First Punic War (264-241 BC)
Background
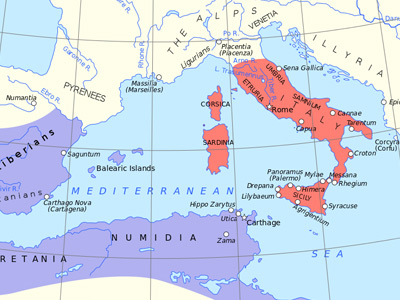
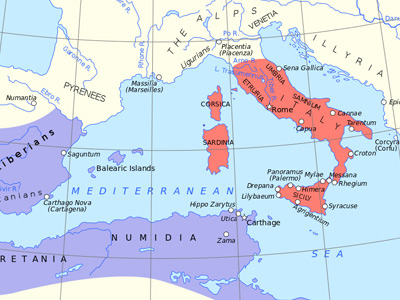
Rome
Rome had recently emerged as the leading city-state in the Italian Peninsula, a wealthy, powerful, expansionist republic with a successful citizen army. Over the past one hundred years, Rome had come into conflict, and defeated rivals on the Italian peninsula, then incorporated them into the Roman political world. First the Latin League was forcibly dissolved during the Latin War, then the power of the Samnites was broken during the three prolonged Samnite wars, and then the Greek cities of Magna Graecia (southern Italy) submitted to Roman The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. power at the conclusion of the Pyrrhic War. By the beginning of the First Punic War, the Romans had secured the whole of the Italian peninsula, except Gallia Cisalpina in the Po Valley.
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. power at the conclusion of the Pyrrhic War. By the beginning of the First Punic War, the Romans had secured the whole of the Italian peninsula, except Gallia Cisalpina in the Po Valley.
Carthage
Carthage was a republic that dominated the political, military and economic affairs of the western Mediterranean Sea, especially on the North African coasts and islands, and above all, due to its navy. It originated as a Phoenician colony in Africa, near modern Tunis. Carthage had become a wealthy center for trade networks extending from Gadir (Cádiz) along the coasts of southern Iberia and North Africa, across the Balearic Islands, Corsica, Sardinia, and the western half of Sicily, to the ports of the eastern Mediterranean, including Tyre, its mother city, on the shores of the Levant. At the height of power, just before the First Punic War, Carthage was hostile to foreign ships (such as Roman and Greek vessels) in the western Mediterranean.
North African Peoples
North African peoples such as the Berbers in the area around Carthage were loosely associated with Carthage. In the midst of the First Punic War some tribes would rebel against Carthage, opening a second front while the Carthaginians battled the Romans in Sicily.
Greek Colonists
Greek colonists were also a major presence in the western Mediterranean, following centuries of colonial settlement, trade and conflicts with Rome over Magna Graecia and with Carthage over places such as Sicily. The rich, strategically influential, and well-fortified Greek colony of Syracuse was politically independent of Rome and Carthage. Hostilities of the First Punic War began with developments involving the Romans, Carthaginians, and Greek colonists in Sicily and southern Italy.
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "First Punic War (264-241 BC)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.