Soccer

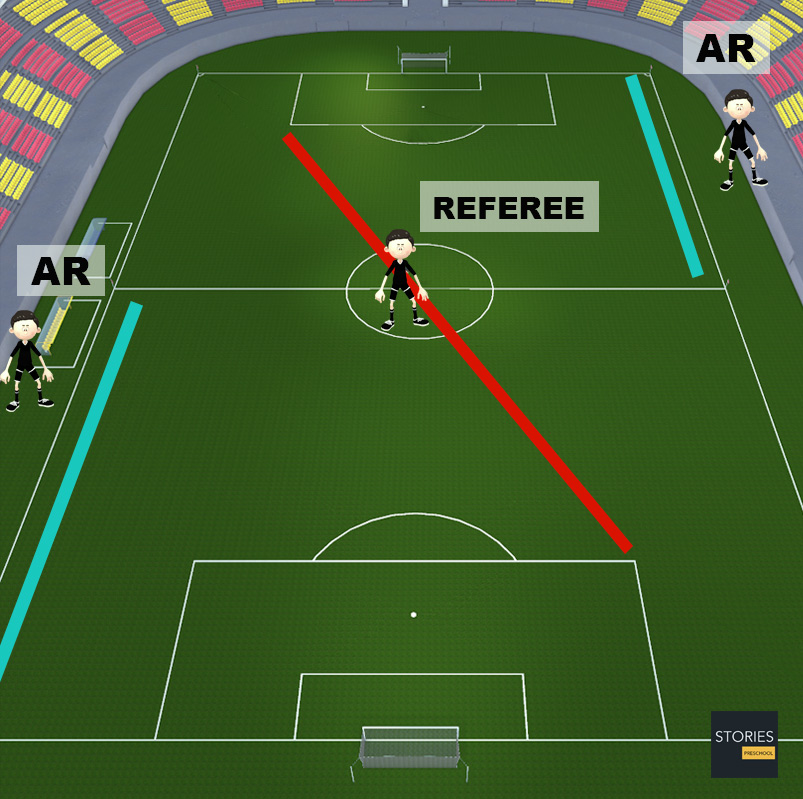
Law 6: The Assistant Referees
In association football, an assistant referee (known as a linesman or lines woman before 1996) is an official empowered with assisting the referee in enforcing the Laws of the Game during a match.

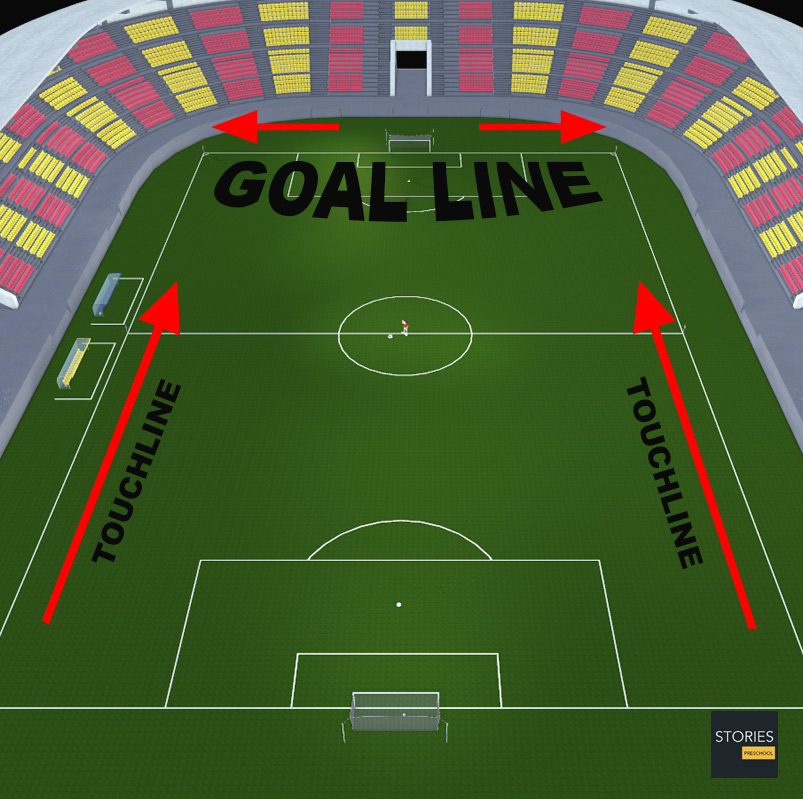
At most organized levels of football the match officiating crew consists of the referee and two assistant referees, with one assistant referee assigned to each touchline. The assistant referee's duties generally consist of judging when the ball has left the field of play – including which team is entitled to return the ball to play, judging when an offside offense has occurred, and advising the referee when an infringement of the Laws of the Game has occurred out of his or her view.

