Vietnam War (1955–1975)
Background to 1949
France began its conquest of Indochina in the late 1850s, and completed pacification by 1893. The 1884 Treaty of Huế formed the basis for French colonial rule in Vietnam for the next seven decades. In spite of military resistance, most notably by the Cần Vương of Phan Đình Phùng, by 1888 the area of the current-day nations of Cambodia and Vietnam was made into the colony of French Indochina (Laos was later added to the colony). Various Vietnamese opposition movements to French rule existed during this period, such as the Việt Nam Quốc Dân Đảng who staged the failed Yên Bái mutiny in 1930, but none were ultimately as successful as the Viet Minh common front, which was founded in 1941, controlled by the Indochinese Communist Party, and funded by the U.S. and the Chinese Nationalist Party in its fight against Imperial Japanese occupation.
In 1940, during World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. World War II is generally considered to have begun on 1 September 1939, when Nazi Germany, under Adolf Hitler, invaded Poland. View World War II », the French
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. World War II is generally considered to have begun on 1 September 1939, when Nazi Germany, under Adolf Hitler, invaded Poland. View World War II », the French French Third Republic was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France during World War II led to the formation of the Vichy government. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the French colonial empire was the second largest colonial empire in the world only behind the British Empire. were defeated by the Germans. The French State (commonly known as Vichy France) was established as a client state of Nazi Germany. The French colonial authorities, in French Indochina, sided with the Vichy regime. In September 1940, Japan invaded Indochina. Following the cessation of fighting and the beginning of the Imperial Japanese
French Third Republic was the system of government adopted in France from 4 September 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed during the Franco-Prussian War, until 10 July 1940, after the Fall of France during World War II led to the formation of the Vichy government. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the French colonial empire was the second largest colonial empire in the world only behind the British Empire. were defeated by the Germans. The French State (commonly known as Vichy France) was established as a client state of Nazi Germany. The French colonial authorities, in French Indochina, sided with the Vichy regime. In September 1940, Japan invaded Indochina. Following the cessation of fighting and the beginning of the Imperial Japanese The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s led to the rise of militarism, nationalism and totalitarianism eventually culminating in Japan's membership in the Axis alliance. occupation, the French colonial authorities collaborated with the Japanese. The French continued to run affairs in Indochina, but ultimate power resided in the hands of the Imperial Japanese.
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. Economic and political turmoil in the 1920s led to the rise of militarism, nationalism and totalitarianism eventually culminating in Japan's membership in the Axis alliance. occupation, the French colonial authorities collaborated with the Japanese. The French continued to run affairs in Indochina, but ultimate power resided in the hands of the Imperial Japanese.
The Viet Minh was founded as a league for independence from France, but also opposed Japanese occupation in 1945 for the same reason. The United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City. and Chinese Nationalist Party supported them in the fight against the Imperial Japanese. However, they did not have enough power to fight actual battles at first. Viet Minh leader Ho Chi Minh was suspected of being a communist and jailed for a year by the Chinese Nationalist Party.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City. and Chinese Nationalist Party supported them in the fight against the Imperial Japanese. However, they did not have enough power to fight actual battles at first. Viet Minh leader Ho Chi Minh was suspected of being a communist and jailed for a year by the Chinese Nationalist Party.
Double occupation by France and Japan continued until the German forces were expelled from France and the French Indochina colonial authorities started holding secret talks with the Free French. Fearing that they could no longer trust the French authorities, the Imperial Japanese military interned the French authorities and troops on 9 March 1945 and created the puppet Empire of Vietnam state, under Bảo Đại instead.
During 1944–1945, a deep famine struck northern Vietnam due to a combination of bad weather and French/Japanese exploitation (French Indochina had to supply grains to Japan). Between 400,000 and 2 million people died of starvation (out of a population of 10 million in the affected area). Exploiting the administrative gap that the internment of the French had created, the Viet Minh in March 1945 urged the population to ransack rice warehouses and refuse to pay their taxes. Between 75 and 100 warehouses were consequently raided. This rebellion against the effects of the famine and the authorities that were partially responsible for it bolstered the Viet Minh's popularity and they recruited many members during this period.
On 22 August 1945, following the Imperial Japanese surrender, OSS agents Archimedes Patti and Carleton B. Swift Jr. arrived in Hanoi on a mercy mission to liberate allied POWs and were accompanied by Jean Sainteny, a French government official. The Japanese forces informally surrendered (the official surrender took place on 2 September 1945 in Tokyo Bay) but being the only force capable of maintaining law and order the Imperial Japanese military remained in power while keeping French colonial troops and Sainteny detained.
