Genghis Khan (1162-1227)

Military Campaigns
Western Xia Dynasty
During the 1206 political rise of Genghis Khan, the Mongol Empire created by Genghis Khan and his allies shared its western borders with the Western Xia dynasty of the Tanguts. To the east and south was the Jin dynasty, founded by the Manchurian Jurchens, who ruled northern China as well as being the traditional overlords of the Mongolian tribes for centuries.
Genghis Khan organized his people, army, and his state to first prepare for war with Western Xia, or Xi Xia, which was close to the Mongolian lands. He correctly believed that the more powerful young ruler of the Jin dynasty would not come to the aid of Xi Xia. When the Tanguts requested help from the Jin dynasty, they were refused. Despite initial difficulties in capturing its well-defended cities, Genghis Khan managed to force the emperor of Xi Xia to submit to vassal status.

Battle between Mongol warriors and the Chinese
Jin Dynasty
In 1211, after the conquest of Western Xia, Genghis Khan planned again to conquer the Jin dynasty. Wanyan Jiujin, the field commander of the Jin army, made a tactical mistake in not attacking the Mongols at the first opportunity. Instead, the Jin commander sent a messenger, Ming'an, to the Mongol side, who defected and told the Mongols that the Jin army was waiting on the other side of the pass. At this engagement fought at Yehuling, the Mongols massacred hundreds of thousands of Jin troops. In 1215, Genghis besieged, captured, and sacked the Jin capital of Zhongdu (modern-day Beijing). This forced the Jin ruler, Emperor Xuanzong, to move his capital south to Kaifeng, abandoning the northern half of his empire to the Mongols. Between 1232 and 1233, Kaifeng fell to the Mongols under the reign of Genghis's third son, Ögedei Khan. The Jin dynasty collapsed in 1234, after the siege of Caizhou.
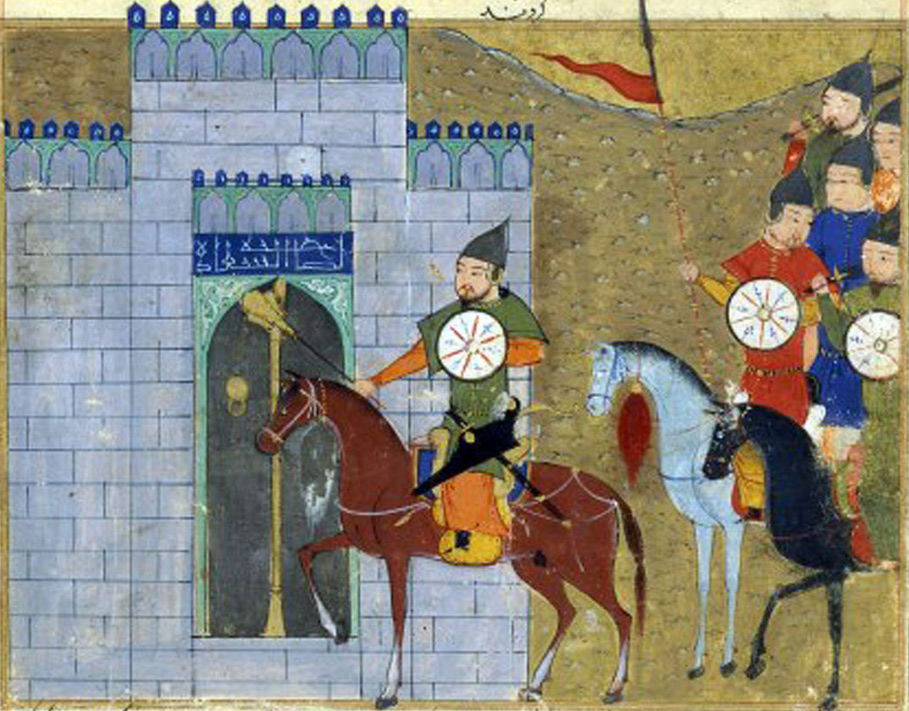

Genghis Khan Entering Beijing
Qara Khitai
Kuchlug, the deposed Khan of the Naiman confederation that Temüjin defeated and folded into his Mongol Empire, fled west and usurped the khanate of Qara Khitai (also known as the Western Liao, as it was originally established as remnants of the Liao dynasty). Genghis Khan decided to conquer the Qara Khitai and defeat Kuchlug, possibly to take him out of power. By this time the Mongol army was exhausted from ten years of continuous campaigning in China against the Western Xia and Jin dynasty. Therefore, Genghis sent only two tumen (20,000 soldiers) against Kuchlug, under his younger general, Jebe, known as "The Arrow".