Depending on the local match rules and the discretion of the referee, an assistant referee may also be responsible for various administrative tasks, for example managing substitutions, helping the referee control the players, or replacing the referee if he or she is unable to continue. The assistant referee functions in an advisory role, and all judgements made by an assistant referee may be overruled by the referee.
At higher levels of play the referee is also assisted by a fourth official. The fourth official's duties are usually administrative in nature and vary depending on the match rules and the discretion of the referee. Common duties for a fourth official may include managing technical areas and substitutions, maintaining a backup record of the score, and cautions and sendings off, and displaying information on substitutions and extra time to spectators. Depending on the local match rules, the fourth official may replace the referee or one of the assistant referees if they are unable to continue.

General Duties
Law 6 of the Laws of the Game specifies that "two assistant referees may be appointed". It also outlines the general duties of the assistant referees; however, their duties in a given game remain subject to the decision of the referee. These duties usually include indicating:
- when the whole ball has passed outside the field of play
- which side is entitled to return the ball into the field of play
- when a player may be penalized for an offside offense
- when a substitution is being requested, or assisting the fourth official (if present) in doing the same
- when offenses or other infringements of the Laws of the Game have been committed of which the referee does not have an adequate view
All decisions by the assistant referees are only advisory to the referee, i.e. their decisions are not binding and the referee is allowed to overrule an assistant. An assistant referee may also be called upon by the referee to provide an opinion regarding matters which the referee requires clarification on. Occasionally the assistant referee will assist in player management during free kicks, as well as provide visual assistance during penalty kicks. The assistant referees also usually assist the referee with preparatory and administrative functions.

Assistant referees wear a uniform identical to that of the referee and carry brightly-coloured flags (usually red, yellow, or some pattern involving those colours) which are used to indicate their decisions to the referee, players, and spectators.
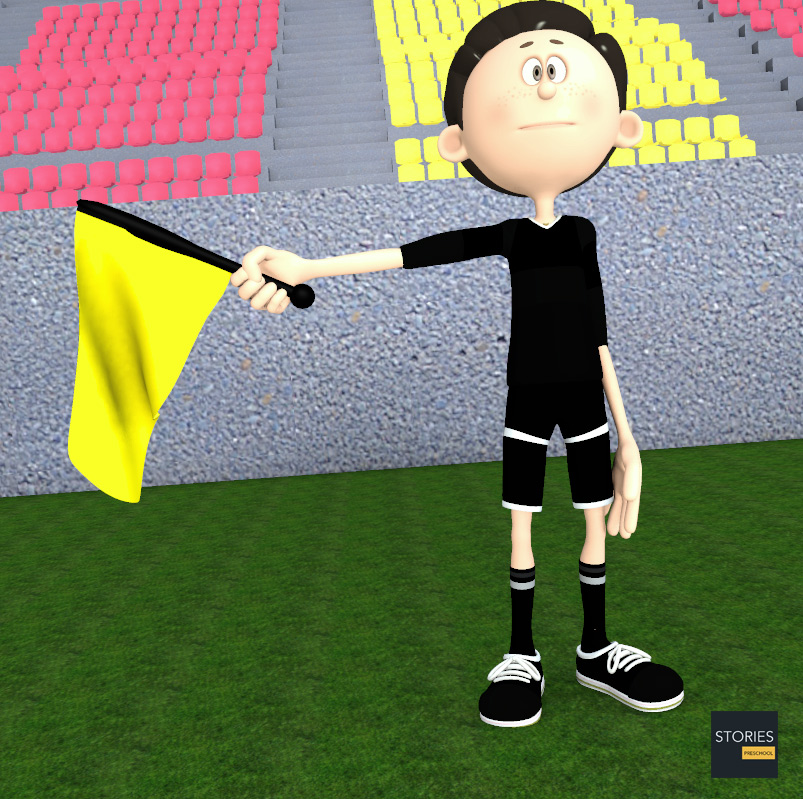

During the game each assistant referee oversees one touch-line and one end of the field utilizing the diagonal system of control. The more senior of the two assistants will normally occupy the side of the field containing the technical areas, to help oversee substitutions. At higher levels of play, the assistant referees' flags may be equipped with buttons that the assistant referee may press to send an audible signal to the referee in order to get the referee's attention. Also at the highest levels of play, particularly in matches held in large stadiums, the entire officiating crew may be equipped with wireless microphones and earpieces to facilitate vocal communication across long distances or through loud stadium noise.

