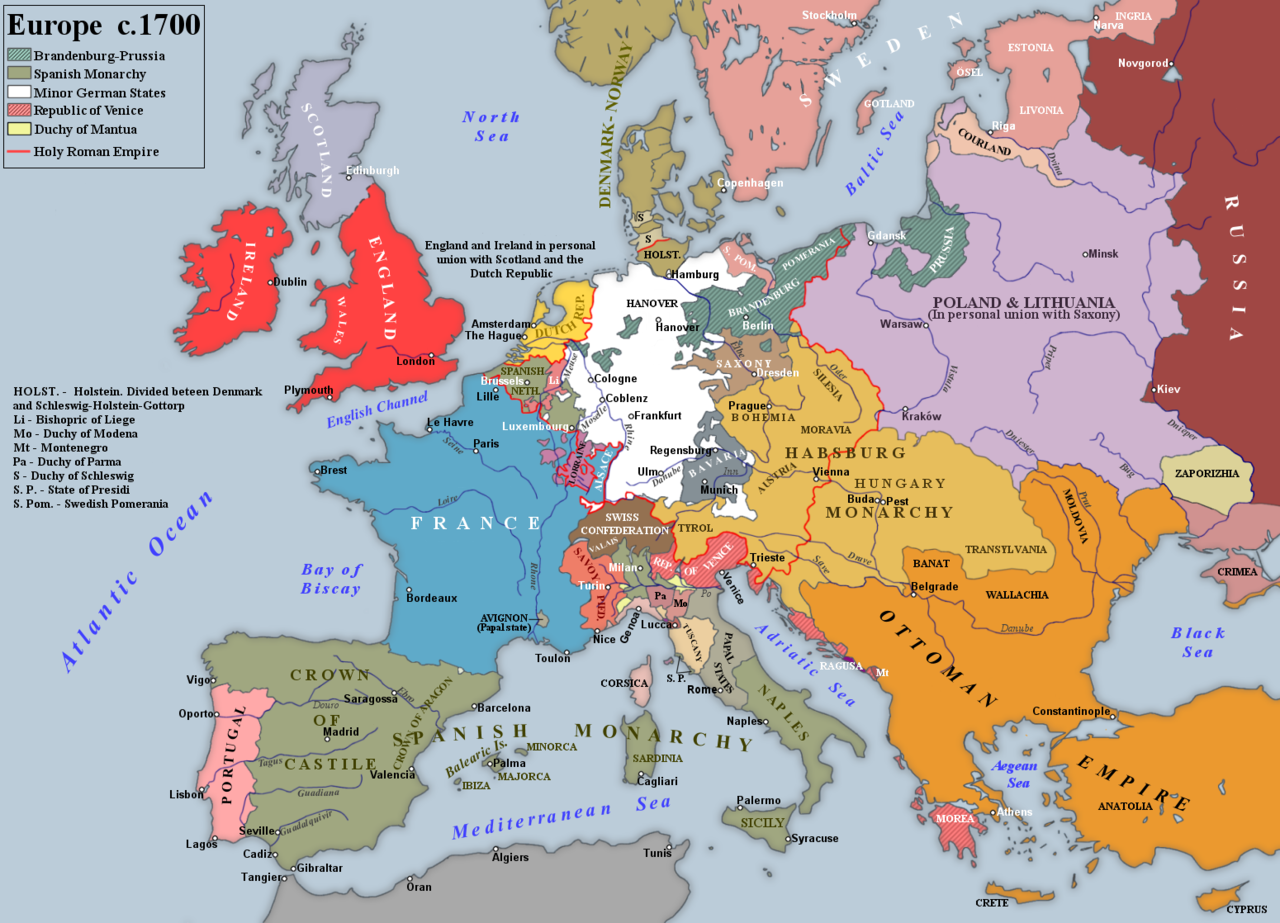
Nine Years' War (1688–97)

Rhineland and the Empire
Marshal Duras, Vauban, and 30,000 men – all under the nominal command of the Dauphin – besieged the Elector of Trier's fortress of Philippsburg on 27 September 1688; after a vigorous defence it fell on 30 October. Louis XIV's army proceeded to take Mannheim, which capitulated on 11 November, shortly followed by Frankenthal. Other towns fell without resistance, including Oppenheim, Worms, Bingen, Kaiserslautern, Heidelberg, Speyer and, above all, the key fortress of Mainz. After Coblenz failed to surrender Boufflers put it under heavy bombardment, but it did not fall to the French The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic..
