. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Arausio (105 BC)

The Battle of Arausio took place on 6 October 105 BC, at a site between the town of Arausio and the Rhône River. Ranged against the migratory tribes of the Cimbri under Boiorix and the Teutoni under Teutobod were two Roman armies, commanded by the proconsul Quintus Servilius Caepio and consul Gnaeus Mallius Maximus. View Historic Battles »
Jugurthine War (112-105 BC)
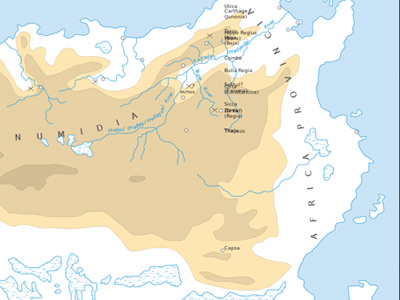
The Jugurthine War took place in 112–105 BC, between Rome and Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. The Romans defeated Jugurtha. The war constituted an important phase in the Roman subjugation of Northern Africa, but Numidia did not become a Roman province until 46 BC. View Historic Battles »
Cimbrian War (113-101 BC)

War fought between the Roman Republic and the Germanic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutones. The Cimbrian War was the first time since the Second Punic War that Italia and Rome itself had been seriously threatened. The timing of the war had a great effect on the internal politics of Rome, and the organization of its military. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Carthage (149-146 BC)

The Battle of Carthage was the main engagement of the Third Punic War between the Punic city of Carthage in Africa and the Roman Republic. It was a siege operation, starting sometime between 149 and 148 BC, and ending in spring 146 BC with the sack and complete destruction of the city of Carthage. View Historic Battles »
Third Punic War (149–146 BC)

Third Punic War was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage and the Roman Republic. This war was a much smaller engagement than the two previous Punic Wars and focused on Tunisia. View Historic Battles »
Fourth Macedonian War (150-148 BC)

Fourth Macedonian War was fought between the Roman Republic and a Greek uprising led by the Macedonian pretender to the throne Andriscus. Andriscus sought to re-establish the old Macedonian Kingdom. Two years later Macedonia became a Roman province. View Historic Battles »
Lusitanian War (155-139 BC)
Lusitanian War was a war of resistance fought by the Lusitanian tribes of Hispania Ulterior against the advancing legions of the Roman Republic from 155 to 139 BC. The Lusitanians revolted on two separate occasions (155 BC, and again in 146 BC) and were pacified. View Historic Battles »
Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC)

War fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman feelings around Macedonia. View Historic Battles »
Galatian War (189 BC)

The Galatian War was a war between the Galatian Gauls and the Roman Republic supported by their allies Pergamum in 189 BC. The war was fought in Galatia in central Asia Minor, in present-day Turkey. View Historic Battles »
Aetolian War (191–189 BC)
Was fought between the Romans and their Achaean and Macedonian allies and the Aetolian League and their allies, the kingdom of Athamania. The Aetolians had invited Antiochus III the Great to Greece, who after his defeat by the Romans had returned to Asia. View Historic Battles »
Roman-Seleucid War (192-188 BC)

Roman-Seleucid War also known as the War of Antiochos or the Syrian War, was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting took place in Greece, the Aegean Sea and Asia Minor. View Historic Battles »
Roman-Spartan War (195 BC)

The War against Nabis, or the Laconian War, of 195 BC was fought between the Greek city-state of Sparta and a coalition composed of Rome, the Achaean League, Pergamum, Rhodes, and Macedon. As a result of the war, Sparta lost its position as a major power in Greece. View Historic Battles »
Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC)

Fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. The result was the defeat of Philip who was forced to abandon all his possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Minor. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Zama (202 BC)

A Roman army led by Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus, with crucial support from Numidian leader Masinissa, defeated the Carthaginian army led by the commander Hannibal. Hannibal's force was greater in numbers than Scipio's, and he had eighty war elephants. View Historic Battles »
First Macedonian War (214–205 BC)

First Macedonian War was fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218–201 BC) against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate. View Historic Battles »
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)

The Second Punic War, also referred to as The Hannibalic War and (by the Romans) the War Against Hannibal, lasted from 218 to 201 BC and involved combatants in the western and eastern Mediterranean. The two states fought three major wars with each other over the course of their existence. View Historic Battles »
Second Illyrian War (220-219 BC)
Leading this fleet of 90 ships, Demetrius sailed south of Lissus, violating his earlier treaty and starting the war. Demetrius' fleet first attacked Pylos, where he captured 50 ships after several attempts. View Historic Battles »
Roman-Gallic War (225-200 BC)