During August the Imperial Japanese forces remained inactive as the Viet Minh and other nationalist groups took over public buildings and weapons, which began the August Revolution. OSS officers met repeatedly with Ho Chi Minh and other Viet Minh officers during this period and on 2 September 1945 Ho Chi Minh declared the independent Democratic Republic of Vietnam before a crowd of 500,000 in Hanoi. In an overture to the Americans, he began his speech by paraphrasing the United States Declaration of Independence: "All men are created equal. The Creator has given us certain inviolable Rights: the right to Life, the right to be Free, and the right to achieve Happiness."
The Viet Minh took power in Vietnam in the August Revolution. The Viet Minh, downplaying their Communist agenda and stressing nationalism enjoyed large popular support (Vietnamese independence being popular at the time), although Arthur J. Dommen cautions against a "romanticized view" of their success: "The Viet Minh use of terror was systematic….the party had drawn up a list of those to be liquidated without delay." After their defeat in the war, the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) gave weapons to the Vietnamese, and kept Vichy French officials and military officers imprisoned for a month after the surrender. The Viet Minh had recruited more than 600 Imperial Japanese soldiers and given them roles to train or command Vietnamese soldiers.
However, the major allied victors of World War II, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union., all agreed the area belonged to the French. As the French did not have the means to immediately retake Vietnam, the major powers came to an agreement that British
Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union., all agreed the area belonged to the French. As the French did not have the means to immediately retake Vietnam, the major powers came to an agreement that British The British Empire, was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By the start of the 20th century, Germany and the United States had begun to challenge Britain's economic lead. troops would occupy the south while Nationalist Chinese forces would move in from the north. Nationalist Chinese troops entered the country to disarm Imperial Japanese troops north of the 16th parallel on 14 September 1945. When the British landed in the south, they rearmed the interned French forces as well as parts of the surrendered Imperial Japanese forces to aid them in retaking southern Vietnam, as they did not have enough troops to do this themselves.
The British Empire, was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By the start of the 20th century, Germany and the United States had begun to challenge Britain's economic lead. troops would occupy the south while Nationalist Chinese forces would move in from the north. Nationalist Chinese troops entered the country to disarm Imperial Japanese troops north of the 16th parallel on 14 September 1945. When the British landed in the south, they rearmed the interned French forces as well as parts of the surrendered Imperial Japanese forces to aid them in retaking southern Vietnam, as they did not have enough troops to do this themselves.
On the urging of the Soviet Union, Ho Chi Minh initially attempted to negotiate with the French, who were slowly re-establishing their control across the area. In January 1946, the Viet Minh won elections across central and northern Vietnam. On 6 March 1946, Ho signed an agreement allowing French forces to replace Nationalist Chinese forces, in exchange for French recognition of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam as a "free" republic within the French Union, with the specifics of such recognition to be determined by future negotiation. The French landed in Hanoi by March 1946 and in November of that year they ousted the Viet Minh from the city. British forces departed on 26 March 1946, leaving Vietnam in the hands of the French. Soon thereafter, the Viet Minh began a guerrilla war against the French Union forces, beginning the First Indochina War.
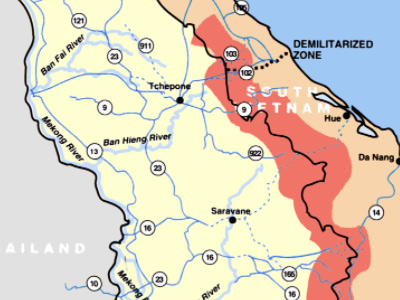
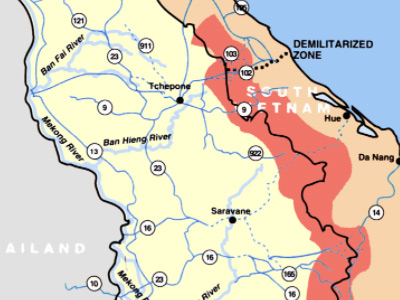
The war spread to Laos and Cambodia, where communists organized the Pathet Lao and the Khmer Serei, both of which were modeled on the Viet Minh. Globally, the Cold War began in earnest, which meant that the rapprochement that existed between the Western powers and the Soviet Union during World War II disintegrated. The Viet Minh fight was hampered by a lack of weapons; this situation changed by 1949 when the Chinese Communists had largely won the Chinese Civil War and were free to provide arms to their Vietnamese allies.
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Vietnam War (1955–1975)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.