Vietnam War (1955–1975)
Transition Period
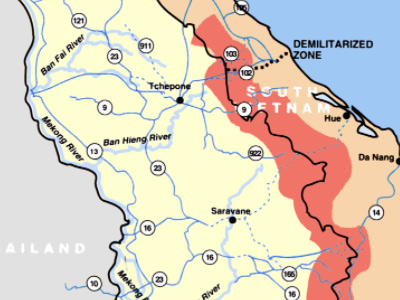
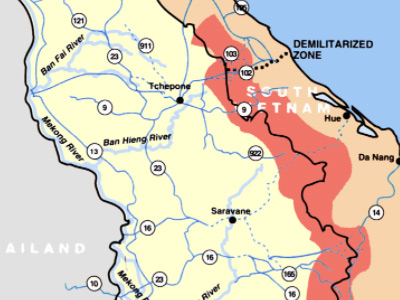
Vietnam was temporarily partitioned at the 17th parallel, and under the terms of the Geneva Accords, civilians were to be given the opportunity to move freely between the two provisional states for a 300-day period. Elections throughout the country were to be held in 1956 to establish a unified government. Around one million northerners, mainly minority Catholics, fled south, fearing persecution by the communists following an American propaganda campaign using slogans such as "The Virgin Mary is heading south", and aided by a U.S.-funded $93 million relocation program, which included the use of the Seventh Fleet to ferry refugees. As many as two million more would have left had they not been stopped by the Viet Minh. The northern, mainly Catholic refugees were meant to give the later Ngô Đình Diệm regime a strong anti-communist constituency. Diệm later went on to staff his administration's key posts mostly with northern and central Catholics.
In addition to the Catholics flowing south, up to 130,000 "Revolutionary Regroupees" went to the north for "regroupment", expecting to return to the south within two years. The Viet Minh left roughly 5,000 to 10,000 cadres in the south as a "politico-military substructure within the object of its irredentism." The last French soldiers were to leave Vietnam in April 1956. The PRC completed its withdrawal from North Vietnam at around the same time. Around 52,000 Vietnamese civilians moved from south to north.
Between 1953 and 1956, the North Vietnamese government instituted various agrarian reforms, including "rent reduction" and "land reform", which resulted in significant political oppression. During the land reform, testimony from North Vietnamese witnesses suggested a ratio of one execution for every 160 village residents, which extrapolated nationwide would indicate nearly 100,000 executions. Because the campaign was concentrated mainly in the Red River Delta area, a lower estimate of 50,000 executions became widely accepted by scholars at the time. However, declassified documents from the Vietnamese and Hungarian archives indicate that the number of executions was much lower than reported at the time, although likely greater than 13,500. In 1956, leaders in Hanoi admitted to "excesses" in implementing this program and restored a large amount of the land to the original owners.

These books are available for download with Apple Books on your Mac or iOS device
The south, meanwhile, constituted the State of Vietnam, with Bảo Đại as Emperor and Ngô Đình Diệm (appointed in July 1954) as his prime minister. Neither the United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City. government nor Ngô Đình Diệm's State of Vietnam signed anything at the 1954 Geneva Conference. With respect to the question of reunification, the non-communist Vietnamese delegation objected strenuously to any division of Vietnam, but lost out when the French
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country in North America. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. The United States shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south. The national capital is Washington, D.C., and the most populous city and financial center is New York City. government nor Ngô Đình Diệm's State of Vietnam signed anything at the 1954 Geneva Conference. With respect to the question of reunification, the non-communist Vietnamese delegation objected strenuously to any division of Vietnam, but lost out when the French France, officially the French Republic is transcontinental country predominantly located in Western Europe and spanning overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire. accepted the proposal of Viet Minh delegate Phạm Văn Đồng, who proposed that Vietnam eventually be united by elections under the supervision of "local commissions". The United States countered with what became known as the "American Plan", with the support of South Vietnam and the United Kingdom. It provided for unification elections under the supervision of the United Nations (UN)
France, officially the French Republic is transcontinental country predominantly located in Western Europe and spanning overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. France reached its political and military zenith in the early 19th century under Napoleon Bonaparte, subjugating much of continental Europe and establishing the First French Empire. accepted the proposal of Viet Minh delegate Phạm Văn Đồng, who proposed that Vietnam eventually be united by elections under the supervision of "local commissions". The United States countered with what became known as the "American Plan", with the support of South Vietnam and the United Kingdom. It provided for unification elections under the supervision of the United Nations (UN) United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. The UN was established after World War II with the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective., but was rejected by the Soviet
United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. The UN was established after World War II with the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective., but was rejected by the Soviet Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union. delegation. The United States said, "With respect to the statement made by the representative of the State of Vietnam, the United States reiterates its traditional position that peoples are entitled to determine their own future and that it will not join in any arrangement which would hinder this".
