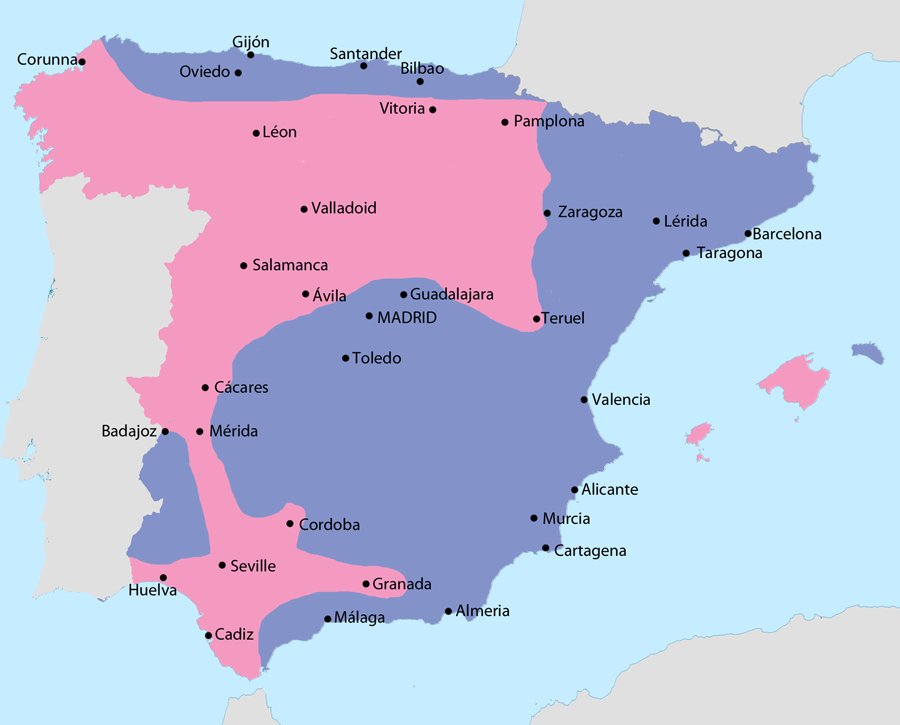
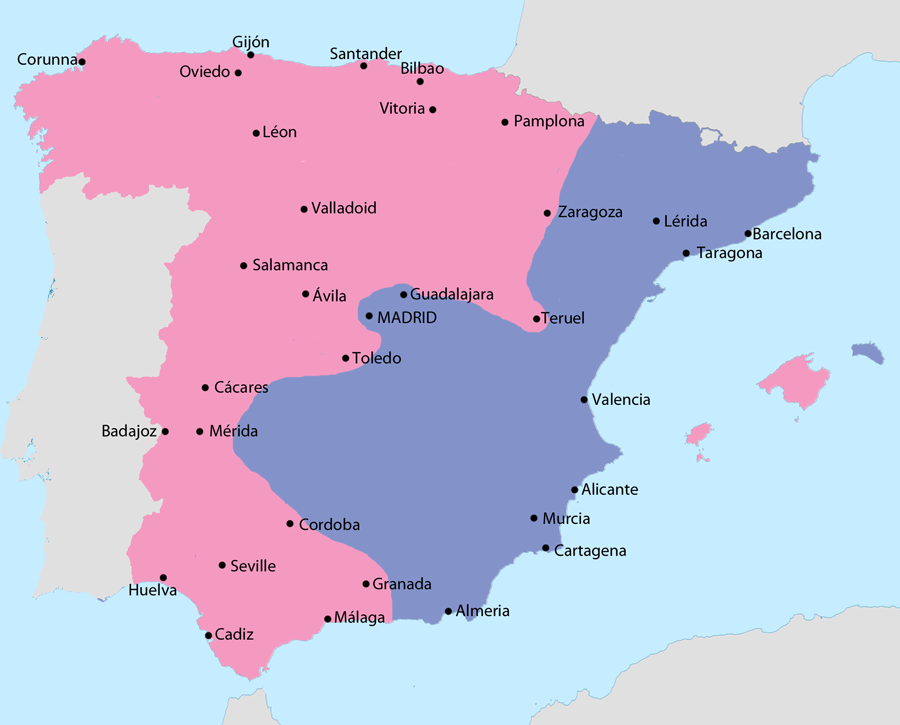
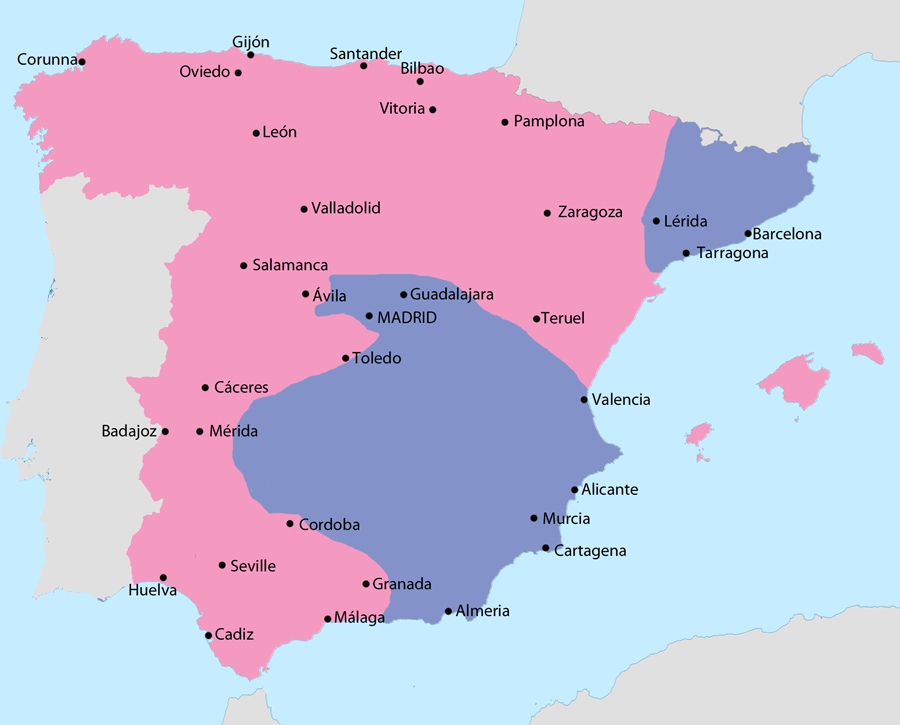
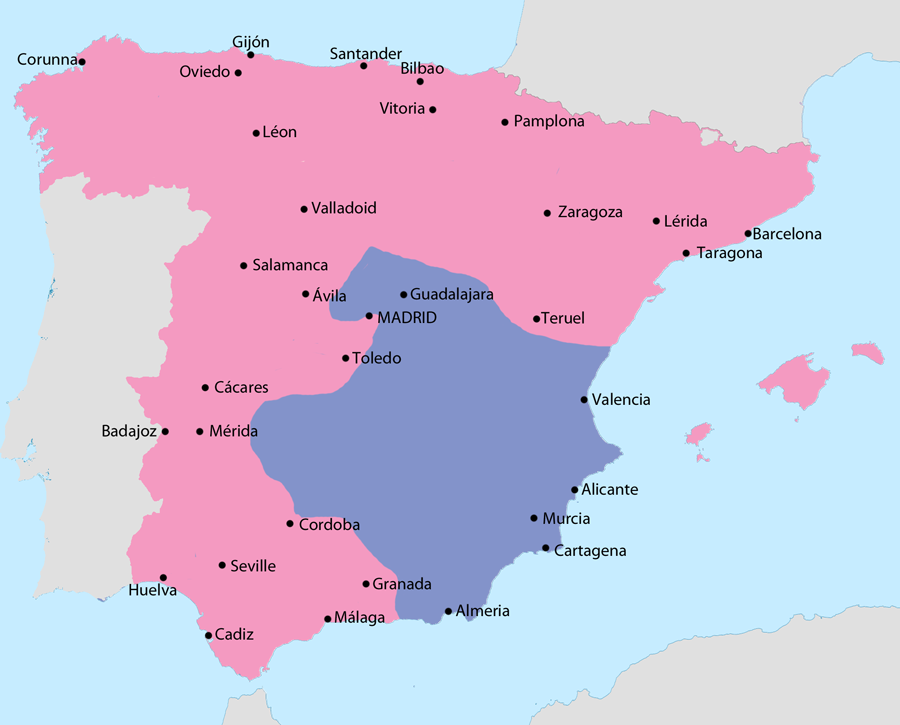
Spanish Civil War (1936 to 1939)

Social Revolution
In the anarchist-controlled areas, Aragon and Catalonia, in addition to the temporary military success, there was a vast social revolution in which the workers and peasants collectivised land and industry and set up councils parallel to the paralyzed Republican government. This revolution was opposed by the Soviet-supported communists who, perhaps surprisingly, campaigned against the loss of civil property rights.
As the war progressed, the government and the communists were able to exploit their access to Soviet arms to restore government control over the war effort, through diplomacy and force. Anarchists and the Workers' Party of Marxist Unification (Partido Obrero de Unificación Marxista, POUM) were integrated into the regular army, albeit with resistance. The POUM Trotskyists were outlawed and falsely denounced as an instrument of the fascists. In the May Days of 1937, many thousands of anarchist and communist Republican soldiers fought for control of strategic points in Barcelona.

These books are available for download with Apple Books on your Mac or iOS device
