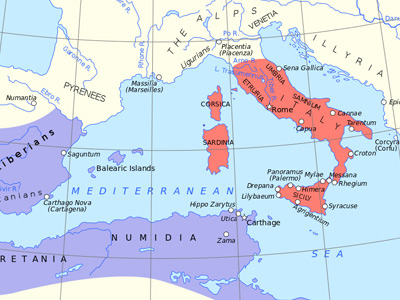
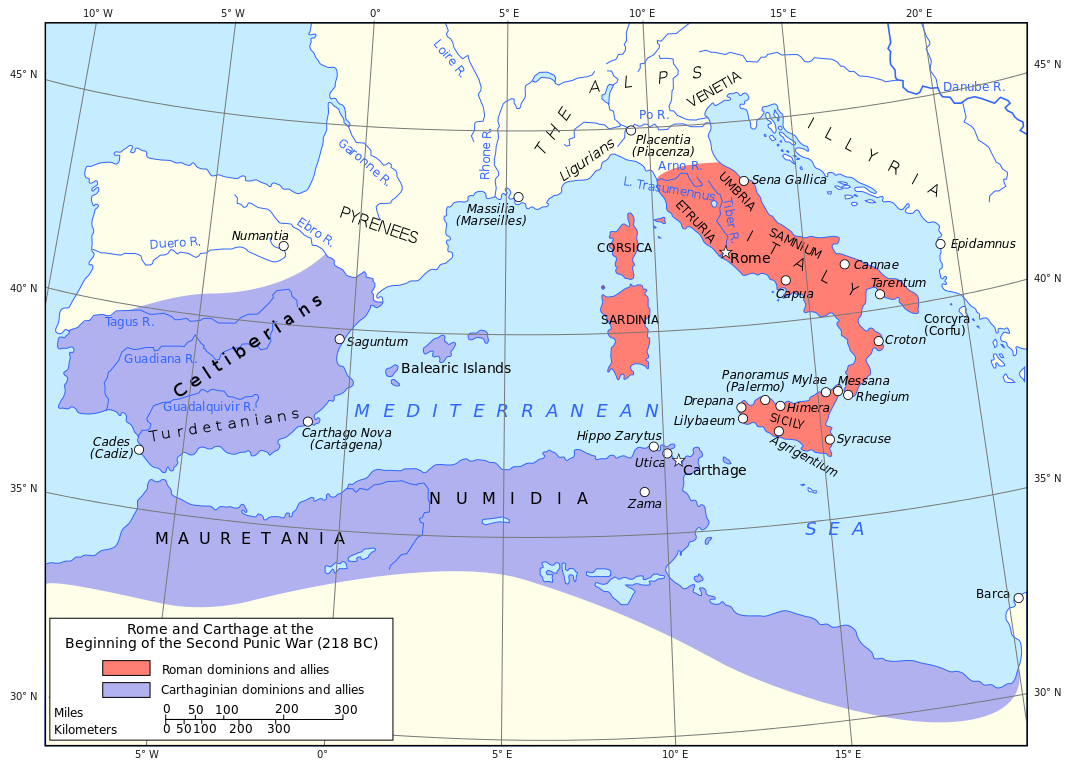
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)

Naval Raids and Expeditions
In 218 BC, the Carthaginian navy was scouting Sicilian waters and preparing for a surprise attack on their former key stronghold of Lilybaeum on the western tip of the island. Twenty quinqueremes, loaded with 1,000 soldiers, raided the Aegadian Islands west of Sicily and eight ships intended to attack the Aeolian Islands, but were blown off-course in a storm towards the Straits of Messina. The Syracusan navy, then at Messina, captured three of those without resistance. Learning from their crews that a Carthaginian fleet was to attack Lilybaeum, Hiero II warned the Roman praetor Marcus Amellius there. As a result, the Romans The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. prepared 20 quinqueremes to intercept, and defeated the 35 Carthaginian quinqueremes in the Battle of Lilybaeum.