Series of conflicts between the forces of Ancient Rome and various groups identified as Gauls. Broadly, the Gauls crossed the Alps and tried to expand south through Etruria toward Rome. After centuries, Rome was victorious in Italy and took the battle across the Alps into France. View Historic Battles »
First Illyrian War (229-228 BC)

Were a set of wars fought in the period 229–168 BC between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the First Punic War at a time when Ardiaei power increased under queen Teuta. View Historic Battles »
First Punic War (264-241 BC)
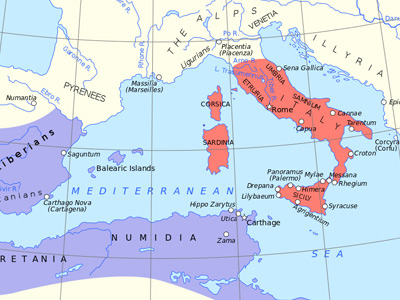
The first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For more than 20 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. Carthage began the war as the great sea-power of the western Mediterranean, while Rome had but a small fleet of fighting ships. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Sparta (272 BC)

The Siege of Sparta took place in 272 BC and was a battle fought between Epirus, led by King Pyrrhus, (r. 297–272 BC) and an alliance consisting of Sparta, under the command of King Areus I (r. 309–265 BC) and his heir Acrotatus, and Macedon. The battle was fought at Sparta and ended in a Spartan-Macedonian victory. View Historic Battles »
Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC)
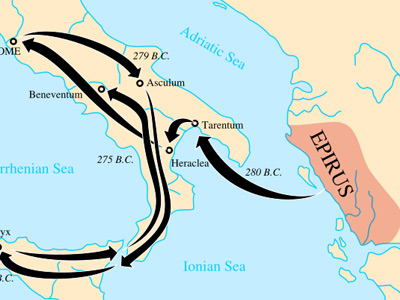
The Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC) was a war Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus, in Greece, fought in southern Italy and Sicily. Pyrrhus was asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to go to Italy to help them in their war with the Roman Republic. View Historic Battles »
Third Samnite War (298 to 290 BC)

The wars extended over half a century and the peoples to the east, north and west of Samnium as well as the peoples of central Italy north of Rome and the Senone Gauls got involved to various degrees and at various points in time. View Historic Battles »
Second Samnite War (326 to 304 BC)

The second one was the result of Rome's intervention in the politics of the city of Naples and developed into a contest over the control of much of central and southern Italy. The Samnites were one of early Rome's most formidable rivals. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Gaugamela (331 BC)

The Battle of Gaugamela, also called the Battle of Arbela, was the decisive battle of Alexander the Great's invasion of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. In 331 BC Alexander's army of the Hellenic League met the Persian army of Darius III near Gaugamela. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Tyre (332 BC)

The Siege of Tyre was orchestrated by Alexander the Great in 332 BC during his campaigns against the Persians. The Macedonian army was unable to capture the city, which was a strategic coastal base on the Mediterranean Sea, through conventional means because it was on an island and had walls right up to the sea. View Historic Battles »
Battle of the Granicus River (334 BC)

The Battle of the Granicus River was the first of three major battles fought between Alexander the Great and the Persian Empire. Fought in Northwestern Asia Minor, near the site of Troy, it was here that Alexander defeated the forces of the Persian satraps of Asia Minor, including a large force of Greek mercenaries led by Memnon of Rhodes. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Chaeronea (338 BC)

The Battle of Chaeronea was fought in 338 BC, near the city of Chaeronea in Boeotia, between the Macedonians led by Philip II of Macedon and an alliance of some of the Greek city-states led by Athens and Thebes. The battle was the culmination of Philip's campaign in Greece (339–338 BC) and resulted in a decisive victory for the Macedonians. View Historic Battles »
Second Latin War (340-338 BC)
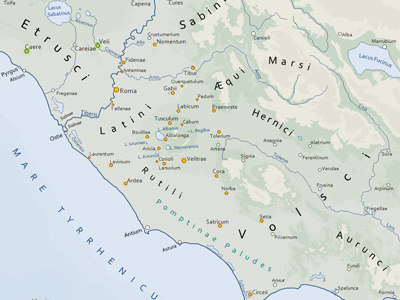
A conflict between the Roman Republic and its neighbors the Latin peoples of ancient Italy. It ended in the dissolution of the Latin League, and incorporation of its territory into the Roman sphere of influence, with the Latins gaining partial rights and varying levels of citizenship. View Historic Battles »
First Samnite War (343-341 BC)

