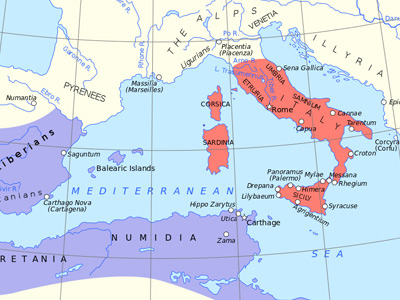
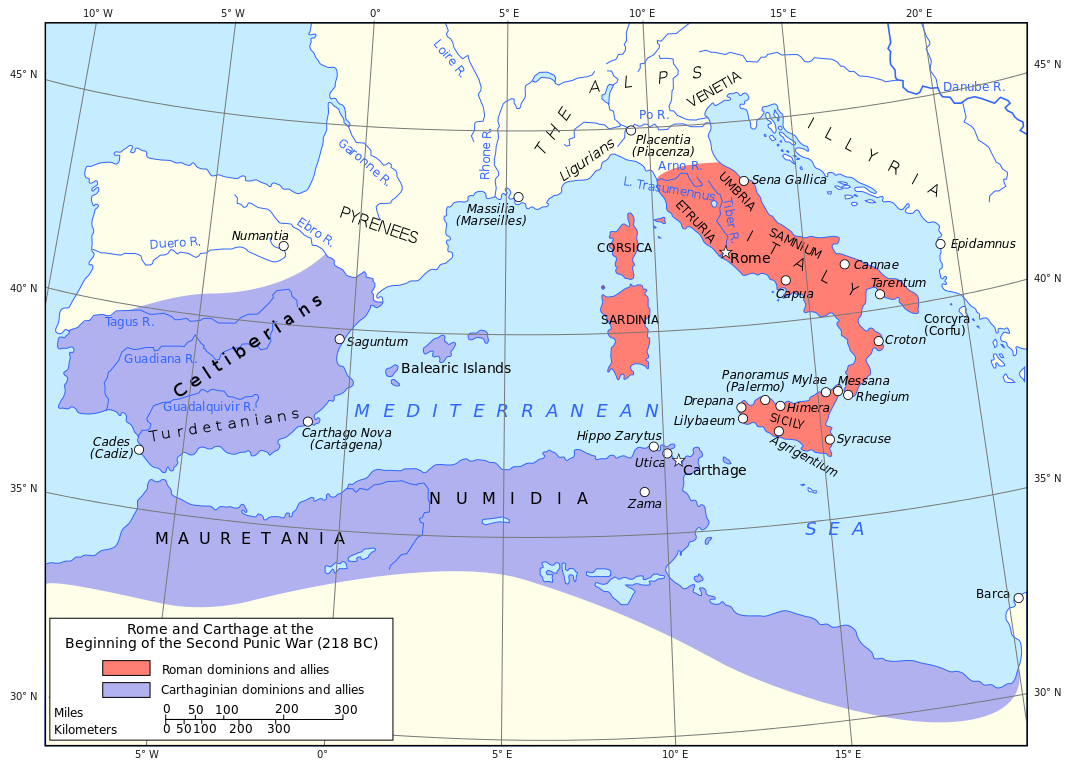
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)

Establishing a Carthaginian Alliance in Italy
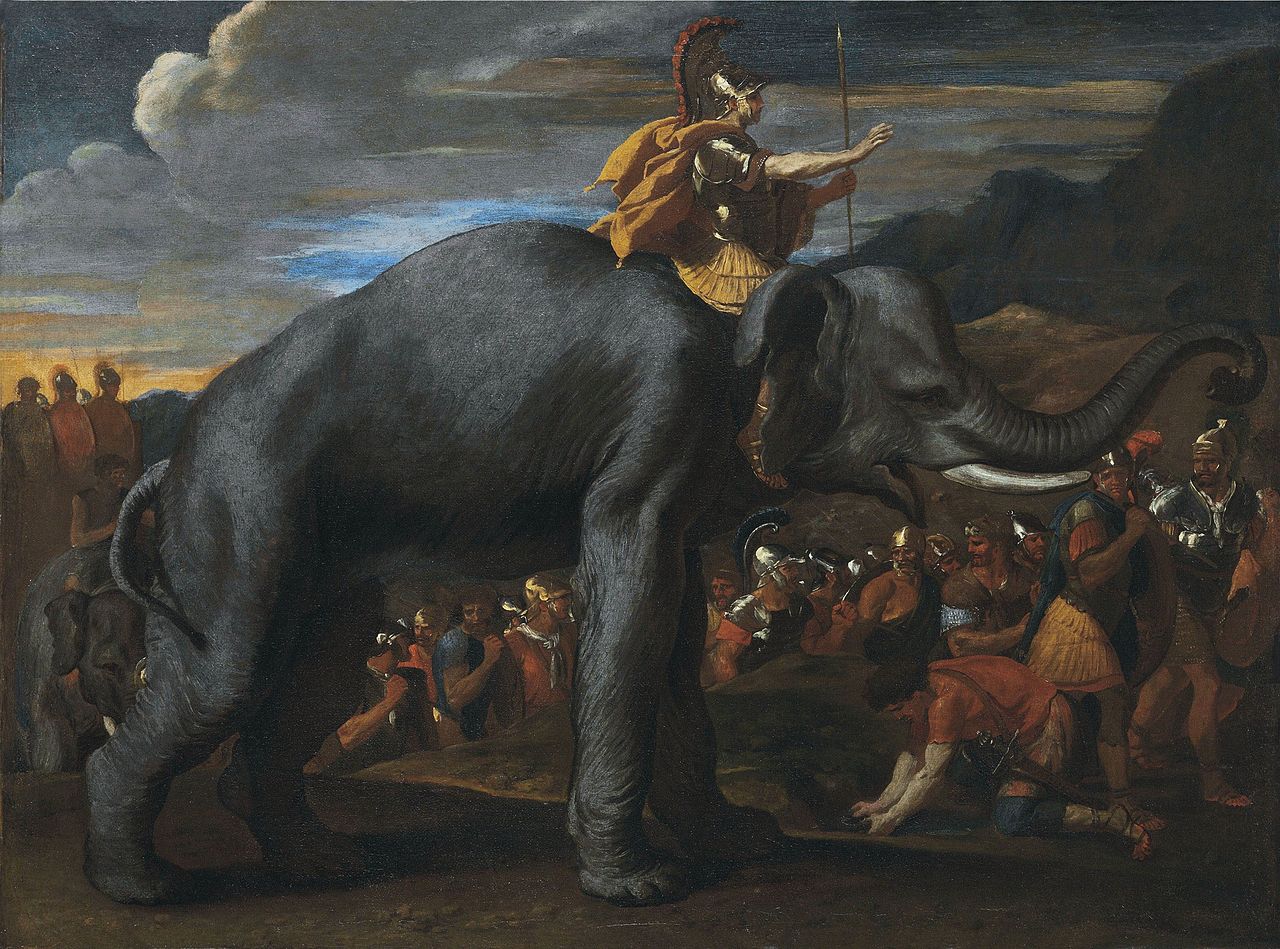
After Cannae, several south Italian cities allied themselves to Hannibal: the Apulian towns of Salapia, Arpi and Herdonia and many of the Lucanians. Mago marched south with a Carthaginian army detachment and, some weeks later, the Bruttians joined him. Simultaneously, Hannibal Hannibal Barca (247-183 BC), was a Carthaginian general, considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the western Mediterranean Basin, when the Roman Republic established its supremacy over other great powers such as ancient Carthage. One of his most famous achievements was at the outbreak of the Second Punic War, when he marched an army which included war elephants from Iberia over the Pyrenees and the Alps into Italy. Hannibal Barca » marched north with part of his forces and was joined by the Hirpini and the Caudini, two of the three Samnite cantons. The greatest gain was the second largest city of Italy, Capua, when Hannibal's army marched into Campania in 216 BC. The inhabitants of Capua held limited Roman citizenship and the aristocracy was linked to the Romans via marriage and friendship, but the possibility of becoming the supreme city of Italy after the evident Roman
Hannibal Barca (247-183 BC), was a Carthaginian general, considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the western Mediterranean Basin, when the Roman Republic established its supremacy over other great powers such as ancient Carthage. One of his most famous achievements was at the outbreak of the Second Punic War, when he marched an army which included war elephants from Iberia over the Pyrenees and the Alps into Italy. Hannibal Barca » marched north with part of his forces and was joined by the Hirpini and the Caudini, two of the three Samnite cantons. The greatest gain was the second largest city of Italy, Capua, when Hannibal's army marched into Campania in 216 BC. The inhabitants of Capua held limited Roman citizenship and the aristocracy was linked to the Romans via marriage and friendship, but the possibility of becoming the supreme city of Italy after the evident Roman The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. disasters proved too strong a temptation. The treaty between them and Hannibal can be described as an agreement of friendship, since the Capuans had no obligations, but provided the harbour through which Hannibal was reinforced.