The Roman Republic was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period - from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. prepared 20 quinqueremes to intercept, and defeated the 35 Carthaginian quinqueremes in the Battle of Lilybaeum.
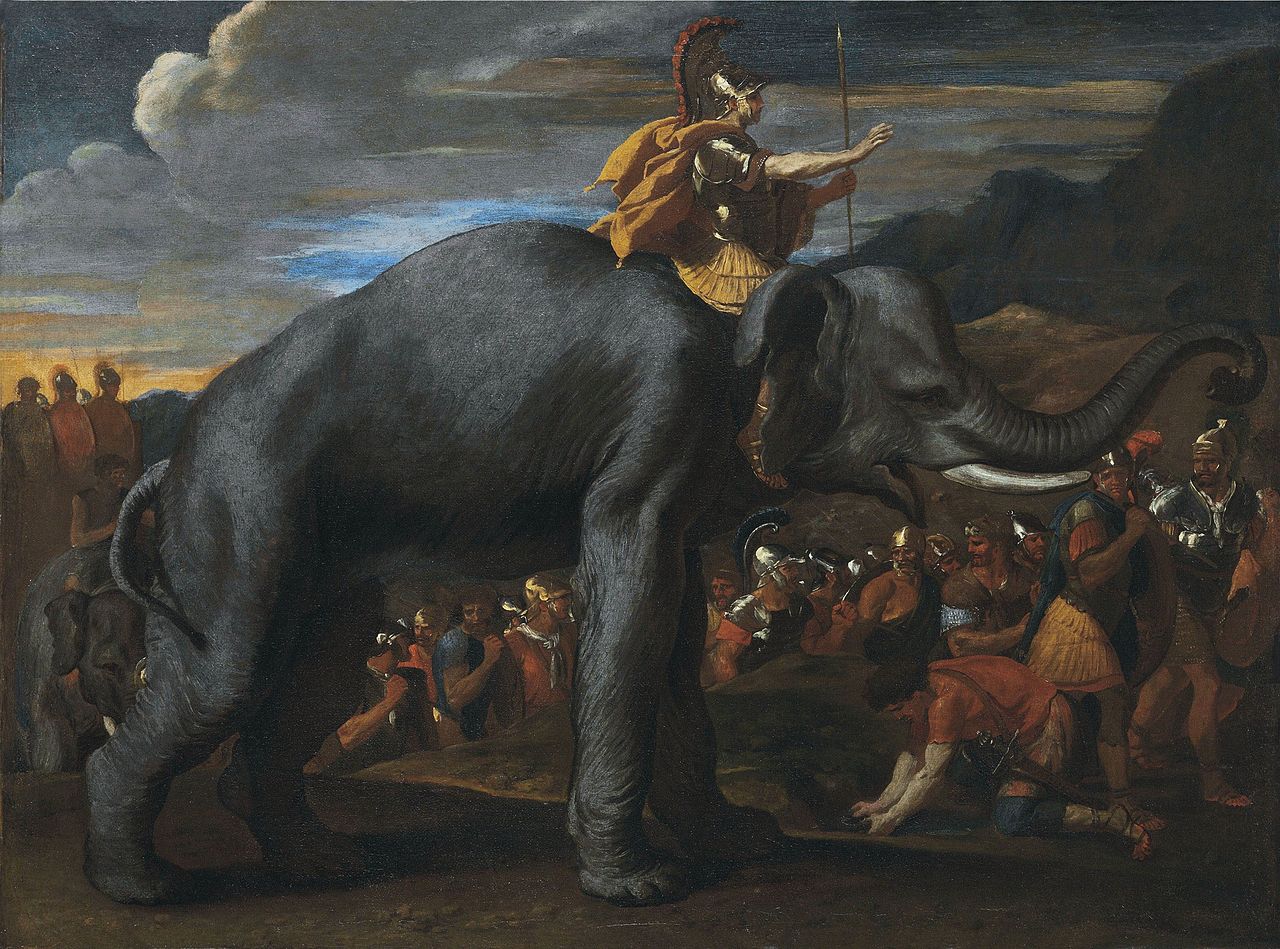
In 218 BC, preparations were made to launch a Roman expedition from Lilybaeum against Africa. Hannibal Hannibal Barca (247-183 BC), was a Carthaginian general, considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the western Mediterranean Basin, when the Roman Republic established its supremacy over other great powers such as ancient Carthage. One of his most famous achievements was at the outbreak of the Second Punic War, when he marched an army which included war elephants from Iberia over the Pyrenees and the Alps into Italy. Hannibal Barca » had anticipated the move and reinforced the defending army in Africa with 13,850 Iberian heavy infantry, 870 Balearic slingers and 1,200 Iberian cavalry. In addition, some 4,000 Iberian men "of good family were called up who were under orders to be conveyed to Carthage to strengthen its defence, and also to serve as hostages for the loyalty of their people." In return, 11,850 Libyan infantry, 300 Ligurians, and 500 Balearic slingers were sent to Iberia to strengthen the local defence against the other anticipated Roman invasion.