These books are available for download with Apple Books on your Mac or iOS device
Assistant referees were formerly called linesmen. In 1996, the name was changed, primarily to better reflect the modern role of these officials, and secondarily to become non-gender specific. They are also sometimes incorrectly referred to as "referee's assistants". However the term "linesman" is still commonly used, including at lower levels of play where, if the match governing body does not appoint assistant referees to a match, a referee may be empowered to appoint volunteer "club linesmen" who may usually only assist the referee in judging whether the ball has left the field of play.
Fourth Official
The fourth official assists the referee in a variety of tasks, and may be called upon to replace another match official.
The fourth official is a recent addition to the officiating crew. English referee and administrator Ken Aston introduced the practice of having a named replacement referee in 1966, but the International Football Association Board (IFAB) did not officially create the position until 1991, and listed only areas of responsibility. The fourth official is simply instructed to assist the referee at all times, and his duties are largely at the discretion of the referee. His usual duties can be broadly divided into assisting functions and a replacement function (see below).
The fourth official typically has a table a short distance from the touchline between the two teams' technical areas, however his positioning is not defined by the Laws of the Game.
In usual practice, the fourth official assists the referee in the following ways:
- Assisting with administrative functions before, during and after the match;
- Assessment of players' equipment;
- Ensuring substitutions are conducted in an orderly manner;
- Notifying the referee of the details of the substitution, by means of numbered boards or electronic displays (where supplied);
- Notifying the teams and spectators, by means of numbered boards or electronic displays where supplied, of the amount of time added on at the end of each half, after having been advised of this by the referee;
- Acting as the contact point between the match officiating crew and any non-participants (such as stadium managers, security personnel, broadcast crews, and ball retrievers);
- Maintaining decorum in the teams' technical areas and interceding in situations where coaches, bench personnel, or substitutes become agitated;
In practice, the fourth official becomes a key member of the officiating team, who can watch the field and players and advise the referee on situations that are going on out of his sight. The fourth official keeps an extra set of records, and helps make sure the Referee does not make a serious error such as cautioning the wrong player, or giving two cautions to the same player and forgetting to send off the player.
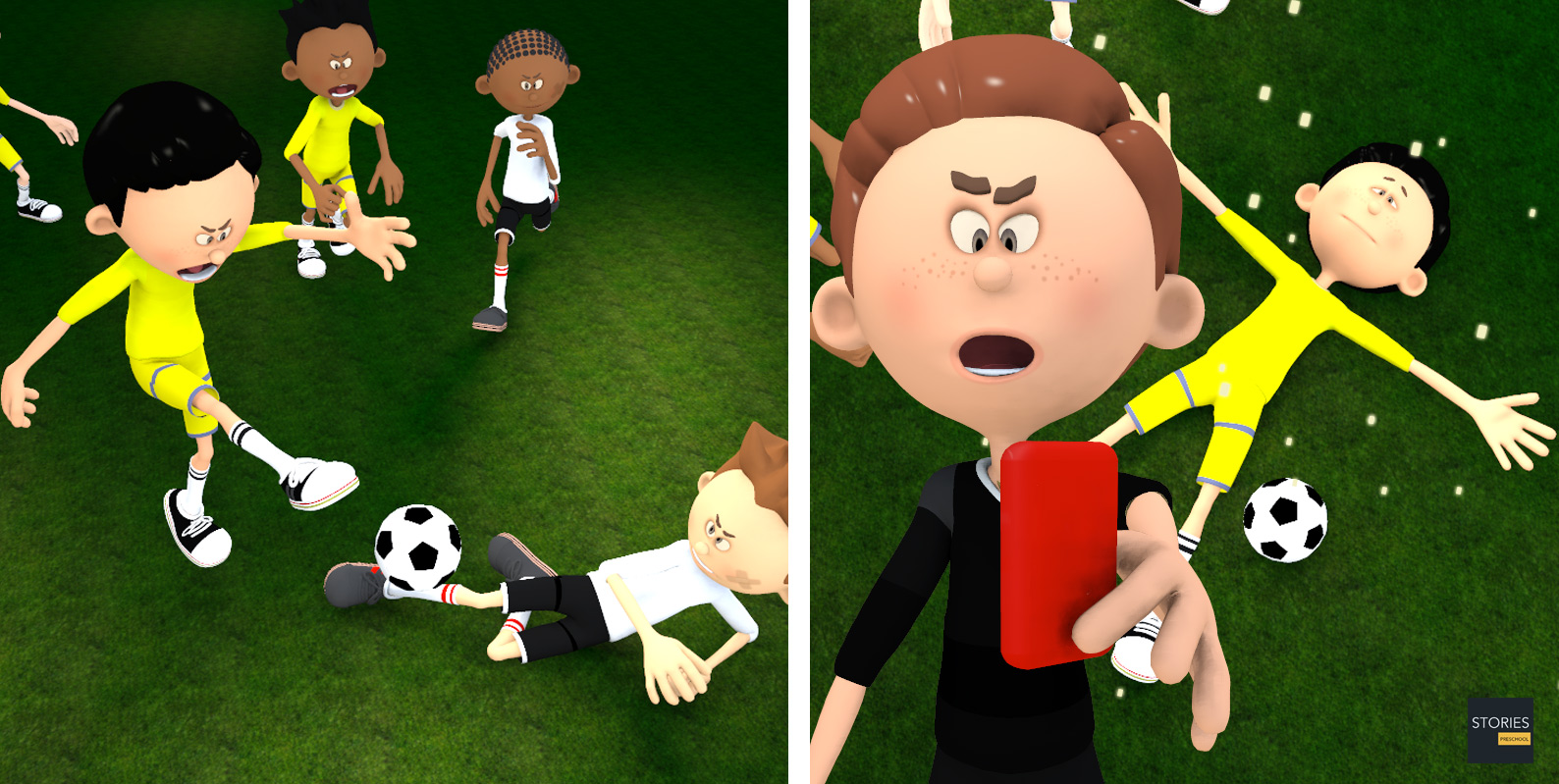