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic..
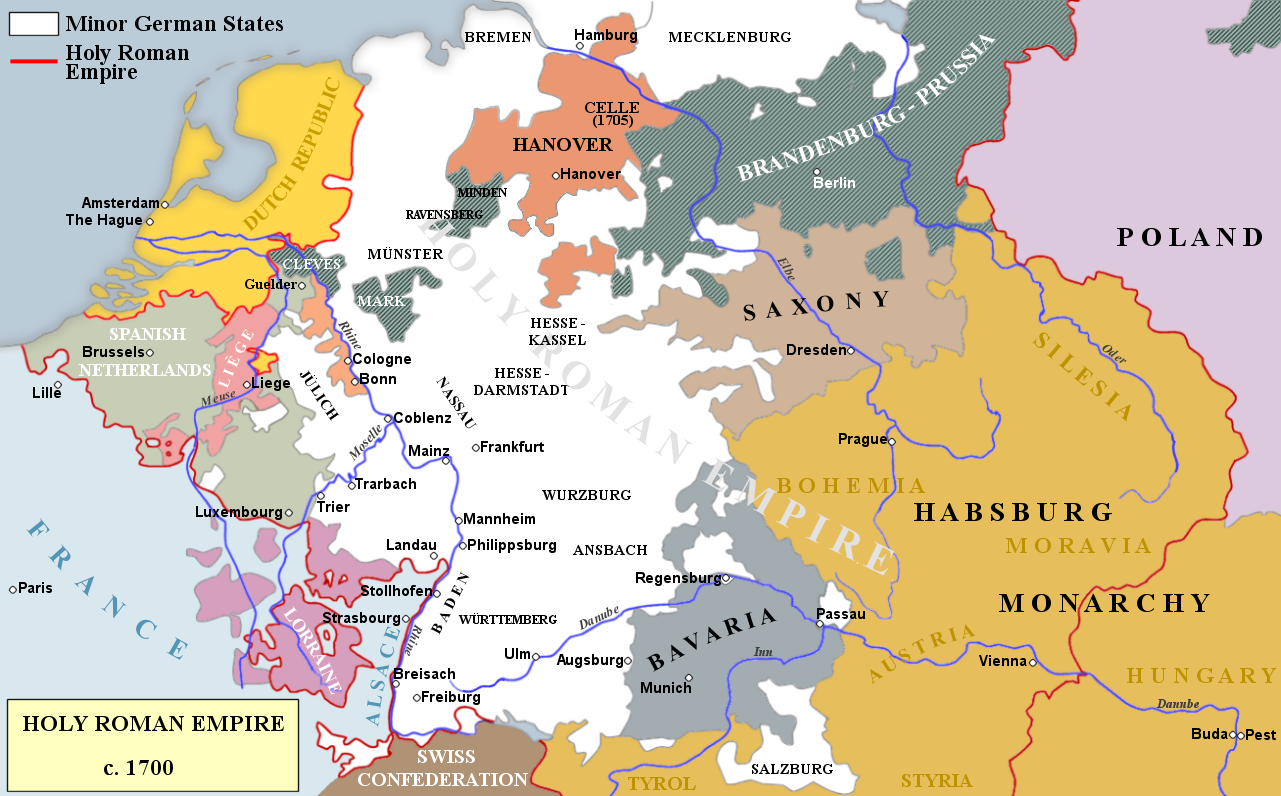
Rhine campaign 1688–89. French forces cross the Rhine at Strasbourg and proceed to invest Philippsburg – the key to the middle Rhine – on 27 September 1688

Rhine campaign 1688–89. French forces cross the Rhine at Strasbourg and proceed to invest Philippsburg – the key to the middle Rhine – on 27 September 1688
( Click image to enlarge)
Louis XIV now mastered the Rhine south of Mainz to the Swiss border, but although the attacks kept the Turks fighting in the east, the impact on Leopold I and the German states had the opposite effect of what had been intended. The League of Augsburg was not strong enough to meet the threat, but on 22 October the powerful German princes, including the Elector of Brandenburg, John George III, Elector of Saxony, Ernest Augustus of Hanover, and Charles I, Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, reached an agreement in Magdeburg that mobilised the forces of north Germany. Meanwhile, the Emperor recalled the Bavarian, Swabian, and Franconian troops under the Elector of Bavaria from the Ottoman The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. front to defend south Germany. The French had not prepared for such an eventuality. Realising that the war in Germany was not going to end quickly and that the Rhineland blitz would not be a brief and decisive parade of French glory, Louis XIV and Louvois resolved upon a scorched-earth policy in the Palatinate, Baden and Württemberg, intent on denying enemy troops local resources and prevent them from invading French territory. By 20 December 1688 Louvois had selected all the cities, towns, villages and châteaux intended for destruction. On 2 March 1689 Count of Tessé torched Heidelberg; on 8 March Montclar levelled Mannheim. Oppenheim and Worms were finally destroyed on 31 May, followed by Speyer on 1 June, and Bingen on 4 June. In all, French troops burnt over 20 substantial towns as well as numerous villages.
The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. front to defend south Germany. The French had not prepared for such an eventuality. Realising that the war in Germany was not going to end quickly and that the Rhineland blitz would not be a brief and decisive parade of French glory, Louis XIV and Louvois resolved upon a scorched-earth policy in the Palatinate, Baden and Württemberg, intent on denying enemy troops