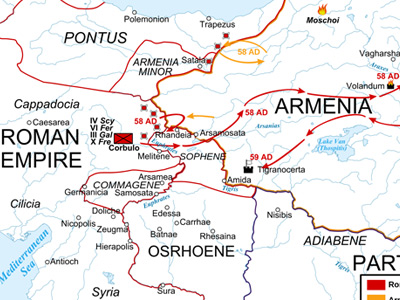
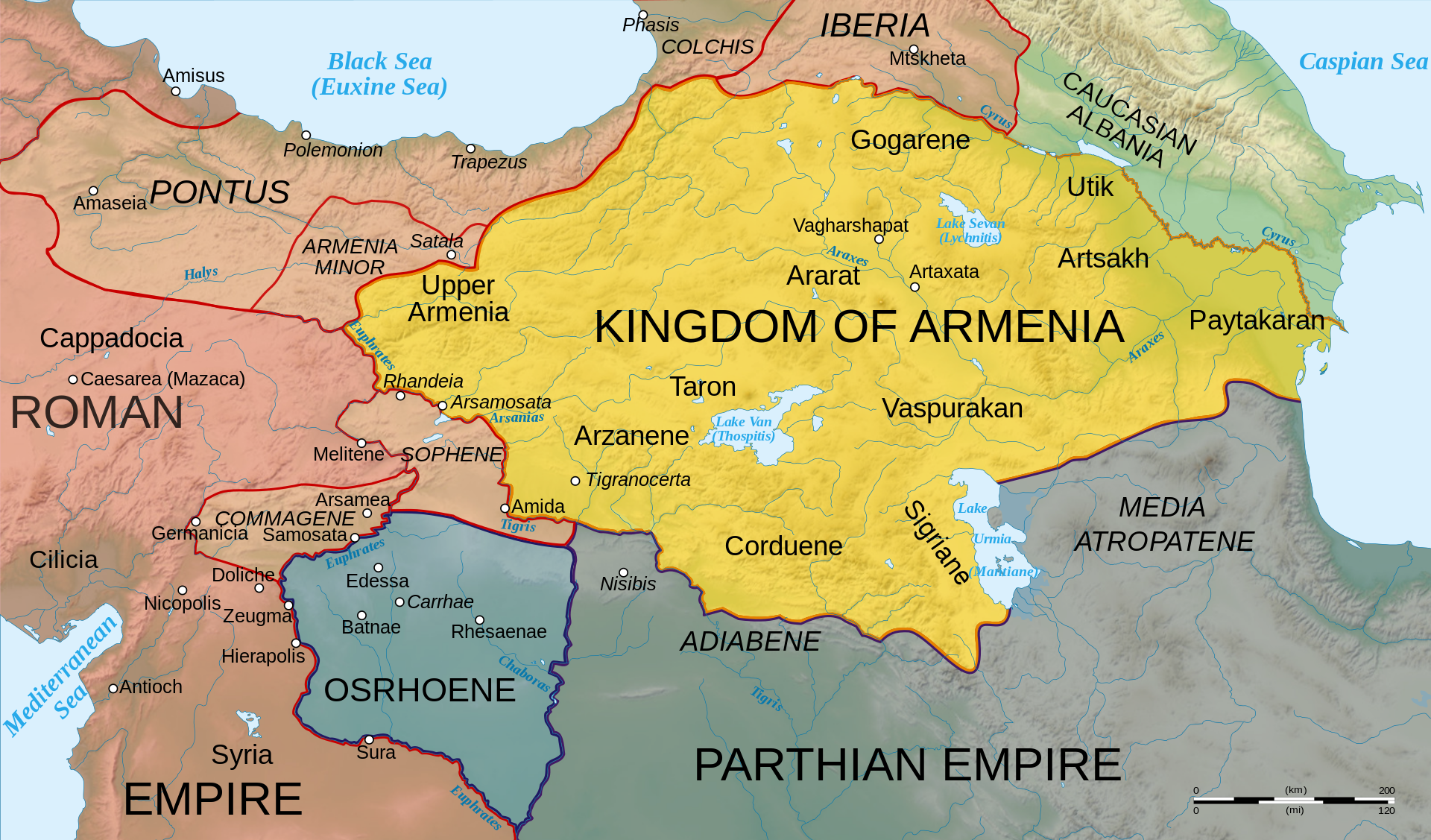
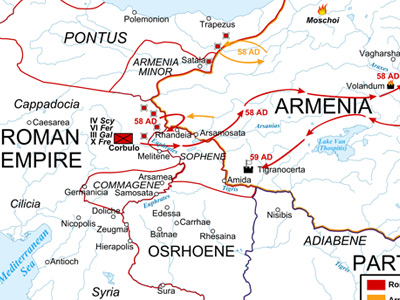
Roman–Parthian War (58–63 AD)
Outbreak of the War - The Roman Offensive
Corbulo had placed a large number of his auxiliaries in a line of forts near the Armenian frontier under a former primus pilus, Paccius Orfitus. Disobeying Corbulo's orders, he used some newly arrived auxiliary cavalry alae to stage a raid against the Armenians, who appeared to be unprepared. In the event, his raid failed, and the retreating troops even spread their panic amongst the garrisons of the other forts. It was an inauspicious start for a campaign, and Corbulo severely punished the survivors and their commanders.
Having drilled his army for two years Corbulo, despite this misadventure, was ready. He had three legions at his disposal (III Gallica and VI Ferrata from Syria and IV Scythica), to which were added a large number of auxiliaries and allied contingents from Eastern client kings like Aristobulus of Lesser Armenia and Polemon II of Pontus. The situation was furthermore favorable to the Romans The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire.: Vologases faced a serious revolt by the Hyrcanians in the region of the Caspian Sea as well as incursions of Dahae and Sacae nomads from Central Asia, and was unable to support his brother.
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire.: Vologases faced a serious revolt by the Hyrcanians in the region of the Caspian Sea as well as incursions of Dahae and Sacae nomads from Central Asia, and was unable to support his brother.
The war thus far had featured mostly skirmishing along the Roman–Armenian border. Corbulo tried to protect the pro-Roman Armenian settlements from attack, and simultaneously retaliated against the Parthians' supporters. Given that Tiridates avoided confrontation in a pitched battle, Corbulo divided his force, so that they could attack several places simultaneously, and instructed his allies, Kings Antiochus IV of Commagene and Pharasmanes I of Iberia to raid Armenia from their own territories. In addition, an alliance was concluded with the Moschoi, a tribe living in northwestern Armenia.
Tiridates reacted by sending envoys to ask why he was under attack, since hostages had been given. To this, Corbulo reiterated the demand to seek the recognition of his crown from Nero. Eventually, the two sides agreed on a meeting. Tiridates announced that he would bring 1,000 men to the meeting, implying that Corbulo should bring the same number of men "in peaceful fashion, without breastplates and helmets". Tacitus suggests that Tiridates intended to overwhelm the Romans, as the Parthian cavalry would be superior to an equal number of Roman infantry in any case. At any rate, in a show of force Corbulo decided to take with him the larger part of his force, not only IV Ferrata, but also 3,000 men from III Gallica plus the auxiliaries. Tiridates also appeared at the agreed site, but, seeing the Romans in full battle array, and in turn distrusting their intentions, he did not come closer and withdrew during the night. Tiridates then resorted to a tactic that had worked well a century earlier against Mark Antony: he sent forces to raid the Roman army's supply route, which stretched over the mountains back to Trapezus in the Black Sea. They failed however, since the Romans had taken care to secure the mountain routes by a series of forts.
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Roman–Parthian War (58–63 AD)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.