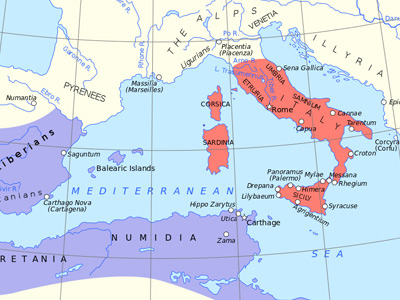
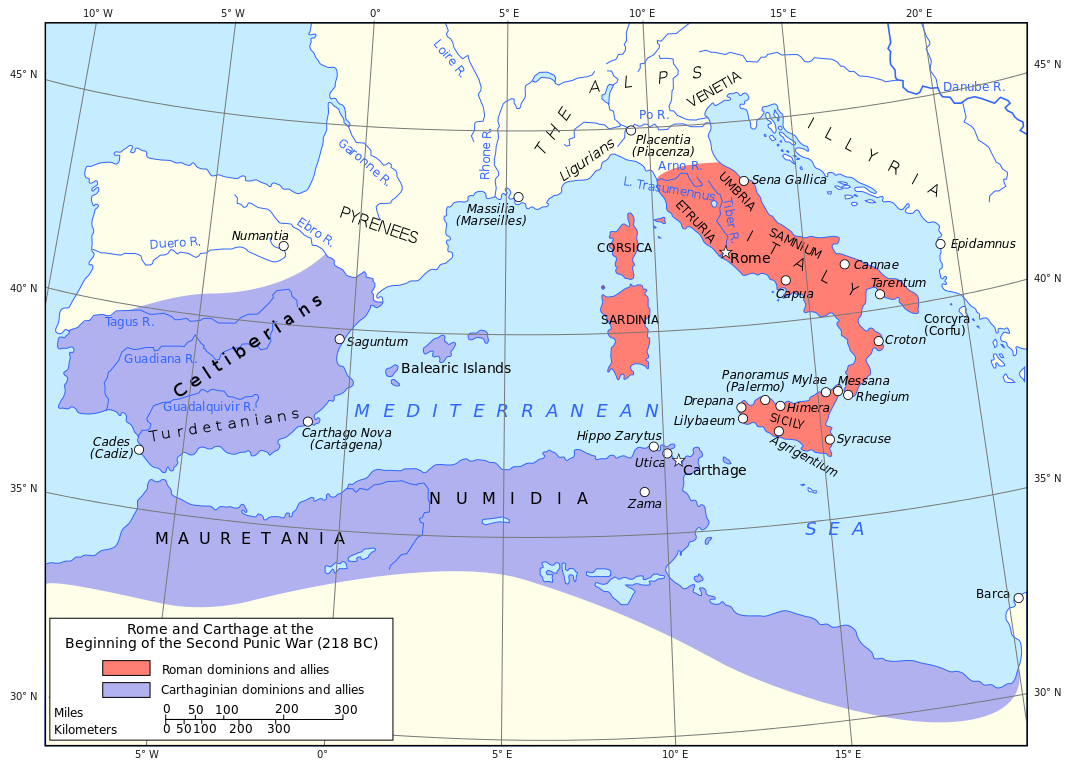
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)

Hannibal's Overland Journey
The Carthaginian army in Iberia, excluding the forces in Africa, totaled, according to Polybius, 90,000 infantry, 12,000 cavalry and 37 war elephants: it was thus one of the largest in the Hellenistic world and equal in numbers to any that the Romans The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. had yet fielded. Hannibal departed with this army from New Carthage (Cartagena, Spain) northwards along the coast in late spring of 218 BC. At the Ebro, he split the army into three columns and subdued the tribes from there to the Pyrenees within weeks, but with severe losses. At the Pyrenees, he left a detachment of 11,000 Iberian troops, who showed reluctance to leave their homeland, as a garrison for the newly conquered region. Hannibal
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. had yet fielded. Hannibal departed with this army from New Carthage (Cartagena, Spain) northwards along the coast in late spring of 218 BC. At the Ebro, he split the army into three columns and subdued the tribes from there to the Pyrenees within weeks, but with severe losses. At the Pyrenees, he left a detachment of 11,000 Iberian troops, who showed reluctance to leave their homeland, as a garrison for the newly conquered region. Hannibal Hannibal Barca (247-183 BC), was a Carthaginian general, considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the western Mediterranean Basin, when the Roman Republic established its supremacy over other great powers such as ancient Carthage. One of his most famous achievements was at the outbreak of the Second Punic War, when he marched an army which included war elephants from Iberia over the Pyrenees and the Alps into Italy. Hannibal Barca » reportedly entered Gaul with 50,000 infantry and 9,000 cavalry. He took his army by an inland route, avoiding the Roman allies along the coast. In Gaul, negotiations helped him to move unmolested except for the Battle of Rhone Crossing, where a force of the Allobroges unsuccessfully tried to oppose his 38,000 infantry (this number may exclude light infantry), 8,000 cavalry, and 37 war elephants.
Hannibal Barca (247-183 BC), was a Carthaginian general, considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the western Mediterranean Basin, when the Roman Republic established its supremacy over other great powers such as ancient Carthage. One of his most famous achievements was at the outbreak of the Second Punic War, when he marched an army which included war elephants from Iberia over the Pyrenees and the Alps into Italy. Hannibal Barca » reportedly entered Gaul with 50,000 infantry and 9,000 cavalry. He took his army by an inland route, avoiding the Roman allies along the coast. In Gaul, negotiations helped him to move unmolested except for the Battle of Rhone Crossing, where a force of the Allobroges unsuccessfully tried to oppose his 38,000 infantry (this number may exclude light infantry), 8,000 cavalry, and 37 war elephants.