Soviet Union, officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. The Soviet Union fall process began with growing unrest in the Union's various constituent national republics developing into an incessant political and legislative conflict between them and the central government. Estonia was the first Soviet republic to declare state sovereignty inside the Union. delegation. The United States said, "With respect to the statement made by the representative of the State of Vietnam, the United States reiterates its traditional position that peoples are entitled to determine their own future and that it will not join in any arrangement which would hinder this".
U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower wrote in 1954, "I have never talked or corresponded with a person knowledgeable in Indochinese affairs who did not agree that had elections been held as of the time of the fighting, possibly eighty percent of the population would have voted for the Communist Ho Chi Minh as their leader rather than Chief of State Bảo Đại. Indeed, the lack of leadership and drive on the part of Bảo Đại was a factor in the feeling prevalent among Vietnamese that they had nothing to fight for." According to the Pentagon Papers, however, from 1954 to 1956 "Ngô Đình Diệm really did accomplish miracles" in South Vietnam: "It is almost certain that by 1956 the proportion which might have voted for Ho—in a free election against Diệm—would have been much smaller than eighty percent." In 1957, independent observers from India, Poland, and Canada representing the International Control Commission (ICC) stated that fair, unbiased elections were not possible, with the ICC reporting that neither South nor North Vietnam had honored the armistice agreement.
From April to June 1955, Diệm eliminated any political opposition in the south by launching military operations against two religious groups: the Cao Đài and Hòa Hảo of Ba Cụt. The campaign also focused on the Bình Xuyên organized crime group which was allied with members of the communist party secret police and had some military elements. As broad-based opposition to his harsh tactics mounted, Diệm increasingly sought to blame the communists.
In a referendum on the future of the State of Vietnam on 23 October 1955, Diệm rigged the poll supervised by his brother Ngô Đình Nhu and was credited with 98.2 percent of the vote, including 133% in Saigon. His American advisors had recommended a more modest winning margin of "60 to 70 percent." Diệm, however, viewed the election as a test of authority. Three days later, he declared South Vietnam to be an independent state under the name Republic of Vietnam (ROV), with himself as president. Likewise, Ho Chi Minh and other communist officials always won at least 99% of the vote in North Vietnamese "elections".
The domino theory, which argued that if one country fell to communism, then all of the surrounding countries would follow, was first proposed as policy by the Eisenhower administration. John F. Kennedy, then a U.S. Senator, said in a speech to the American Friends of Vietnam: "Burma, Thailand, India, Japan Japan is an island country in East Asia. Beginning in the 12th century, political power was held by a series of military dictators (shōgun) and feudal lords (daimyō) and enforced by a class of warrior nobility (samurai). In the Meiji period, the empire adopted a Western-modeled constitution and pursued a program of industrialization and modernization. A global leader in the automotive, robotics and electronics industries, Japan has made significant contributions to science and technology., the Philippines and obviously Laos and Cambodia are among those whose security would be threatened if the Red Tide of Communism overflowed into Vietnam."
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Beginning in the 12th century, political power was held by a series of military dictators (shōgun) and feudal lords (daimyō) and enforced by a class of warrior nobility (samurai). In the Meiji period, the empire adopted a Western-modeled constitution and pursued a program of industrialization and modernization. A global leader in the automotive, robotics and electronics industries, Japan has made significant contributions to science and technology., the Philippines and obviously Laos and Cambodia are among those whose security would be threatened if the Red Tide of Communism overflowed into Vietnam."
HISTORY
RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Vietnam War (1955–1975)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.