The Samnite Wars were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites. The first of these wars was the result of Rome's intervening to rescue the Campanian city of Capua from a Samnite attack. The Samnites were one of early Rome's most formidable rivals. View Historic Battles »
Third Sacred War (356–346 BC)
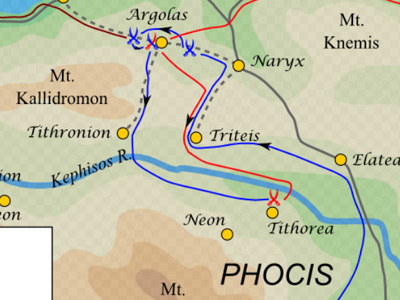
The war was caused by a large fine imposed in 357 BC on the Phocians by the Amphictyonic League, for the offense of cultivating sacred land; refusing to pay, the Phocians instead seized the Temple of Apollo in Delphi, and used the accumulated treasures to fund large mercenary armies. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Leuctra (371 BC)
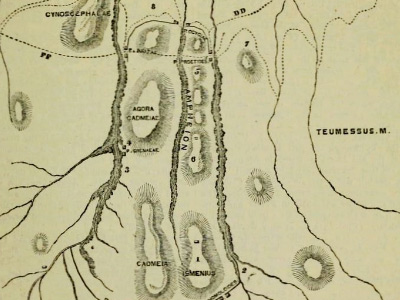
Battle fought between the Boeotians led by Thebans and the Spartans along with their allies amidst the post-Corinthian War conflict. The battle took place in the neighbourhood of Leuctra, a village in Boeotia in the territory of Thespiae. The Theban victory shattered Sparta’s immense influence over the Greek peninsula. View Historic Battles »
Boeotian War (378-372 BC)

The Boeotian or Theban War broke out in 378 BC as the result of a revolt in Thebes against Sparta. The war would last six years. Upon the seizure of the Theban citadel by the Spartans (383 or 382 BC), Pelopidas and other leading Theban democrats fled to Athens where Pelopidas took the lead in a conspiracy to liberate Thebes. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Mantinea (418 BC)

The First Battle of Mantinea of 418 BC was a significant engagement in the Peloponnesian War. Sparta and its allies defeated an army led by Argos and Athens. Their success at Mantinea marked a reversal of the trend and the Greeks again recognized the near-invincibility of the Spartans in hoplite combat. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Pylos (425 BC)

The naval Battle of Pylos took place in 425 BC during the Peloponnesian War at the peninsula of Pylos, on the present-day Bay of Navarino in Messenia, and was an Athenian victory over Sparta. An Athenian fleet had been driven ashore at Pylos by a storm, and, at the instigation of Demosthenes, the Athenian soldiers fortified the peninsula, and a small force was left there when the fleet departed again. View Historic Battles »
Second Peloponnesian War (431-404 BC)

An ancient Greek war fought by the Delian League led by Athens against the Peloponnesian League led by Sparta. In the first phase, the Archidamian War, Sparta launched repeated invasions of Attica, while Athens took advantage of its naval supremacy to raid the coast of the Peloponnese and attempt to suppress signs of unrest in its empire. View Historic Battles »
Second Sacred War (449—448 BC)

The Second Sacred War took place during 449 BC and 448 BC and resulted in an indirect confrontation between Athens and Sparta during the First Peloponnesian War. The Athenians who had gained control over Boeotia and Phocis decided to detach the city of Delphi from the Ampictyony and hand it over to the Phocians. View Historic Battles »
First Peloponnesian War (460-445 BC)

Fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Mycale (479 BC)

Battle of Mycale was one of the two major battles that ended the second Persian invasion of Greece during the Greco-Persian Wars. It took place on or about August 27, 479 BC on the slopes of Mount Mycale, on the coast of Ionia, opposite the island of Samos. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Plataea (479 BC)

