Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–1718)

The Siege of Corfu
After their success in the Morea, the Ottomans moved against the Venetian-held Ionian Islands. They occupied the island of Lefkada (Santa Maura), which the Venetians had taken in 1684, and the fort of Butrinto opposite the city of Corfu.
On 8 July 1716, an Ottoman Empire The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. army of 33,000 men landed on Corfu, the most important of the Ionian islands. Despite an indecisive naval battle on the same day, the Ottoman land army continued its disembarkment and advanced towards the city of Corfu.
The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. army of 33,000 men landed on Corfu, the most important of the Ionian islands. Despite an indecisive naval battle on the same day, the Ottoman land army continued its disembarkment and advanced towards the city of Corfu.
On 19 July, after capturing the outlying forts of Mantouki, Garitsa, Avrami and of the Saviour, the siege began. The defence was led by Count Johann Matthias von der Schulenburg, who had roughly 8,000 men at his command. The extensive fortifications and the determination of the defenders withstood several assaults.
After a great storm on 9 August—which the defenders attributed to the intervention of Corfu's patron saint, Saint Spyridon—caused significant casualties among the besiegers, the siege was broken off on 11 August and the last Ottoman forces withdrew on 20 August.
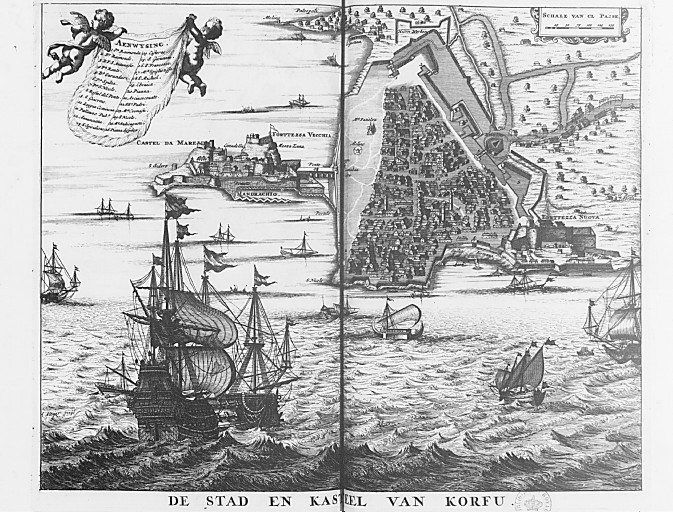
City plan of Corfu in 1688, depicting its fortifications
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–1718)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.