Route of Hannibal's invasion of Italy

Route of Hannibal's invasion of Italy
( Click image to enlarge)
In the meantime, a Roman fleet with an invasion force was underway to northern Iberia. Its commanders, the brothers Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus and Publius Cornelius Scipio, knew that Hannibal had crossed the Ebro, but were surprised by the Carthaginian army's presence at the Rhone upstream of their ally Massalia, where they had landed. A scouting party of 300 cavalry was sent to discover the whereabouts of the enemy. These eventually defeated a Carthaginian scouting troop of 500 mounted Numidians and chased them back to their main camp. Thus, with knowledge of the location of the enemy, the Romans marched upstream, ready for battle. Hannibal evaded this force and by an unknown route reached (the Isère or the Durance) at the foot of the Alps in autumn. He also received messengers from his Gallic allies in Italy that urged him to come to their aid and offered to guide him over the Alps. Before setting out to cross the Alps, he was re-supplied by a native tribe, some of whose hereditary disputes he had helped solve.
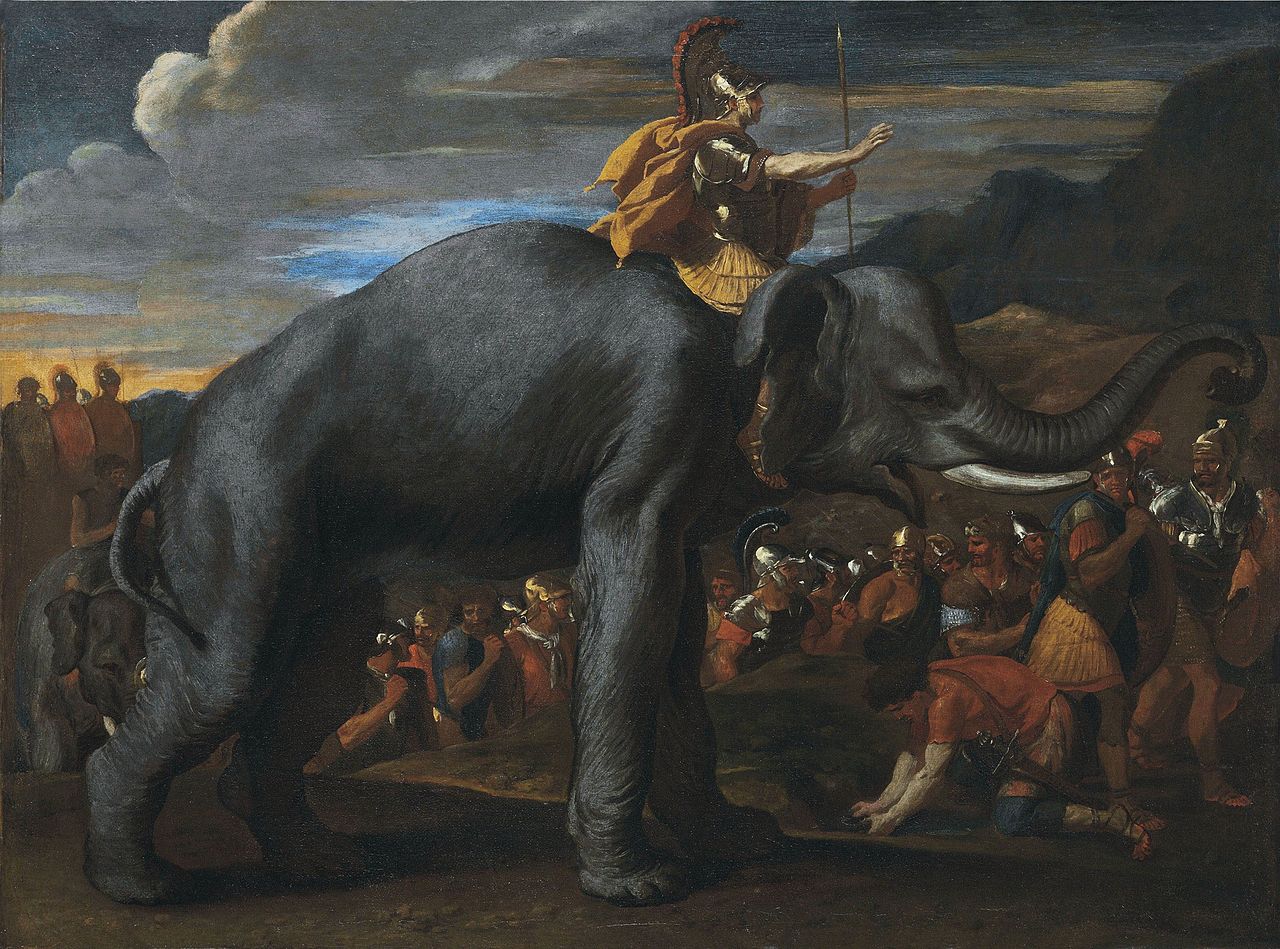

Hannibal won fame for trekking across the Alps with 37 war elephants. His surprise tactics and brilliant strategies put Rome against the ropes

Hannibal won fame for trekking across the Alps with 37 war elephants. His surprise tactics and brilliant strategies put Rome against the ropes
( Click image to enlarge)
Related Articles
First Punic War (264-241 BC)
The first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For more than 20 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. View First Punic War (264-241 BC) »
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)
The Second Punic War, also referred to as The Hannibalic War and (by the Romans) the War Against Hannibal, lasted from 218 to 201 BC and involved combatants in the western and eastern Mediterranean. View Second Punic War (218-201 BC) »
Third Punic War (149–146 BC)
Was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage and the Roman Republic. This war was a much smaller engagement than the two previous Punic Wars and focused on Tunisia. View Third Punic War (149–146 BC) »
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Second Punic War (218-201 BC)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.