Roman conquest of Britain (43-96 AD)
Crossing and Landing
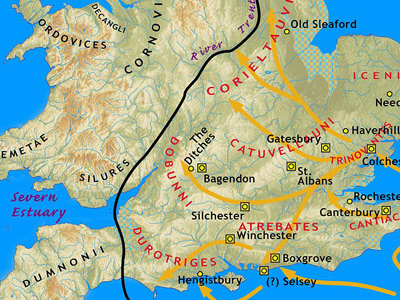
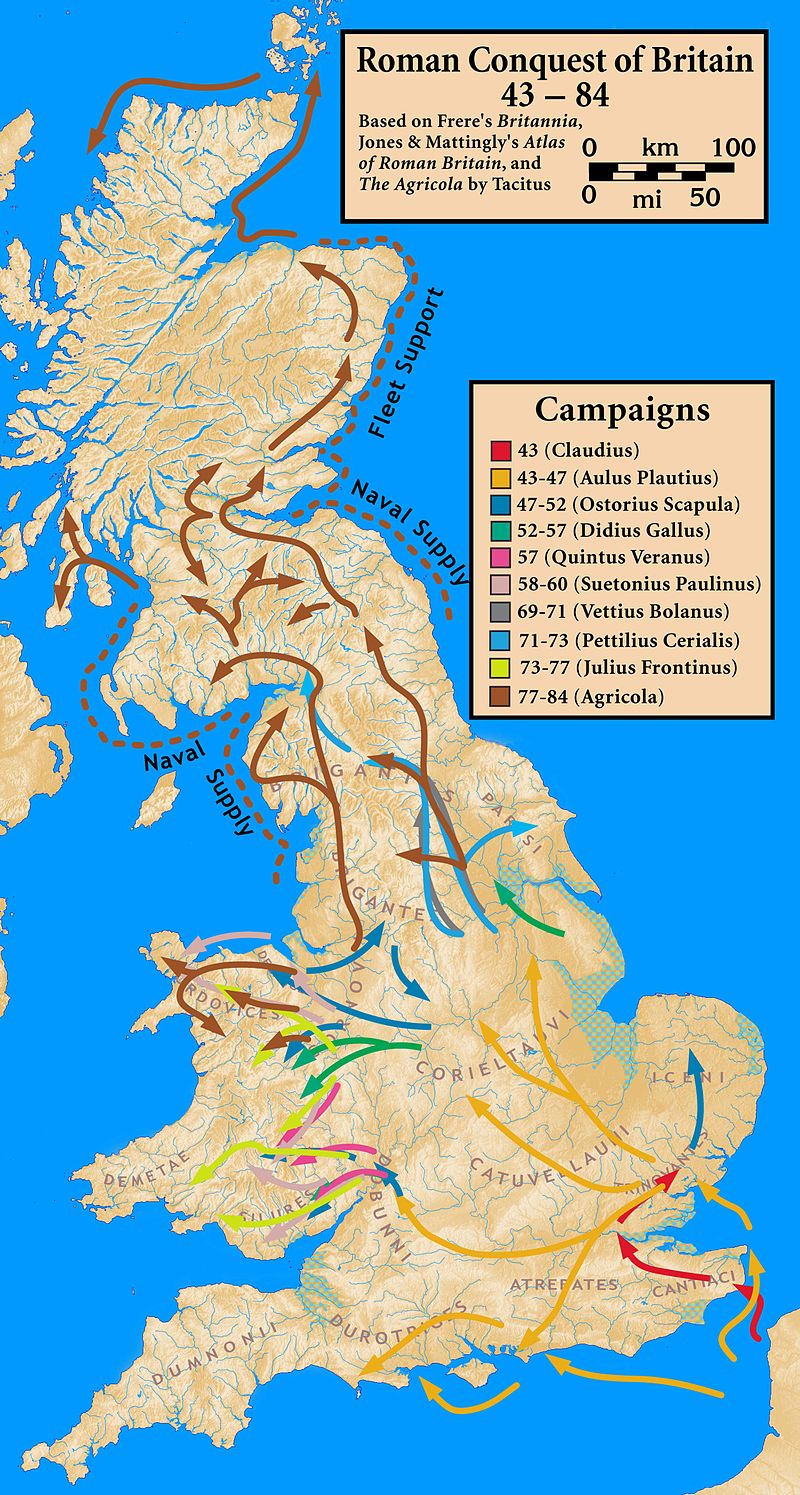
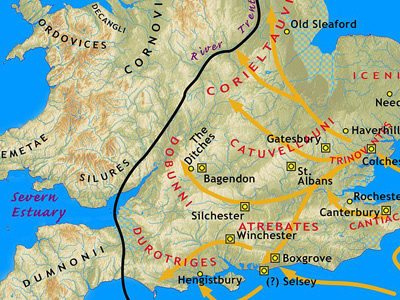
The main invasion force under Aulus Plautius crossed in three divisions. The port of departure is usually taken to have been Boulogne, and the main landing at Rutupiae (Richborough, on the east coast of Kent). Neither of these locations is certain. Dio does not mention the port of departure, and although Suetonius says that the secondary force under Claudius sailed from Boulogne, it does not necessarily follow that the entire invasion force did. Richborough has a large natural harbour which would have been suitable, and archaeology shows Roman The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. military occupation at about the right time. However, Dio says the Romans sailed east to west, and a journey from Boulogne to Richborough is south to north. Some historians suggest a sailing from Boulogne to the Solent, landing in the vicinity of Noviomagus (Chichester) or Southampton, in territory formerly ruled by Verica. An alternative explanation might be a sailing from the mouth of the Rhine to Richborough, which would be east to west.
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. military occupation at about the right time. However, Dio says the Romans sailed east to west, and a journey from Boulogne to Richborough is south to north. Some historians suggest a sailing from Boulogne to the Solent, landing in the vicinity of Noviomagus (Chichester) or Southampton, in territory formerly ruled by Verica. An alternative explanation might be a sailing from the mouth of the Rhine to Richborough, which would be east to west.
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Roman conquest of Britain", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.