The Battle of Plataea was the final land battle during the second Persian invasion of Greece. It took place in 479 BC near the city of Plataea in Boeotia, and was fought between an alliance of the Greek city-states (including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and Megara), and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Salamis (480 BC)

Battle of Salamis was a naval battle fought between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles and the Persian Empire under King Xerxes in 480 BC which resulted in a decisive victory for the outnumbered Greeks. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Artemisium (480 BC)

The battle took place simultaneously with the more famous land battle at Thermopylae, in August or September 480 BC, off the coast of Euboea and was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, including Sparta, Athens, Corinth and others, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Thermopylae (480 BC)
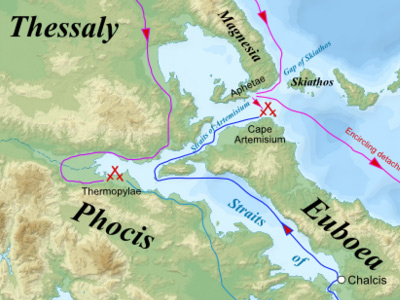
The battle was fought between an alliance of Greek city-states, led by King Leonidas of Sparta, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I over the course of three days, during the second Persian invasion of Greece. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Marathon (490 BC)

The battle took place during the first Persian invasion of Greece. Fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia, under King Darius I, to subjugate Greece. View Historic Battles »
Latin War (498–493 BC)

The Latin War was a war fought between the Roman Republic and the Latin League from 498 BC to 493 BC. According to the historical chronicles, the beginnings of this war between the Romans and Latins can be seen as early as 501 BC, though the root causes date back much farther. View Historic Battles »
Battle of the 300 Champions (546 BC)

Battle fought in roughly 546 BC between Argos and Sparta. Rather than commit full armies both sides agreed to pitting 300 of their best men against each other. Neither side would allow for any injured men to be taken. The day called for complete destruction of the enemy force for victory. View Historic Battles »
First Sacred War (595—585 BC)

In the beginning of the 6th century B.C. the attempt of the Pylaeo-Delphic Amphictyony, controlled by the Thessalians, to take hold of the Sacred Land of Apollo ended up in this war. The war is notable for the use of chemical warfare at the Siege of Kirrha, in the form of hellebore being used to poison the city's water supply. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Nineveh (612 BC)

Battle of Nineveh is conventionally dated between 613 and 611 BC, with 612 BC being the most supported date. An allied army composed of Medes and the Chaldeans, rebelling against the Assyrians, together with Scythians and Cimmerians, besieged it and sacked 750 hectares of what was at that time, the greatest city in the world. View Historic Battles »
Fall of Ashdod (635 BC)

The Fall of Ashdod refers to the successful Egyptian assault on the city of Ashdod in Palestine in c. 635 BC. According to the Greek historian Herodotus, pharaoh Psamtik I, besieged Ashdod for 29 years. Ashdod had lost most of its inhabitants during those long years of siege. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Susa (647 BC)

Battle of Susa was a battle involving Assyrians and Elamites. The Assyrian king Ashurbanipal, had grown tired of the Elamites' attacks on the Mesopotamians, and he decided to destroy Susa as punishment. In 647 BC, the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal leveled the city during the war. View Historic Battles »
Second Messenian War (685—668 BC)
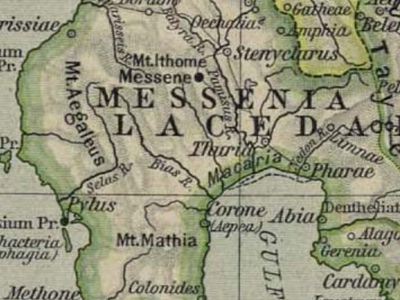
It started around 40 years after the end of the First Messenian War with the uprising of a slave rebellion. Other scholars, however, assign later dates, claiming, for example, that 668 is the date of the war's start, pointing at Sparta's defeat at the First Battle of Hysiae as a possible catalyst for the uprising. View Historic Battles »
First Messenian War (743—724 BC)

The First Messenian War was a war between Messenia and Sparta. It began in 743 BC and ended in 724 BC, according to the dates given by Pausanias. The war continued the rivalry between the Achaeans and the Dorians that had been initiated by the Return of the Heracleidae. View Historic Battles »
Battle of the Delta (1175 BC)

