The next year, 258 BC, the Romans were able to regain the initiative by retaking Enna and Camarina. In central Sicily, they took the town of Mytistraton, which they had attacked twice previously. The Romans also moved in the north by marching across the northern coast toward Panormus, but were not able to take the city.
-
Outline of the First Punic War (264-241 BC)
HISTORIC BATTLES
First Punic War (264-241 BC)
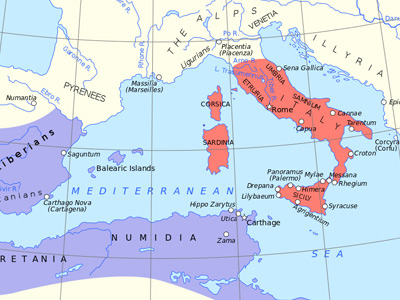
The First Punic War (264 to 241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For more than 20 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. View Historic Battle »
Background: Rome had recently emerged as the leading city-state in the Italian Peninsula, a wealthy, powerful, expansionist republic with a successful citizen army.
Beginning: However, the rivalry between Rome and Carthage had grown since the war with Pyrrhus and that alliance was simply no longer feasible.
Roman landing and advance to Syracuse: Land operations were confined to small scale raids and skirmishes, with few pitched battles. Sieges and land blockades were the most common large-scale operations for the regular army.
Carthage prepares for war: Carthage had begun to build a mercenary army in Africa, which was to be shipped to Sicily to meet the Romans.
Battle of Agrigentum: In 262 BC, Rome besieged Agrigentum, an operation that involved both consular armies—a total of four Roman legions—and took several months to resolve.
Rome builds a fleet: At the beginning of the First Punic War, Rome had virtually no experience in naval warfare, whereas the strong and powerful Carthage had a great deal of experience on the seas thanks to its centuries of sea-based trade.
Battle of Mylae: The Roman fleet under the command of Gaius Duilius, engaged the Carthaginians under general Hannibal Gisco, off northern Mylae in 260 BC.
Hamilcar's counterattack: The Carthaginians took advantage of this victory by counterattacking, in 259 BC, and seizing Enna.
Continued Roman advance: The Romans also moved in the north by marching across the northern coast toward Panormus, but were not able to take the city.
Invasion of Africa: Rome attempted (256/255 BC) the second large scale land operation of the war.
Carthage's respite: Although the Romans defeated the Carthaginian fleet and were successful in rescuing its army in Africa, a storm destroyed nearly the entire Roman fleet on the return trip.
Renewed Roman offensive: The Romans were able to rally, however, and quickly resumed the offensive. With a new fleet of 140 ships, Rome returned to the strategy of taking the Carthaginian cities in Sicily one by one.
Conclusion: Without naval support, Hamilcar Barca was cut off from Carthage and forced to negotiate peace and agree to evacuate Sicily.
Related Articles
First Punic War (264-241 BC)

The first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For more than 20 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. View First Punic War (264-241 BC) »
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)

The Second Punic War, also referred to as The Hannibalic War and (by the Romans) the War Against Hannibal, lasted from 218 to 201 BC and involved combatants in the western and eastern Mediterranean. View Second Punic War (218-201 BC) »
Third Punic War (149–146 BC)

Was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage and the Roman Republic. This war was a much smaller engagement than the two previous Punic Wars and focused on Tunisia. View Third Punic War (149–146 BC) »
First Punic War (264-241 BC)
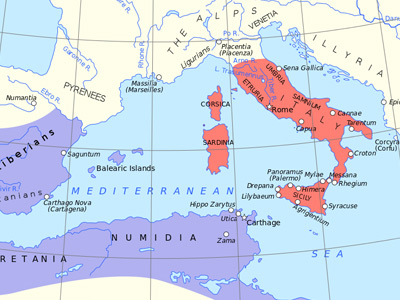
BATTLESThe First Punic War (264 to 241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For more than 20 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa.
- Background
- Beginning of War
- Roman Landing and Advance to Syracuse
- Carthage Prepares for War
- Battle of Agrigentum
- Rome Builds a Fleet
- Battle of Mylae
- Hamilcar's Counterattack
- Continued Roman Advance
- Invasion of Africa
- Carthage's Respite
- Renewed Roman Offensive
- Conclusion

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "First Punic War (264-241 BC)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.
"Building Cool Educational Stuff for Children and Adults!"


Historic Battles
Wars and military campaigns are guided by strategy, whereas battles take place on a level of planning and execution known as operational mobility.
View Historic Battles »


Historic People
A historical figure is a famous person in history, such as Alexander the Great, Admiral Yi Sun-Shin, Abraham Lincoln, George Washington, Christopher Columbus, or Napoleon Bonaparte.
View Historic People »


Historic Timeline
Describes the history of humanity as determined by the study of archaeological and written records. Ancient recorded history begins with the invention of writing.
View Historic Timeline »

Historic Legends
Beings in myths are generally gods and goddesses, heroes and heroines, or animals and plants. Most myths are set in a timeless past before recorded time or beginning of the critical history.
View Historic Legends »

Sports World
Includes competitive games which, through casual or organized participation, aim to use, maintain or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants.
View Sports World »

Untold Stories
If you have any questions, feedback or suggestions for us, we'd like to hear from you. Please feel free to contact us!
Contact Us

Historic Battles
Wars and military campaigns are guided by strategy, whereas battles take place on a level of planning and execution known as operational mobility.
View Historic Battles »

Historic People
A historical figure is a famous person in history, such as Alexander the Great, Admiral Yi Sun-Shin, Abraham Lincoln, George Washington, Christopher Columbus, or Napoleon Bonaparte.
View Historic People »

Historic Timeline
Describes the history of humanity as determined by the study of archaeological and written records. Ancient recorded history begins with the invention of writing.
View Historic Timeline »

Historic Legends
Beings in myths are generally gods and goddesses, heroes and heroines, or animals and plants. Most myths are set in a timeless past before recorded time or beginning of the critical history.
View Historic Legends »

Sports World
Includes competitive games which, through casual or organized participation, aim to use, maintain or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants.
View Sports World »

Untold Stories
If you have any questions, feedback or suggestions for us, we'd like to hear from you. Please feel free to contact us!
Contact Us
Historic Battles
Wars and military campaigns are guided by strategy, whereas battles take place on a level of planning and execution known as operational mobility.
View Historic Battles »

Historic People
A historical figure is a famous person in history, such as Alexander the Great, Admiral Yi Sun-Shin, Abraham Lincoln, George Washington, Christopher Columbus, or Napoleon Bonaparte.
View Historic People »

Historic Timeline
Describes the history of humanity as determined by the study of archaeological and written records. Ancient recorded history begins with the invention of writing.
View Historic Timeline »

Historic Legends
Beings in myths are generally gods and goddesses, heroes and heroines, or animals and plants. Most myths are set in a timeless past before recorded time or beginning of the critical history.
View Historic Legends »

Sports World
Includes competitive games which, through casual or organized participation, aim to use, maintain or improve physical ability and skills while providing enjoyment to participants.
View Sports World »

Untold Stories
If you have any questions, feedback or suggestions for us, we'd like to hear from you. Please feel free to contact us!
Contact Us