Battle of Salamis (480 BC)

Strategic and tactical considerations
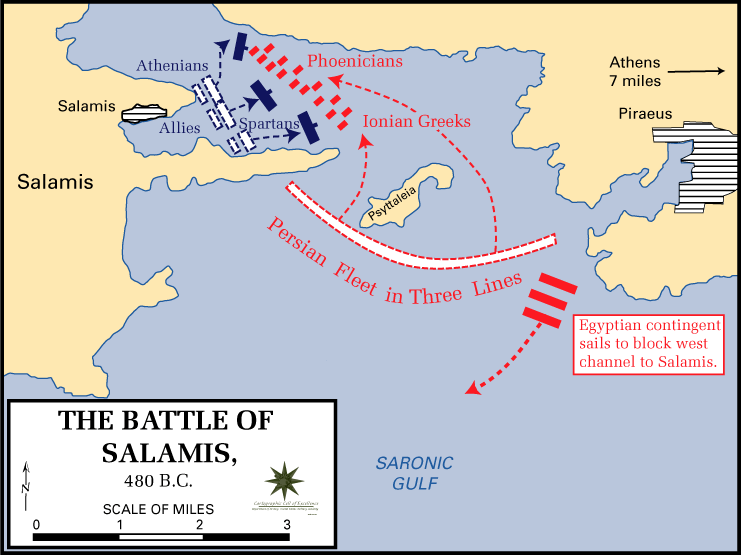
The overall Persian strategy for the invasion of 480 BC was to overwhelm the Greeks with a massive invasion force, and complete the conquest of Greece in a single campaigning season. Conversely, the Greeks sought to make the best use of their numbers by defending restricted locations and to keep the Persians in the field for as long as possible. Xerxes had obviously not anticipated such resistance, or he would have arrived earlier in the campaigning season (and not waited 4 days at Thermopylae for the Greeks to disperse). Time was now of the essence for the Persians – the huge invasion force could not be reasonably supported indefinitely, nor probably did Xerxes wish to be at the fringe of his empire for so long. Thermopylae had shown that a frontal assault against a well defended Greek position was useless; with the Allies now dug in across the narrow Isthmus, there was little chance of conquering the rest of Greece by land. However, as equally demonstrated by Thermopylae, if the Greeks could be outflanked, their smaller numbers of troops could be destroyed. Such an outflanking of the Isthmus required the use of the Persian navy, and thus the destruction of the Allied navy. Therefore, if Xerxes could destroy the Allied navy, he would be in a strong position to force a Greek surrender; this seemed the only hope of concluding the campaign in that season. Conversely by avoiding destruction, or as Themistocles hoped, by crippling the Persian fleet, the Greeks could effectively thwart the invasion.
However, it was strategically not necessary for the Persians to actually fight this battle at Salamis. According to Herodotus, Queen Artemisia of Caria pointed this out to Xerxes in the run-up to Salamis. Artemisia suggested that fighting at sea was an unnecessary risk, recommending instead:
If you do not hurry to fight at sea, but keep your ships here and stay near land, or even advance into the Peloponnese, then, my lord, you will easily accomplish what you had in mind on coming here. The Hellenes are not able to hold out against you for a long time, but you will scatter them, and they will each flee to their own cities.
The Persian fleet was still large enough to both bottle up the Allied navy in the straits of Salamis, and send ships to land troops in the Peloponnese. However, in the final reckoning, both sides were prepared to stake everything on a naval battle, in the hope of decisively altering the course of the war.
The Persians were at a significant tactical advantage, outnumbering the Allies, but also having "better sailing" ships. The "better sailing" that Herodotus mentions was probably due to the superior seamanship of the crews; most of the Athenian ships (and therefore the majority of the fleet) were newly built as according to Themistocles' request to the Athenians to build a fleet of 200 triremes in 483 BC, and had inexperienced crews. It is important to note that despite the inexperienced crew on part of the Athenians, these newly constructed triremes would ultimately prove crucial in the forthcoming conflict with Persia. The most common naval tactics in the Mediterranean area at the time were ramming (triremes being equipped with a ram at the bows), or boarding by ship-borne marines (which essentially turned a sea battle into a land one). The Persians and Asiatic Greeks had by this time begun to use a manoeuver known as diekplous. It is not entirely clear what this was, but it probably involved rowing into gaps between enemy ships and then ramming them in the side. This maneuver would have required skilled crews, and therefore the Persians would have been more likely to employ it; the Allies however, developed tactics specifically to counter this.
There has been much debate as to the nature of the Allied fleet compared to the Persian fleet. Much of this centres on the suggestion, from Herodotus, that the Allied ships were heavier, and by implication less maneuverable. The source of this heaviness is uncertain; possibly the Allied ships were bulkier in construction, or that the ships were water-logged since they had not been dried out in the winter (though there is no real evidence for either suggestion). Another suggestion is that the heaviness was caused by the weight of fully armored hoplite marines (20 fully armored hoplites would have weighed 2 tons). This 'heaviness', whatever its cause, would further reduce the likelihood of them employing the diekplous. It is therefore probable that the Allies had extra marines on board if their ships were less maneuverable, since boarding would then be the main tactic available to them (at the cost of making the ships even heavier). Indeed, Herodotus refers to the Greeks capturing ships at Artemisium, rather than sinking them. It has been suggested that the weight of the Allied ships may also have made them more stable in the winds off the coast of Salamis, and made them less susceptible to ramming (or rather, less liable to sustain damage when rammed).
The Persians preferred a battle in the open sea, where they could better utilize their superior seamanship and numbers. For the Greeks, the only realistic hope of a decisive victory was to draw the Persians into a constricted area, where their numbers would count for little.The battle at Artemisium had seen attempts to negate the Persian advantage in numbers, but ultimately the Allies may have realised that they needed an even more constricted channel in order to defeat the Persians. Therefore, by rowing into the Straits of Salamis to attack the Greeks, the Persians were playing into the Allies' hands. It seems probable that the Persians would not have attempted this unless the Persians were confident of the collapse of the Allied navy, and thus Themistocles's subterfuge appears to have played a key role in tipping the balance in the favor of the Greeks. Salamis was, for the Persians, an unnecessary battle and a strategic mistake.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Battle of Salamis", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.