The Battle of the Delta was a sea battle between Egypt and the Sea Peoples when the Egyptian pharaoh Ramesses III repulsed a major sea invasion. The conflict occurred somewhere at the shores of the eastern Nile Delta and partly on the borders of the Egyptian Empire in Syria. This major conflict is recorded on the temple walls of the mortuary temple of pharaoh Ramesses III at Medinet Habu. View Historic Battles »
Trojan War (1194–1184 BC)

In Greek mythology, the Trojan War (1194–1184 BC) was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The hollow horse was filled with soldiers led by Odysseus. The rest of the army burned the camp and sailed for Tenedos. View Historic Battles »
Siege of Dapur (1269 BC)
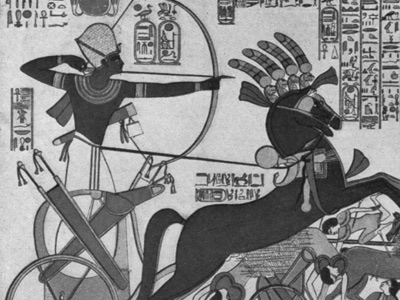
Siege of Dapur occurred as part of Ramesses II's campaign to suppress Galilee and conquer Syria in 1269 BC. He described his campaign on the wall of his mortuary temple, the Ramesseum in Thebes. From Egyptian reliefs we can see that Dapur was a city, heavily fortified with both inner and outer walls, and situated on a rocky hill which was usual for Syrian cities and many other cities in the Bronze Age. View Historic Battles »
Battle of Kadesh (1274 BC)

Battle of Kadesh or Battle of Qadesh took place between the forces of the Egyptian Empire under Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire under Muwatalli II at the city of Kadesh on the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs near the modern Syrian-Lebanese border. It is believed to have been the largest chariot battle ever fought, involving between 5,000 and 6,000 chariots in total. View Historic Battles »