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. disasters proved too strong a temptation. The treaty between them and Hannibal can be described as an agreement of friendship, since the Capuans had no obligations, but provided the harbour through which Hannibal was reinforced.
By 215 BC, Hannibal's alliance system covered the bulk of southern Italy, save for the Greek cities along the coast (except Croton that was conquered by his allies), Rhegium, and the Latin colonies Beneventum, Luceria in Samnium, Venusia in Apulia, Brundisium and Paestum. The independent Gaul he had established in northern Italy was still out of Roman control.
Hannibal had been able to win over a major allied base by his tremendous military success. He also regarded it as essential to take the city of Nola, a Roman fortress in Campania, a region that linked his various allies geographically and contained his most important harbour for supply. Prior to his first attempt, the pro-Carthage faction in the city had been eliminated by the Romans, so there was no chance of the city being betrayed. Hannibal tried three times, by assault or siege, to take this city, which was defended by Marcus Claudius Marcellus in the Battle of Nola (216 BC), Battle of Nola (215 BC) and Battle of Nola (214 BC), but failed each time. By 215 Hannibal was able to take Casilinum, the other important site for controlling Campania.
Syracuse on Sicily as it was on the sea routs Hannibal needed to secure supply, and Lilybaeum on Sicily remained in Roman hands. Hannibal was aided by the fact that Hiero II, the old tyrant of Syracuse and a staunch Roman ally, had died and his successor Hieronymus was discontented with his position in the Roman alliance. Hannibal dispatched two of his lieutenants, who were of Syracusian origin to negotiate with Hieronymus. They succeeded in winning Syracuse over, at the price, however, of making the whole of Sicily a Syracusan possession. The Syracusans' ambitions were great, but the army they fielded was no match for the arriving Roman force, leading to the Siege of Syracuse from 214 BC onwards. During this siege, the ingenuity of Archimedes' machines defeated all Roman attacks.
The essence of Hannibal's campaign in Italy was to fight the Romans by using local resources and raising recruits from among the local population. His subordinate Hanno was able to raise troops in Samnium, but the Romans intercepted these new levies in the Battle of Beneventum (214 BC) and eliminated them before they came under the feared leadership of Hannibal. Hannibal could win allies, but defending them against the Romans was a new and difficult problem, as the Romans could still field multiple armies greatly outnumbering his own forces. Thus Fabius was able to take the Carthagenian ally Arpi in 213 BC.
Related Articles
First Punic War (264-241 BC)
The first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For more than 20 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. View First Punic War (264-241 BC) »
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)
The Second Punic War, also referred to as The Hannibalic War and (by the Romans) the War Against Hannibal, lasted from 218 to 201 BC and involved combatants in the western and eastern Mediterranean. View Second Punic War (218-201 BC) »
Third Punic War (149–146 BC)
Was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage and the Roman Republic. This war was a much smaller engagement than the two previous Punic Wars and focused on Tunisia. View Third Punic War (149–146 BC) »
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Second Punic War (218-201 BC)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.