With such a small force, the invading Mongols were forced to change strategies and resort to inciting internal revolt among Kuchlug's supporters, leaving the Qara Khitai more vulnerable to Mongol conquest. As a result, Kuchlug's army was defeated west of Kashgar. Kuchlug fled again, but was soon hunted down by Jebe's army and executed. By 1218, as a result of defeat of Qara Khitai, the Mongol Empire and its control extended as far west as Lake Balkhash, which bordered Khwarazmia, a Muslim state that reached the Caspian Sea to the west and Persian Gulf and the Arabian Sea to the south.
Khwarazmian Empire
In the early 13th century, the Khwarazmian dynasty was governed by Shah Ala ad-Din Muhammad. Genghis Khan saw the potential advantage in Khwarazmia as a commercial trading partner using the Silk Road, and he initially sent a 500-man caravan to establish official trade ties with the empire. However, Inalchuq, the governor of the Khwarazmian city of Otrar, attacked the caravan, claiming that the caravan contained spies and therefore was a conspiracy against Khwarazmia. The situation became further complicated because the governor later refused to make repayments for the looting of the caravans and hand over the perpetrators. Genghis Khan then sent a second group of three ambassadors (two Mongols and a Muslim) to meet the Shah himself, instead of the governor Inalchuq. The Shah had all the men shaved and the Muslim beheaded and sent his head back with the two remaining ambassadors. This was seen as an affront and insult to Genghis Khan. Outraged, Genghis Khan planned one of his largest invasion campaigns by organizing together around 100,000 soldiers (10 tumens), his most capable generals and some of his sons. He left a commander and number of troops in China, designated his successors to be his family members and likely appointed Ögedei to be his immediate successor and then went out to Khwarazmia.
The Mongol army under Genghis Khan, generals and his sons crossed the Tien Shan mountains by entering the area controlled by the Khwarazmian Empire. After compiling intelligence from many sources Genghis Khan carefully prepared his army, which was divided into three groups. His son Jochi led the first division into the northeast of Khwarazmia. The second division under Jebe marched secretly to the southeast part of Khwarazmia to form, with the first division, a pincer attack on Samarkand. The third division under Genghis Khan and Tolui marched to the northwest and attacked Khwarazmia from that direction.
The Shah's army was split by diverse internecine feuds and by the Shah's decision to divide his army into small groups concentrated in various cities. This fragmentation was decisive in Khwarazmia's defeats, as it allowed the Mongols, although exhausted from the long journey, to immediately set about defeating small fractions of the Khwarazmian forces instead of facing a unified defense. The Mongol army quickly seized the town of Otrar, relying on superior strategy and tactics. Genghis Khan ordered the wholesale massacre of many of the civilians, enslaved the rest of the population and executed Inalchuq by pouring molten silver into his ears and eyes, as retribution for his actions. Near the end of the battle the Shah fled rather than surrender. Genghis Khan ordered Subutai and Jebe to hunt him down, giving them 20,000 men and two years to do this. The Shah died under mysterious circumstances on a small island within his empire.
The Mongols' conquest, even by their own standards, was brutal. After the capital Samarkand fell, the capital was moved to Bukhara by the remaining men, while Genghis Khan ordered two of his generals and their forces to completely destroy the remnants of the Khwarazmian Empire, including not only royal buildings, but entire towns, populations, and even vast swaths of farmland.
The Mongols attacked Samarkand using captured enemies as body shields. After several days only a few remaining soldiers, loyal supporters of the Shah, held out in the citadel. After the fortress fell, Genghis supposedly reneged on his surrender terms and executed every soldier that had taken arms against him at Samarkand. The people of Samarkand were ordered to evacuate and assemble in a plain outside the city, where they were killed and pyramids of severed heads raised as a symbol of victory. Ata-Malik Juvayni, a high official in the service of the Mongol empire, wrote that in Termez, on the Oxus, "all the people, both men and women, were driven out onto the plain, and divided in accordance with their usual custom, then they were all slain".
