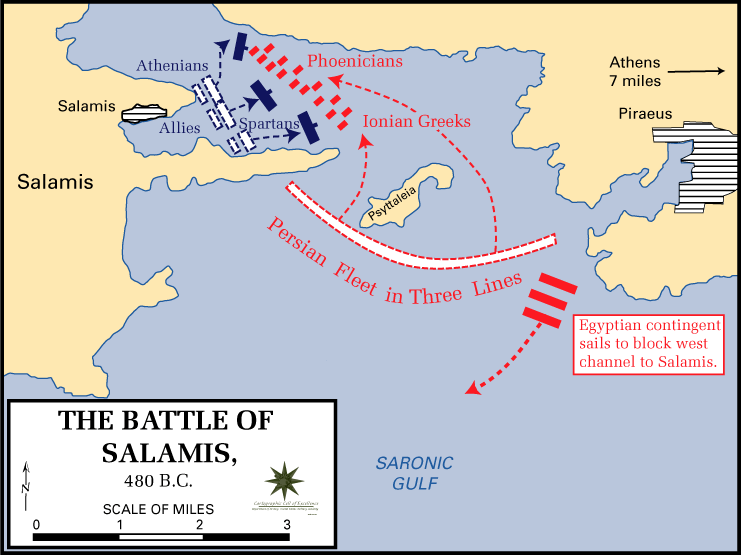
Battle of Salamis (480 BC)

Sources
The main source for the Greco-Persian Wars is the Greek historian Herodotus. Herodotus, who has been called the 'Father of History', was born in 484 BC in Halicarnassus, Asia Minor (then under Persian overlordship). He wrote his Enquiries (Greek: Ιστορίαι; English: (The) Histories) around 440–430 BC, trying to trace the origins of the Greco-Persian Wars, which would still have been relatively recent history (the wars finally ending in 450 BC). Herodotus's approach was entirely novel, and at least in Western society, he does seem to have invented "history" as we know it. As Holland has it: "For the first time, a chronicler set himself to trace the origins of a conflict not to a past so remote so as to be utterly fabulous, nor to the whims and wishes of some god, nor to a people's claim to manifest destiny, but rather explanations he could verify personally."
Some subsequent ancient historians, despite following in his footsteps, criticised Herodotus, starting with Thucydides. Nevertheless, Thucydides chose to begin his history where Herodotus left off (at the Siege of Sestos), and therefore evidently felt that Herodotus's history was accurate enough not to need re-writing or correcting. Plutarch criticised Herodotus in his essay "On the Malignity of Herodotus", describing Herodotus as "Philobarbaros" (barbarian-lover), for not being pro-Greek enough, which suggests that Herodotus might actually have done a reasonable job of being even-handed. A negative view of Herodotus was passed on to Renaissance Europe, though he remained well read. However, since the 19th century his reputation has been dramatically rehabilitated by archaeological finds which have repeatedly confirmed his version of events. The prevailing modern view is that Herodotus generally did a remarkable job in his Historia, but that some of his specific details (particularly troop numbers and dates) should be viewed with skepticism. Nevertheless, there are still some historians who believe Herodotus made up much of his story.
The Sicilian historian Diodorus Siculus, writing in the 1st century BC in his Bibliotheca Historica, also provides an account of the Greco-Persian wars, partially derived from the earlier Greek historian Ephorus. This account is fairly consistent with Herodotus's. The Greco-Persian wars are also described in less detail by a number of other ancient historians including Plutarch, Ctesias of Cnidus, and are alluded by other authors, such as the playwright Aeschylus. Archaeological evidence, such as the Serpent Column, also supports some of Herodotus's specific claims.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Battle of Salamis", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.