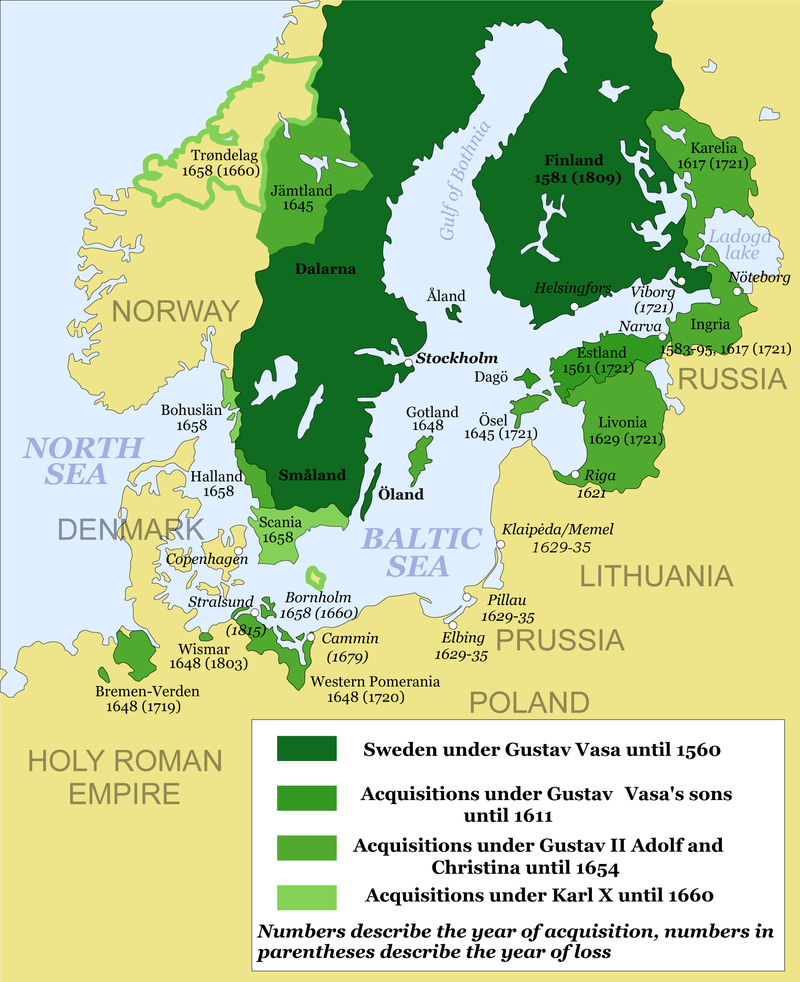
Second Northern War (1655–1660)

Austro–Brandenburgian–Polish alliance, Danish campaigns in Sweden
Like Sweden, John II Casimir was also looking for allies to break the deadlock of the war. On 1 December 1656, he signed an alliance with Ferdinand III of Habsburg in Vienna, essentially a declaration of Ferdinand III's intend to mediate a peace rather than provide military aid, which did not come into effect until Ferdinand's death on 2 April 1657. The treaty was however renewed and amended on 27 May by Ferdinand's successor Leopold I of Habsburg, who agreed in Vienna to provide John II Casimir with 12,000 troops maintained at Polish expense; in return, Leopold received Kraków and Posen in pawn. Receiving the news, Frederick III of Denmark promptly declared war on Sweden, and by June the Austrian The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. army entered the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from the south, immediatetly stabilizing the situation in southern Poland, while Denmark attacked Swedish Bremen-Verden and turned to Jämtland and Västergötland in July.
The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. army entered the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from the south, immediatetly stabilizing the situation in southern Poland, while Denmark attacked Swedish Bremen-Verden and turned to Jämtland and Västergötland in July.
When Charles X Gustav left the Commonwealth and headed westwards for an anti-Danish counterstrike, the Swedish–Brandenburgian–Transylvanian alliance broke apart. Rákóczi of Transylvania was unable to withstand the combined Austrian and Polish–Lithuanian forces without Swedish support, and after a pursuit into Ukraine he was encircled and forced to capitulate, with the rest of the Transylvanian army defeated by the Tartars.
