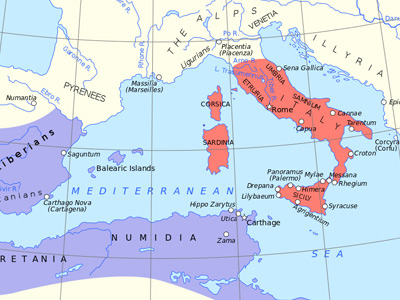
Third Punic War (149–146 BC)

Aftermath
Many Carthaginians died from starvation during the later part of the siege, while many others died in the final six days of fighting. When the war ended, the remaining 50,000 Carthaginians, a small part of the original pre-war population, were sold into slavery by the victors. Carthage was systematically burned for 17 days; the city's walls and buildings were utterly destroyed. The remaining Carthaginian territories were annexed by Rome and reconstituted to become the Roman province of Africa.
The notion that Roman The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. forces then sowed the city with salt to ensure that nothing would grow there again is almost certainly a 19th-century invention. Contemporary accounts show that the land surrounding Carthage was declared ager publicus and that it was shared between local farmers, and Roman and Italian ones. North Africa soon became a vital source of grain for the Romans. Roman Carthage was the main hub transporting these supplies to the capital.
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. forces then sowed the city with salt to ensure that nothing would grow there again is almost certainly a 19th-century invention. Contemporary accounts show that the land surrounding Carthage was declared ager publicus and that it was shared between local farmers, and Roman and Italian ones. North Africa soon became a vital source of grain for the Romans. Roman Carthage was the main hub transporting these supplies to the capital.
Numerous significant Punic cities, such as those in Mauretania, were taken over and rebuilt by the Romans. Examples of these rebuilt cities are Volubilis, Chellah and Mogador. Volubilis, for example, was an important Roman town situated near the westernmost border of Roman conquests. It was built on the site of the previous Punic settlement, but that settlement overlies an earlier neolithic habitation. Utica, the Punic city which changed loyalties at the beginning of the siege, became the capital of the Roman province of Africa.
A century later, the site of Carthage was rebuilt as a Roman city by Julius Caesar Julius Caesar (100-44 BC), was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. Caesar is considered by many historians to be one of the greatest military commanders in history. Julius Caesar », and would later become one of the main cities of Roman Africa by the time of the Empire
Julius Caesar (100-44 BC), was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. Caesar is considered by many historians to be one of the greatest military commanders in history. Julius Caesar », and would later become one of the main cities of Roman Africa by the time of the Empire The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire..
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The first two centuries of the Roman Empire saw a period of unprecedented stability and prosperity known as the Pax Romana ('Roman Peace'). The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire..
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Third Punic War (149–146 BC)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.