local resources and prevent them from invading French territory. By 20 December 1688 Louvois had selected all the cities, towns, villages and châteaux intended for destruction. On 2 March 1689 Count of Tessé torched Heidelberg; on 8 March Montclar levelled Mannheim. Oppenheim and Worms were finally destroyed on 31 May, followed by Speyer on 1 June, and Bingen on 4 June. In all, French troops burnt over 20 substantial towns as well as numerous villages.
The Germans prepared to take back what they had lost, and in 1689 formed three armies along the Rhine. The smallest of these, initially under the Elector of Bavaria, protected the upper Rhine between the lines north of Strasbourg to the Black Forest. On the middle Rhine stood the largest army under the best Imperial general, and commander-in-chief, Charles V, Duke of Lorraine. Charles V cleared away the French threat on Frankfurt and opened trenches around Mainz on 22/23 July. After a bloody two months siege the Marquis of Huxelles finally yielded the town on 8 September. Meanwhile, on the lower Rhine stood the Elector of Brandenburg who, aided by the celebrated Dutch The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined. engineer Menno van Coehoorn, besieged Kaiserswerth. Kaiserswerth fell on 26 June before the Elector led his army on Bonn, which, having endured a heavy bombardment, finally capitulated on 10 October. The invasion of the Rhineland had united the German princes in their opposition to Louis XIV who had lost more than he had gained that year along the Rhine. The campaign had also created a diversion of French forces and sufficient time for William of Orange to invade England
The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined. engineer Menno van Coehoorn, besieged Kaiserswerth. Kaiserswerth fell on 26 June before the Elector led his army on Bonn, which, having endured a heavy bombardment, finally capitulated on 10 October. The invasion of the Rhineland had united the German princes in their opposition to Louis XIV who had lost more than he had gained that year along the Rhine. The campaign had also created a diversion of French forces and sufficient time for William of Orange to invade England The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927..
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927..
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Nine Years' War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.