French and Indian War (1754–1763)
Consequences
The war changed economic, political, governmental and social relations between three European powers (Britain, France, and Spain), their colonies and colonists, and the natives that inhabited the territories they claimed. France The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. and Britain
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. and Britain The Kingdom of Great Britain was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. both suffered financially because of the war, with significant long-term consequences.
The Kingdom of Great Britain was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of England (which included Wales) and Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. both suffered financially because of the war, with significant long-term consequences.

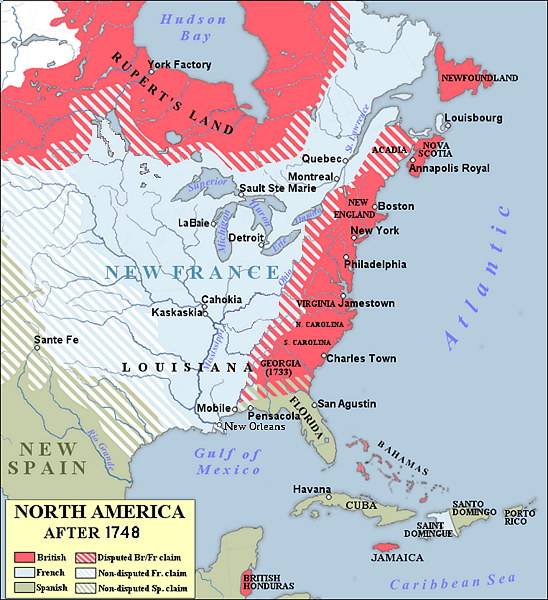
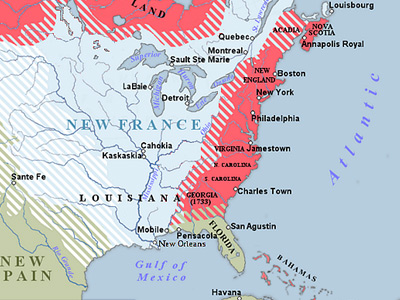
Map showing territorial gains of Britain and Spain following the French and Indian War. Also shown are boundary changes within the territory the British had acquired between 1763 to 1783. Territorial lands held by the British before 1763 is shown in red, land gained by Britain in 1763 is shown in pink. The lands ceded to the Kingdom of Spain in secret during 1762 are in light yellow.

Map showing territorial gains of Britain and Spain following the French and Indian War. Also shown are boundary changes within the territory the British had acquired between 1763 to 1783. Territorial lands held by the British before 1763 is shown in red, land gained by Britain in 1763 is shown in pink. The lands ceded to the Kingdom of Spain in secret during 1762 are in light yellow.
( Click image to enlarge)
Britain gained control of French Canada and Acadia, colonies containing approximately 80,000 primarily French-speaking Roman Catholic residents. The deportation of Acadians beginning in 1755 resulted in land made available to migrants from Europe and the colonies further south. The British resettled many Acadians throughout its North American provinces, but many went to France, and some went to New Orleans, which they had expected to remain French. Some were sent to colonize places as diverse as French Guiana and the Falkland Islands; these latter efforts were unsuccessful. Others migrated to places like Saint-Domingue, and fled to New Orleans after the Haitian Revolution. The Louisiana population contributed to the founding of the modern Cajun population. (The French word "Acadien" evolved to "Cadien", then to "Cajun".)
Following the treaty, King George III issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763 on October 7, 1763, which outlined the division and administration of the newly conquered territory, and to some extent continues to govern relations between the government of modern Canada and the First Nations. Included in its provisions was the reservation of lands west of the Appalachian Mountains to its Indian population, a demarcation that was at best a temporary impediment to a rising tide of westward-bound settlers. The proclamation also contained provisions that prevented civic participation by the Roman Catholic Canadians. When accommodations were made in the Quebec Act in 1774 to address this and other issues, religious concerns were raised in the largely Protestant Thirteen Colonies over the advance of "popery"; the Act maintained French Civil law, including the seigneurial system, a medieval code soon to be removed from France within a generation by the French Revolution.
The Seven Years' War nearly doubled Great Britain's national debt. The Crown, seeking sources of revenue to pay off the debt, attempted to impose new taxes on its colonies. These attempts were met with increasingly stiff resistance, until troops were called in so that representatives of the Crown could safely perform their duties. These acts ultimately led to the start of the American Revolutionary War.
France attached comparatively little value to its North American possessions, apart from the highly profitable sugar-producing Antilles islands, which it managed to retain. Minister Choiseul considered he had made a good deal at the Treaty of Paris, and philosopher Voltaire wrote that Louis XV had lost "a few acres of snow". For France however, the military defeat and the financial burden of the war weakened the monarchy and contributed to the advent of the French Revolution in 1789.
For many native populations, the elimination of French power in North America meant the disappearance of a strong ally and counterweight to British expansion, leading to their ultimate dispossession. The Ohio Country was particularly vulnerable to legal and illegal settlement due to the construction of military roads to the area by Braddock and Forbes. Although the Spanish The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. takeover of the Louisiana territory (which was not completed until 1769) had modest repercussions, the British takeover of Spanish Florida resulted in the westward migration of tribes that did not want to do business with the British, and a rise in tensions between the Choctaw and the Creek, historic enemies whose divisions the British at times exploited. The change of control in Florida also prompted most of its Spanish Catholic population to leave. Most went to Cuba, including the entire governmental records from St. Augustine, although some Christianized Yamasee were resettled to the coast of Mexico.
The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. takeover of the Louisiana territory (which was not completed until 1769) had modest repercussions, the British takeover of Spanish Florida resulted in the westward migration of tribes that did not want to do business with the British, and a rise in tensions between the Choctaw and the Creek, historic enemies whose divisions the British at times exploited. The change of control in Florida also prompted most of its Spanish Catholic population to leave. Most went to Cuba, including the entire governmental records from St. Augustine, although some Christianized Yamasee were resettled to the coast of Mexico.
France returned to North America in 1778 with the establishment of a Franco-American alliance against Great Britain in the American War of Independence.
This time France succeeded in prevailing over Great Britain, in what historian Alfred A. Cave describes as:
"French [...] revenge for Montcalm's death".
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "French and Indian War (1754–1763)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.