The pre-war Falange was a small party of some 30,000–40,000 members. It also called for a social revolution that would have seen Spanish society transformed by National Syndicalism. Following the execution of its leader, José Antonio Primo de Rivera, by the Republicans, the party swelled in size to several hundred thousand members. The leadership of the Falange suffered 60 percent casualties in the early days of the civil war, and the party was transformed by new members and rising new leaders, called camisas nuevas ("new shirts"), who were less interested in the revolutionary aspects of National Syndicalism. Subsequently, Franco united all fighting groups into the Traditionalist Spanish Falange and the National Syndicalist Offensive Juntas (Spanish: Falange Española Tradicionalista de las Juntas de Ofensiva Nacional-Sindicalista, FET y de las JONS).
The 1930s also saw Spain become a focus for pacifist organizations, including the Fellowship of Reconciliation, the War Resisters League, and the War Resisters' International. Many people including, as they are now called, the "insumisos" ("defiant ones", conscientious objectors) argued and worked for non-violent strategies. Prominent Spanish pacifists, such as Amparo Poch y Gascón and José Brocca, supported the Republicans. Brocca argued that Spanish pacifists had no alternative but to make a stand against fascism. He put this stand into practice by various means, including organizing agricultural workers to maintain food supplies, and through humanitarian work with war refugees.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Spanish Civil War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.