Brandenburg changed sides in return for Polish withdrawal of claims to Ducal Prussia, declaring Frederick William the sole sovereign in the Duchy with the treaties of Wehlau on 19 September and Bromberg on 6 November. In addition, the aforementioned treaties secured Brandenburg the Lands of Lauenburg and Bütow at the border of Brandenburgian Pomerania, while the Bishopric of Ermeland was returned to Poland.
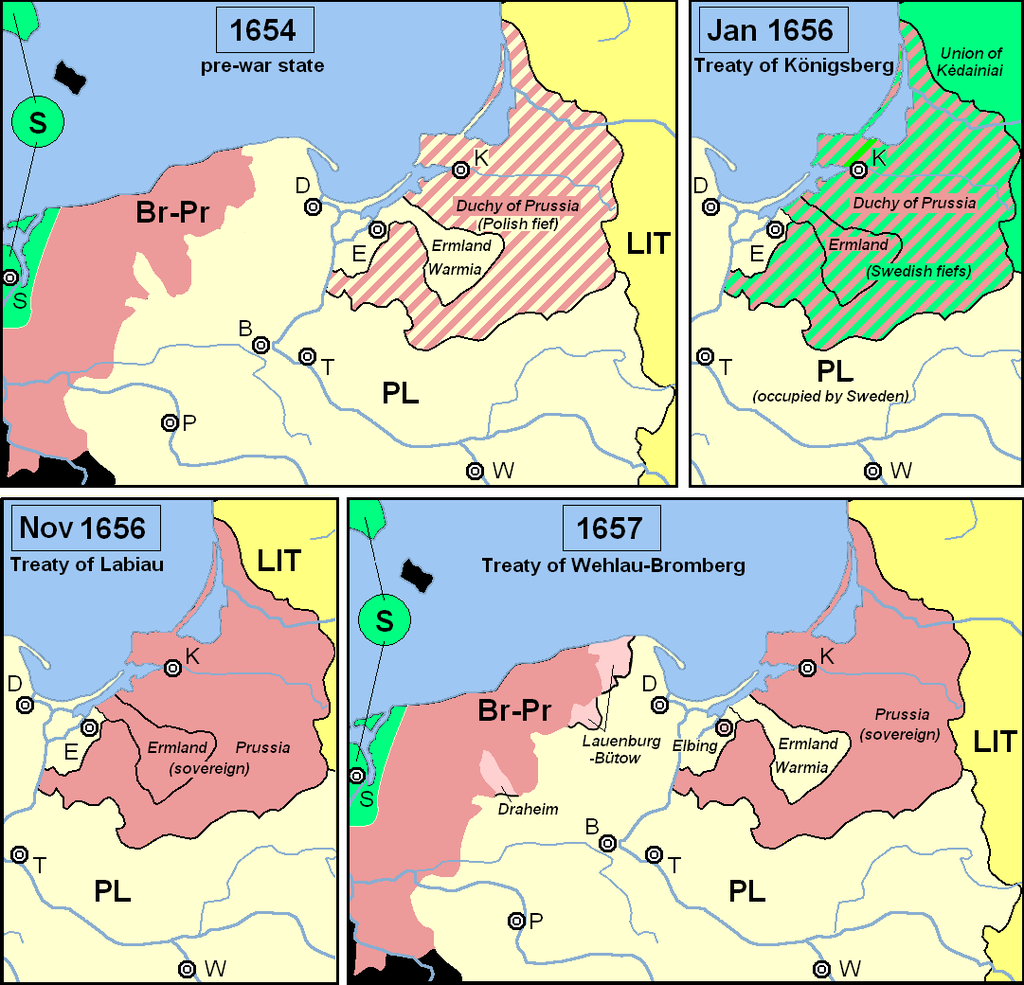
Territorial changes following the Treaty of Wehlau-Bromberg, compared to the pre-war situation (1654) and the treaties of Königsberg (January 1656) and Labiau (November 1656)

Territorial changes following the Treaty of Wehlau-Bromberg, compared to the pre-war situation (1654) and the treaties of Königsberg (January 1656) and Labiau (November 1656)
( Click image to enlarge)
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Second Northern War (1655–1660)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.