Second Northern War (1655–1660)

Peace
Charles X Gustav fell ill in early 1660 and died on 23 February of that year. With his death, one of the major obstacles to peace was gone and the Treaty of Oliwa was signed on 23 April. Sweden was accepted as sovereign in Swedish Livonia, Brandenburg was accepted as sovereign in Ducal Prussia, and John II Casimir withdrew his claims to the Swedish throne, though he was to retain the title for life. All occupied territories were restored to their pre-war sovereigns.
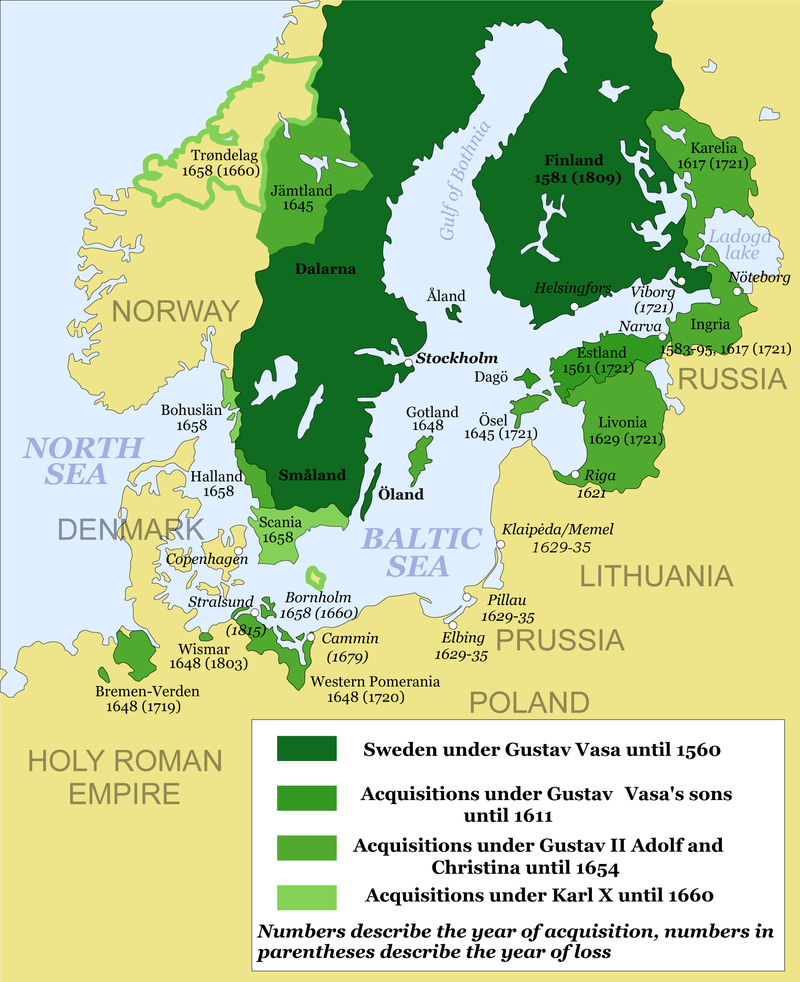
Territorial gains of the Swedish Empire after the Treaty of Roskilde (green outline) and Treaty of Copenhagen (1660) (light green). The Second Northern War marked the height of Sweden's stormaktstiden
However, Denmark was not keen on peace after their recent successes and witnessing the weakness of the Swedish efforts. The Netherlands withdrew their blockade, but were soon convinced by Denmark to support them again. France The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. and England
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. and England The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927. intervened for Sweden and the situation was again teetering on the edge of a major conflict. However, the Danish statesman Hannibal Sehested negotiated a peace treaty without any direct involvement by foreign powers. The conflict was resolved with the Treaty of Copenhagen (1660). Sweden returned Bornholm and Trøndelag to Denmark. The treaty of 1660 established political borders between Denmark, Sweden and Norway which have lasted to the present day, and secured the Swedish dominium maris baltici.
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927. intervened for Sweden and the situation was again teetering on the edge of a major conflict. However, the Danish statesman Hannibal Sehested negotiated a peace treaty without any direct involvement by foreign powers. The conflict was resolved with the Treaty of Copenhagen (1660). Sweden returned Bornholm and Trøndelag to Denmark. The treaty of 1660 established political borders between Denmark, Sweden and Norway which have lasted to the present day, and secured the Swedish dominium maris baltici.
Russia, still engaged in the Russo-Polish War (1654–67), settled her dispute with Sweden in the Treaty of Kardis, which restored Russian-occupied Swedish territory to Sweden.
List of Peace Treaties
- Treaty of Königsberg: Sweden and Brandenburg-Prussia (1656, superseded by Bromberg and Oliva)
- Treaty of Bromberg: Brandenburg-Prussia and Poland-Lithuania
- Treaty of Roskilde: Sweden and Denmark (1658, superseded by Copenhagen)
- Treaty of Oliwa: Sweden and Brandenburg-Prussia, Austria
 The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. and Poland-Lithuania (1660)
The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. and Poland-Lithuania (1660) - Treaty of Copenhagen: Sweden and Denmark (1660)
- Treaty of Kärde: Sweden and Russia (1661)
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Second Northern War (1655–1660)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.










