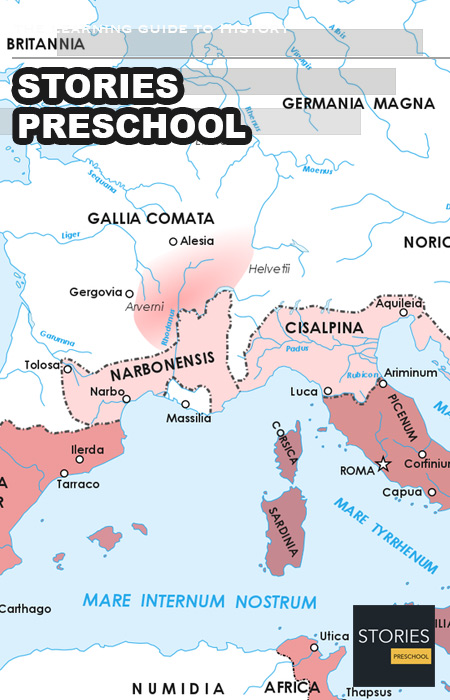
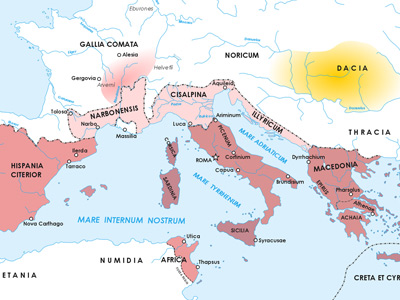
Great Roman Civil War (49–45 BC)
The Great Roman Civil War (49–45 BC), also known as Caesar's Civil War, was one of the last politico-military conflicts in the Roman Republic The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. before the establishment of the Roman Empire
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. before the establishment of the Roman Empire The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire.. It began as a series of political and military confrontations, between Julius Caesar (100–44 BC), his political supporters (broadly known as Populares), and his legions, against the Optimates (or Boni), the politically conservative and socially traditionalist faction of the Roman Senate, who were supported by Pompey (106–48 BC) and his legions.
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire.. It began as a series of political and military confrontations, between Julius Caesar (100–44 BC), his political supporters (broadly known as Populares), and his legions, against the Optimates (or Boni), the politically conservative and socially traditionalist faction of the Roman Senate, who were supported by Pompey (106–48 BC) and his legions.
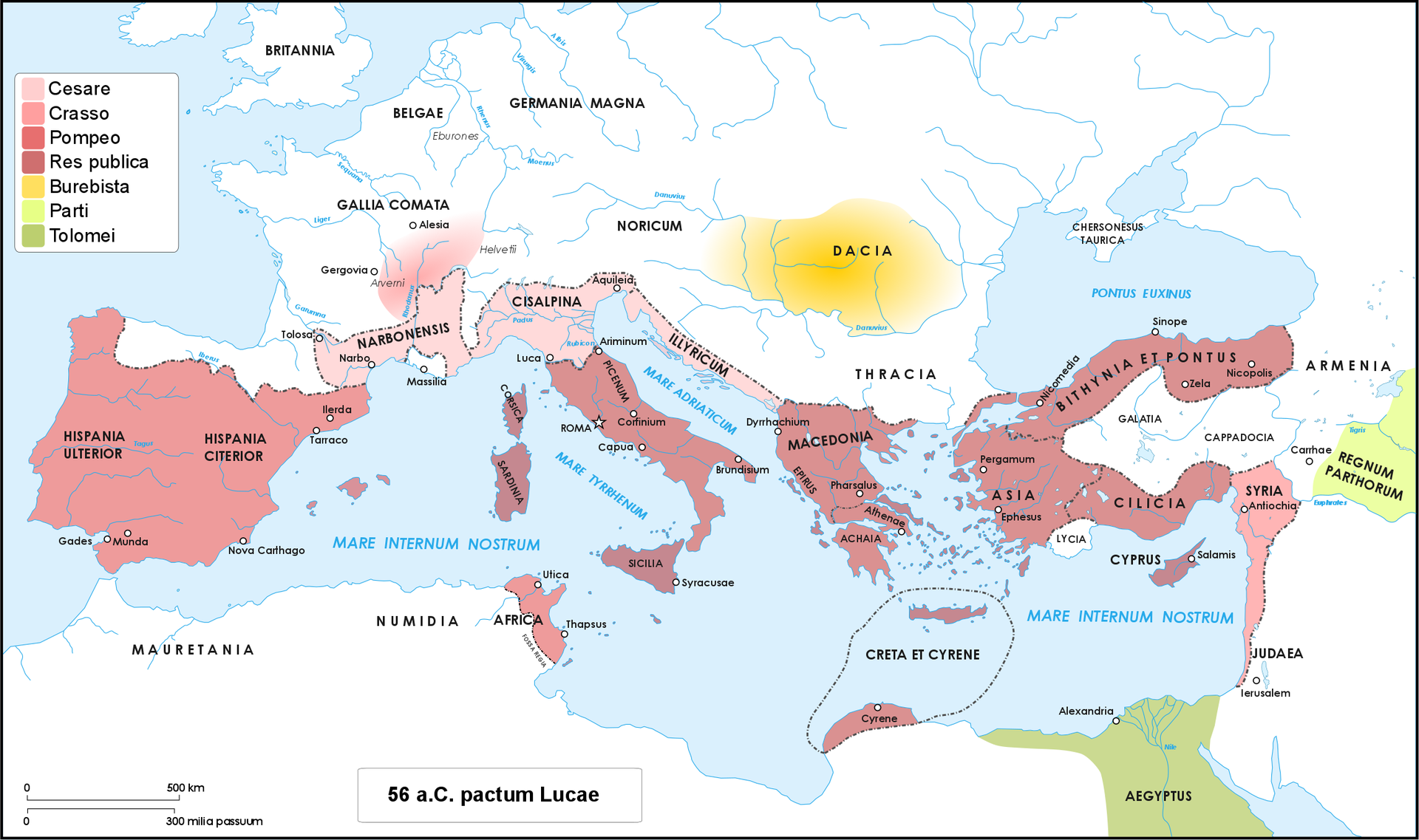
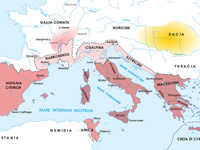
Roman world in 56 BC, when Caesar, Crassus and Pompey meet at Luca for a conference in which they decided: to add another five years to the proconsulship of Caesar in Gaul; to give the province of Syria to Crassus and both Spains and Africa to Pompey

Roman world in 56 BC, when Caesar, Crassus and Pompey meet at Luca for a conference in which they decided: to add another five years to the proconsulship of Caesar in Gaul; to give the province of Syria to Crassus and both Spains and Africa to Pompey.
( Click image to enlarge)
After a five-year-long (49–45 BC) politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania, Caesar Julius Caesar (100-44 BC), was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. Caesar is considered by many historians to be one of the greatest military commanders in history. Julius Caesar » defeated the last of the Optimates in the Battle of Munda and became Dictator perpetuo (Dictator in perpetuity) of Rome. The changes to Roman government concomitant to the war mostly eliminated the political traditions of the Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and led to the Roman Empire (27 BC–AD 476).
Julius Caesar (100-44 BC), was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. Caesar is considered by many historians to be one of the greatest military commanders in history. Julius Caesar » defeated the last of the Optimates in the Battle of Munda and became Dictator perpetuo (Dictator in perpetuity) of Rome. The changes to Roman government concomitant to the war mostly eliminated the political traditions of the Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and led to the Roman Empire (27 BC–AD 476).
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Caesar's Civil War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.