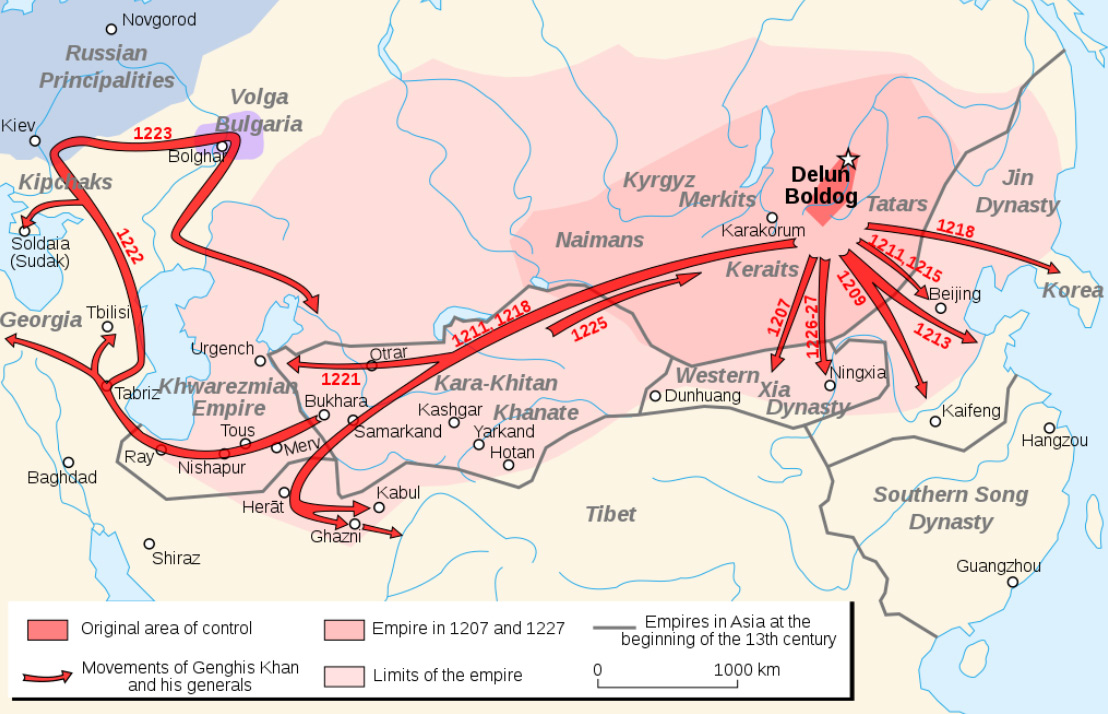
Significant conquests and movements of Genghis Khan and his generals

Significant conquests and movements of Genghis Khan and his generals
( Click image to enlarge)
The city of Bukhara was not heavily fortified, with a moat and a single wall, and the citadel typical of Khwarazmian cities. The city leaders opened the gates to the Mongols, though a unit of Turkish defenders held the city's citadel for another twelve days. Survivors from the citadel were executed, artisans and craftsmen were sent back to Mongolia, young men who had not fought were drafted into the Mongolian army and the rest of the population was sent into slavery. As the Mongol soldiers looted the city, a fire broke out, razing most of the city to the ground. Genghis Khan had the city's surviving population assemble in the main mosque of the town, where he declared that he was the flail of God, sent to punish them for their sins.
Meanwhile, the wealthy trading city of Urgench was still in the hands of Khwarazmian forces. The assault on Urgench proved to be the most difficult battle of the Mongol invasion and the city fell only after the defenders put up a stout defense, fighting block for block. Mongolian casualties were higher than normal, due to the unaccustomed difficulty of adapting Mongolian tactics to city fighting.
As usual, the artisans were sent back to Mongolia, young women and children were given to the Mongol soldiers as slaves, and the rest of the population was massacred. The Persian scholar Juvayni states that 50,000 Mongol soldiers were given the task of executing twenty-four Urgench citizens each, which would mean that 1.2 million people were killed. The sacking of Urgench is considered one of the bloodiest massacres in human history.
In the meantime, Genghis Khan selected his third son Ögedei as his successor before his army set out, and specified that subsequent Khans should be his direct descendants. Genghis Khan also left Muqali, one of his most trusted generals, as the commander of all Mongol forces in Jin China while he was out battling the Khwarezmid Empire to the west.
