Third Punic War (149–146 BC)

Course of the War
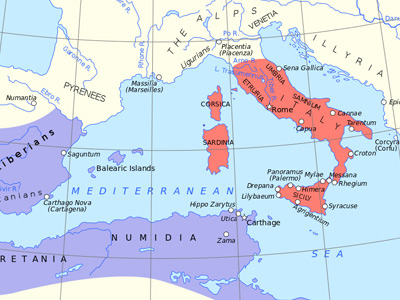
In 151 BC Numidia launched another border raid on Carthaginian soil, besieging the Punic town of Oroscopa, and Carthage launched a large military expedition (25,000 soldiers) to repel the Numidian invaders. As a result, Carthage suffered a military defeat and was charged with another fifty year debt to Numidia. Immediately thereafter, however, Rome showed displeasure with Carthage’s decision to wage war against its neighbour without Roman The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. consent, and told Carthage that in order to avoid a war it had to “satisfy the Roman People.”
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. consent, and told Carthage that in order to avoid a war it had to “satisfy the Roman People.”
In 149 BC, Rome declared war against Carthage. The Carthaginians made a series of attempts to appease Rome, and received a promise that if three hundred children of well-born Carthaginians were sent as hostages to Rome the Carthaginians would keep the rights to their land and self-government. Even after this was done the allied Punic city of Utica defected to Rome, and a Roman army of 80,000 men gathered there. The consuls then demanded that Carthage hand over all weapons and armour. After those had been handed over, Rome additionally demanded that the Carthaginians move at least 16 kilometres inland, while the city was to be burned. When the Carthaginians learned of this, they abandoned negotiations and the city was immediately besieged, beginning the Third Punic War.

These books are available for download with Apple Books on your Mac or iOS device
After the main Roman expedition landed at Utica, consuls Manius Manilius and Lucius Marcius Censorius launched a two-pronged attack on Carthage, but were eventually repulsed by the army of the Carthaginian Generals Hasdrubal the Boeotarch and Himilco Phameas. Censorius lost more than 500 men when they were surprised by the Carthaginian cavalry while collecting timber around the Lake of Tunis. A worse disaster fell upon the Romans when their fleet was set ablaze by fire ships which the Carthaginians released upwind. Manilius was replaced by consul Calpurnius Piso Caesonius in 149 after a severe defeat of the Roman army at Nepheris, a Carthaginian stronghold south of the city. Scipio Aemilianus's intervention saved four cohorts trapped in a ravine. Nepheris eventually fell to Scipio in the winter of 147-146. In the autumn of 148, Piso was beaten back while attempting to storm the city of Aspis, near Cape Bon. Undeterred, he laid siege to the town of Hippagreta in the north, but his army was unable to defeat the Punics there before winter and had to retreat. When news of these setbacks reached Rome, he was replaced as consul by Scipio Aemilianus.
The Carthaginians endured the siege, starting 149 BC to the spring of 146 BC, when Scipio Aemilianus successfully assaulted the city. Though the Punic citizens offered a strong resistance, they were gradually pushed back by the overwhelming Roman military force and destroyed.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Third Punic War (149–146 BC)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.