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia articles "Battle", "Short story", "Pilot (aeronautics)", "Aircrew", "Airline pilot uniforms", "Sailor", "Sailor suit", "World war", "World War I", "World War II", "Cold War (1947–1991)", "2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine", "Iraq War", "2019-2021 Persian Gulf Crisis", "Iraqi Civil War (2014-2017)", "War in Darfur", "Gulf war", "1993 Russian Constitutional Crisis", "Second Congo War", "Russian Invasion of Manchuria", "British Expedition to Tibet", "1905 Russian Revolution", "Mexican Revolution", "First Balkan War", "Second Balkan War", "Russian Civil War", "French Conquest of Algeria", "Battle of Mazagran", "July Revolution", "Battle of Marignano", "Burning of Washington", "Battle of San Domingo",
"Napoleonic Wars", "Napoleon", "Korean War", "Battle of Taegu (1950)", "Goguryeo–Sui War (598-614 AD)", "Vietnam War (1955–1975)", "Seven Years' War", "First Carlist War", "Second Northern War", "Nine Years' War", "Eighty Years' War (1568–1648)", "Franco-Prussian War", "Liberal Wars", "War of the Spanish Succession", "Queen Anne's War", "War of the First Coalition", "War of the Second Coalition", "Russo-Japanese War", "Spanish Civil War", "Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–1718)", "Battle of the Catalaunian Plains", "Battle of Hastings", "Siege of Orléans", "War of the Quadruple Alliance", "Caesar's Civil War", "Gallic Wars", "Battle of Baduhenna Wood (28 AD)", "War against Nabis", "Social War (91–88 BC)", "Battle of Aquae Sextiae (102 BC)", "Battle of Vercellae (101 BC)", "Battle of Arausio (105 BC)", "Battle of Bibracte (58 BC)", "Galatian War",
"Roman-Gallic wars", "First Punic War", "Second Punic War", "Third Punic War", "Battle of Carthage (149-146 BC)", "First Illyrian War", "Second Illyrian War", "First Samnite War", "Second Samnite Wars", "Third Samnite Wars", "First Macedonian War (214–205 BC)", "Roman–Parthian War (58–63 AD)", "Final War of the Roman Republic (32-30 BC)", "Cantabrian Wars", "Third Servile War (73-71 BC)", "Third Mithridatic War (73-63 BC)", "Second Mithridatic War (83-81 BC)", "First Mithridatic War (89-85 BC)", "Lusitanian War (155-139 BC)", "Roman-Seleucid War (192-188 BC)", "Battle of Adrianople (378 AD)", "Vandalic War (533-534 AD)", "Sack of Rome (410)", "First Dacian War", "Second Dacian War", "Year of the Four Emperors", "Latin War (498–493 BC)", "Latin War", "Pyrrhic War", "Battle of the 300 Champions", "Battle of Thermopylae", "Trojan War",
"Battle of Kadesh (1274 BC)", "Siege of Dapur (1269 BC)", "Battle of the Delta (1175 BC)", "Fall of Ashdod (635 BC)", "Battle of Nineveh (612 BC)", "First Messenian War (743—724 BC)", "Second Messenian War (685—668 BC)", "First Sacred War (595—585 BC)", "Second Sacred War (449—448 BC)", "Third Sacred War (356–346 BC)", "First Peloponnesian War (460-445 BC)", "Second Peloponnesian War (431-404 BC)", "Battle of Pylos (425 BC)", "Battle of Mantinea (418 BC)", "Battle of Leuctra (371 BC)", "Boeotian War (378-372 BC)", "Battle of Chaeronea (338 BC)", "Battle of Plataea (479 BC)", "Battle of Artemisium (480 BC)", "Battle of Mycale (479 BC)", "Battle of Marathon (490 BC)", "Battle of Zama (202 BC)", "Siege of Sparta (272 BC)", "Battle of the Granicus", "Siege of Tyre (332 BC)", "Battle of the Milvian Bridge (312 AD)", "Battle of Edessa (260 AD)", "Battle of Gaugamela", "French and Indian War", "Second Macedonian War", "Aetolian War",
"Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC)", "Jugurthine War", "Cimbrian War", "Fourth Macedonian War", "Year of the Five Emperors", "Marcomannic Wars", "Roman conquest of Britain", "Battle of the Teutoburg Forest (9 AD)", "Roman invasion of Caledonia (208–210 AD)", "Battle of Salamis", "Spanish Armada", "Genpei War (1180–1185)", "Battle of Solferino (1859)", "Battle of Magenta (1859)", "Battle of Malakoff (1855)", "Battle of the Chernaya (1855)", "Battle of the Alma (1854)", "Battle of Cetate (1853-1854)", "Storming of the Bastille (1789)", "Battles of Saratoga (1777)", "American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)", "Battle of Taillebourg (1242)", "Battle of Fraga (1134)", "Battle of Muret (1213)", "Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa (1212)", "Battle of Assandun (1016)", "Battle of Svolder (1000)", "Battle of Stiklestad (1030)", "First Crusade (1095–1099)", "Second Crusade (1147–1149)", "Third Crusade (1189–1192)", "Fourth Crusade (1202–04)",
"Second Battle of Komarom", "Peninsular War", "Battle of Tetuan", "Battle of Arbedo", "Battle of Pavia", "Battle of Garigliano (1503)", "Siege of Calais (1558)", "Battle of the Puig", "Siege of Toledo (1085)", "Siege of Lisbon", "Battle of Ourique", "Portuguese Restoration War", "Battle of Aljubarrota", "Battle of Shrewsbury", "Battle of Kressenbrunn", "Battle of Cerignola", "Battle of Ravenna (1512)", "Battle of Ceresole", "Wars of the Roses", "Battle of Towton", "Battle of Barnet", "Battle of Tewkesbury", "Battle of Bosworth Field", "Battle of Manzikert", "Battle of Ascalon", "Battle at Brůdek", "Battle of Fulford", "Siege of Szigetvár", "Battle of Mohács", "Second Battle of Mohács",
"Battle of Zenta", "Long Turkish War", "Anglo-Dutch Wars", "Franco-Dutch War", "Dutch-Portuguese War",
"Fifth Crusade (1213–1221)", "Sixth Crusade (1228–1229)", "Seventh Crusade (1248–1254)", "Eighth Crusade (1270)", "Ninth Crusade (1271–1272)", "Battle of Edington (878)", "Battle of Covadonga (722)", "Battle of Guadalete (711 AD)", "Battle of Stamford Bridge (1066)", "Battle of Tinchebray (1106)", "Battle of Nicopolis (1396)", "Battle of Formigny (1450)", "Second Battle of Kosovo (1448)", "Battle of Varna (1444)", "Battle of Worringen (1288)", "Battle on the Marchfeld (1278)", "Siege of Busanjin (1592)", "Battle of Myeongnyang", "French campaign against Korea (1866)", "Hōgen Rebellion (1156)", "Heiji Rebellion (1160)", "Battle of Shijōnawate (1348)", "Genkō War (1331-1333)", "Battle of Nagashino (1575)", "Battle of Okehazama (1560)", "Siege of Inabayama Castle (1567)", "Siege of Takamatsu (1582)", "Invasion of Shikoku (1585)", "Battle of Sekigahara (1600)", "Invasion of Ryukyu (1609)", "Battles of Kawanakajima (1553-1564)", "Battle of Shiroyama (1877)", "Battle of Tabaruzaka (1877)", "Boshin War (1868-1869)", "47 Ronin 四十七士 (1701-1703)",
"Battle of Hohenfriedberg", "Battle of Blenheim", "Battle of Königgrätz", "Battle of Friedland", "Battle of Langensalza", "Battle of Eylau", "Battle of Jena-Auerstedt", "Battle of Lissa", "Battle of Austerlitz", "Belgian Revolution", "Battle of Manila Bay", "Battle of Leuthen", "Battle of Gettysburg", "Siege of Vicksburg", "American Civil War", "Battle of Antietam", "French Invasion of Russia", "Battle of Balaclava", "Battle of Plassey", "Battle of Vienna", "Battle of Raszyn (1809)", "Battle of Vienna",
"Battle of Grunwald (1410)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.
"Building Cool Educational Stuff for Children and Adults!"