The fourth official played a significant role in the 2006 World Cup Final when fourth official Luis Medina Cantalejo informed referee Horacio Elizondo of the headbutt of France's Zinédine Zidane against Marco Materazzi, resulting in Elizondo showing Zidane a red card and sending him from the field. French manager Raymond Domenech accused Cantalejo of using the replay board to initiate the process that led to Zidane's ejection, which would have broken FIFA rules, but FIFA maintained that Cantalejo did not breach any rules and acted properly.
The fourth official serves as a replacement official in the event that one of the other officials (referee or assistant referees) cannot continue officiating (usually through injury).
In situations where an assistant referee is unable to continue, the fourth official replaces that assistant referee. In situations where the referee is unable to continue, the fourth official replaces the referee directly, or the senior assistant referee replaces the referee, with the fourth official in turn taking an assistant's position. Competition rules are supposed to clarify which of these options is to occur. If for some reason it is not stated, then typically the official with the most refereeing experience (either the fourth official or the senior assistant referee) will replace the referee.
Related Information: Soccer Laws of the Game
The current Laws of the Game (LOTG) consist of seventeen individual laws, each law containing several rules and directions. View Laws of the Game »
- Law 1: The Field of Play
- Law 2: The Ball
- Law 3: The Number of Players
- Law 4: The Players' Equipment
- Law 5: The Referee
- Law 6: The Assistant Referees
- Law 7: The Duration of the Match
- Law 8: The Start and Restart of Play
- Law 9: Ball In and Out of Play
- Law 10: The Method of Scoring
- Law 11: Offside
- Law 12: Fouls and Misconduct
- Law 13: Free Kicks (Direct and Indirect)
- Law 14: The Penalty Kick
- Law 15: The Throw-in
- Law 16: The Goal Kick
- Law 17: The Corner Kick
SPORTS

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia articles "Association Football" and "Assistant Referee (Association Football)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.