Georgia, Crimea, Kievan Rus and Volga Bulgaria
After the defeat of the Khwarazmian Empire in 1220, Genghis Khan gathered his forces in Persia and Armenia to return to the Mongolian steppes. Under the suggestion of Subutai, the Mongol army was split into two forces. Genghis Khan led the main army on a raid through Afghanistan and northern India towards Mongolia, while another 20,000 (two tumen) contingent marched through the Caucasus and into Russia under generals Jebe and Subutai. They pushed deep into Armenia and Azerbaijan. The Mongols destroyed the kingdom of Georgia, sacked the Genoese trade-fortress of Caffa in Crimea and overwintered near the Black Sea. Heading home, Subutai's forces attacked the allied forces of the Cuman–Kipchaks and the poorly coordinated 80,000 Kievan Rus' troops led by Mstislav the Bold of Halych and Mstislav III of Kiev who went out to stop the Mongols' actions in the area. Subutai sent emissaries to the Slavic princes calling for a separate peace, but the emissaries were executed. At the Battle of Kalka River in 1223, Subutai's forces defeated the larger Kievan force. They may have been defeated by the neighbouring Volga Bulgars at the Battle of Samara Bend. There is no historical record except a short account by the Arab historian Ibn al-Athir, writing in Mosul some 1100 miles away from the event. Various historical secondary sources – Morgan, Chambers, Grousset – state that the Mongols actually defeated the Bulgars, Chambers even going so far as to say that the Bulgars had made up stories to tell the (recently crushed) Russians that they had beaten the Mongols and driven them from their territory. The Russian princes then sued for peace. Subutai agreed but was in no mood to pardon the princes. As was customary in Mongol society for nobility, the Russian princes were given a bloodless death. Subutai had a large wooden platform constructed on which he ate his meals along with his other generals. Six Russian princes, including Mstislav III of Kiev, were put under this platform and crushed to death.
The Mongols learned from captives of the abundant green pastures beyond the Bulgar territory, allowing for the planning for conquest of Hungary and Europe. Genghis Khan recalled Subutai back to Mongolia soon afterwards, and Jebe died on the road back to Samarkand. The famous cavalry expedition led by Subutai and Jebe, in which they encircled the entire Caspian Sea defeating all armies in their path, remains unparalleled to this day, and word of the Mongol triumphs began to trickle to other nations, particularly Europe. These two campaigns are generally regarded as reconnaissance campaigns that tried to get the feel of the political and cultural elements of the regions. In 1225 both divisions returned to Mongolia. These invasions added Transoxiana and Persia to an already formidable empire while destroying any resistance along the way. Later under Genghis Khan's grandson Batu and the Golden Horde, the Mongols returned to conquer Volga Bulgaria and Kievan Rus' in 1237, concluding the campaign in 1240.
Western Xia and Jin Dynasty
The vassal emperor of the Tanguts (Western Xia) had earlier refused to take part in the Mongol war against the Khwarezmid Empire. Western Xia and the defeated Jin dynasty formed a coalition to resist the Mongols, counting on the campaign against the Khwarazmians to preclude the Mongols from responding effectively.
In 1226, immediately after returning from the west, Genghis Khan began a retaliatory attack on the Tanguts. His armies quickly took Heisui, Ganzhou, and Suzhou (not the Suzhou in Jiangsu province), and in the autumn he took Xiliang-fu[disambiguation needed]. One of the Tangut generals challenged the Mongols to a battle near Helan Mountains but was defeated. In November, Genghis laid siege to the Tangut city Lingzhou and crossed the Yellow River, defeating the Tangut relief army. According to legend, it was here that Genghis Khan reportedly saw a line of five stars arranged in the sky and interpreted it as an omen of his victory.
In 1227, Genghis Khan's army attacked and destroyed the Tangut capital of Ning Hia and continued to advance, seizing Lintiao-fu, Xining province, Xindu-fu, and Deshun province in quick succession in the spring. At Deshun, the Tangut general Ma Jianlong put up a fierce resistance for several days and personally led charges against the invaders outside the city gate. Ma Jianlong later died from wounds received from arrows in battle. Genghis Khan, after conquering Deshun, went to Liupanshan (Qingshui County, Gansu Province) to escape the severe summer. The new Tangut emperor quickly surrendered to the Mongols, and the rest of the Tanguts officially surrendered soon after. Not happy with their betrayal and resistance, Genghis Khan ordered the entire imperial family to be executed, effectively ending the Tangut lineage.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Genghis Khan (1162-1227)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.