Hannibal Barca (247-183 BC), was a Carthaginian general, considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. Hannibal lived during a period of great tension in the western Mediterranean Basin, when the Roman Republic established its supremacy over other great powers such as ancient Carthage. One of his most famous achievements was at the outbreak of the Second Punic War, when he marched an army which included war elephants from Iberia over the Pyrenees and the Alps into Italy. Hannibal Barca » had anticipated the move and reinforced the defending army in Africa with 13,850 Iberian heavy infantry, 870 Balearic slingers and 1,200 Iberian cavalry. In addition, some 4,000 Iberian men "of good family were called up who were under orders to be conveyed to Carthage to strengthen its defence, and also to serve as hostages for the loyalty of their people." In return, 11,850 Libyan infantry, 300 Ligurians, and 500 Balearic slingers were sent to Iberia to strengthen the local defence against the other anticipated Roman invasion.
The Carthaginian navy had been defeated by the Romans in two major encounters, but neither side was usually able to stop the other from raiding each other's coasts. An exception was in 217 BC, when a Carthaginian fleet of 70 quinqueremes was intercepted off the coast of Etruria by a Roman fleet of 120 quinqueremes and retreated without giving battle.
The first Carthaginian expedition to Sardinia, in 215 BC, was under the command of Hasdrubal The Bald with his subordinate Hampsicora. A previous pro-Carthaginian uprising had been defeated, while a storm had blown the Carthaginian fleet to the Balearic Islands. When they finally arrived at Sardinia, the Romans were aware of their intentions and had reinforced the unpopular garrison under Titus Manlius Torquatus to 20,000 infantry and 1,200 cavalry. These engaged and defeated the Carthaginians' 15,000 infantry and 1,500 cavalry (plus an unknown number of elephants) and the remaining insurgent Sardinians at the Battle of Cornus. In the aftermath, the defeated expedition of 60 quinqueremes and several transports encountered a Roman raiding party from Africa with 100 quinqueremes. The Carthaginian fleet scattered and escaped save for seven ships. As a result, Sardinia, an important grain exporter, remained under Roman occupation.
Related Articles
First Punic War (264-241 BC)
The first of three wars fought between Ancient Carthage and the Roman Republic. For more than 20 years, the two powers struggled for supremacy, primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. View First Punic War (264-241 BC) »
Second Punic War (218-201 BC)
The Second Punic War, also referred to as The Hannibalic War and (by the Romans) the War Against Hannibal, lasted from 218 to 201 BC and involved combatants in the western and eastern Mediterranean. View Second Punic War (218-201 BC) »
Third Punic War (149–146 BC)
Was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between the former Phoenician colony of Carthage and the Roman Republic. This war was a much smaller engagement than the two previous Punic Wars and focused on Tunisia. View Third Punic War (149–146 BC) »
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Second Punic War (218-201 BC)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.