Historic Battles
Wars and military campaigns are guided by strategy, whereas battles take place on a level of planning and execution known as operational mobility.
View Historic Battles »


Historic People
A historical figure is a famous person in history, such as Alexander the Great, Admiral Yi Sun-Shin, Abraham Lincoln, George Washington, Christopher Columbus, or Napoleon Bonaparte.
View Historic People »


Historic Timeline
Describes the history of humanity as determined by the study of archaeological and written records. Ancient recorded history begins with the invention of writing.
View Historic Timeline »

Historic Legends
Beings in myths are generally gods and goddesses, heroes and heroines, or animals and plants. Most myths are set in a timeless past before recorded time or beginning of the critical history.
View Historic Legends »

Sports World
Includes competitive games which, through casual or organized participation, aim to use, maintain or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants.
View Sports World »

Untold Stories
If you have any questions, feedback or suggestions for us, we'd like to hear from you. Please feel free to contact us!
Contact Us

Historic Battles
Wars and military campaigns are guided by strategy, whereas battles take place on a level of planning and execution known as operational mobility.
View Historic Battles »

Historic People
A historical figure is a famous person in history, such as Alexander the Great, Admiral Yi Sun-Shin, Abraham Lincoln, George Washington, Christopher Columbus, or Napoleon Bonaparte.
View Historic People »

Historic Timeline
Describes the history of humanity as determined by the study of archaeological and written records. Ancient recorded history begins with the invention of writing.
View Historic Timeline »

Historic Legends
Beings in myths are generally gods and goddesses, heroes and heroines, or animals and plants. Most myths are set in a timeless past before recorded time or beginning of the critical history.
View Historic Legends »

Sports World
Includes competitive games which, through casual or organized participation, aim to use, maintain or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants.
View Sports World »

Untold Stories
If you have any questions, feedback or suggestions for us, we'd like to hear from you. Please feel free to contact us!
Contact Us
Historic Battles
Wars and military campaigns are guided by strategy, whereas battles take place on a level of planning and execution known as operational mobility.
View Historic Battles »

Historic People
A historical figure is a famous person in history, such as Alexander the Great, Admiral Yi Sun-Shin, Abraham Lincoln, George Washington, Christopher Columbus, or Napoleon Bonaparte.
View Historic People »

Historic Timeline
Describes the history of humanity as determined by the study of archaeological and written records. Ancient recorded history begins with the invention of writing.
View Historic Timeline »

Historic Legends
Beings in myths are generally gods and goddesses, heroes and heroines, or animals and plants. Most myths are set in a timeless past before recorded time or beginning of the critical history.
View Historic Legends »

Sports World
Includes competitive games which, through casual or organized participation, aim to use, maintain or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants.
View Sports World »

Untold Stories
If you have any questions, feedback or suggestions for us, we'd like to hear from you. Please feel free to contact us!
Contact Us