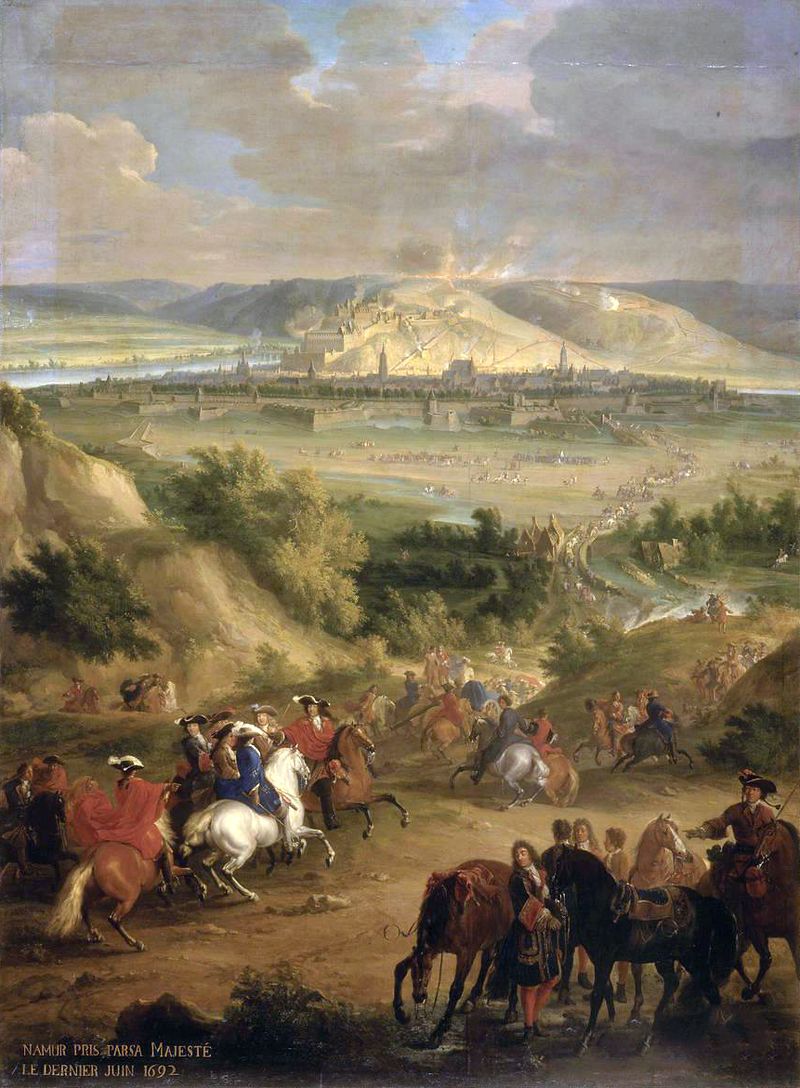
Nine Years' War (1688–97)

Road to Ryswick: 1696–97
Most fronts were relatively quiet throughout 1696: the armies in Flanders, along the Rhine, and in Catalonia, marched and counter-marched but little was achieved. Louis XIV's hesitancy to engage with the Allies (despite the confidence of his generals) may have reflected his knowledge of the secret talks that had begun more than a year earlier—with François de Callières acting for Louis XIV, and Jacob Boreel and Everhard van Weede Dijkvelt representing the Dutch The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined.. By the spring of 1696 the talks covered the whole panorama of problems that were proving an obstacle to peace. The most difficult of these were the recognition of the Prince of Orange as the King of England
The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined.. By the spring of 1696 the talks covered the whole panorama of problems that were proving an obstacle to peace. The most difficult of these were the recognition of the Prince of Orange as the King of England The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927. and the subsequent status of James II in France
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927. and the subsequent status of James II in France The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic.; the Dutch demand for a barrier against future French aggression; French tariffs on Dutch commerce; and the territorial settlements in the Rhine–Moselle areas regarding the Reunions and the recent conquests, particularly the strategically important city of Strasbourg. Louis XIV had succeeded in establishing the principle that a new treaty would be fixed within the framework of the Treaties of Westphalia and Nijmegen, and the Truce of Ratisbon, but with the Emperor's demands for Strasbourg, and William III's insistence that he be recognized as King of England before the conclusion of hostilities, it hardly seemed worthwhile in calling for a peace conference.
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic.; the Dutch demand for a barrier against future French aggression; French tariffs on Dutch commerce; and the territorial settlements in the Rhine–Moselle areas regarding the Reunions and the recent conquests, particularly the strategically important city of Strasbourg. Louis XIV had succeeded in establishing the principle that a new treaty would be fixed within the framework of the Treaties of Westphalia and Nijmegen, and the Truce of Ratisbon, but with the Emperor's demands for Strasbourg, and William III's insistence that he be recognized as King of England before the conclusion of hostilities, it hardly seemed worthwhile in calling for a peace conference.
In Italy the secret negotiations were proving more productive, with the French possession of Pinerolo now central to the talks. When Amadeus threatened to besiege Pinerolo the French, concluding that its defence was not now possible, agreed to hand back the stronghold on condition that its fortifications were demolished. The terms were formalised as the Treaty of Turin on 29 August 1696, by which provision Louis XIV also returned, intact, Montmélian, Nice, Villefranche, Susa, and other small towns. Amongst other concessions Louis XIV also promised not to interfere in Savoy's religious policy regarding the Vaudois, provided the Duke prevents any communication between them and French Huguenots. In return, Amadeus agreed to abandon the Grand Alliance and join with Louis XIV – if necessary – to secure the neutralisation of northern Italy. The Emperor, diplomatically outmanoeuvred, was compelled to accept peace in the region by signing the Treaty of Vigevano of 7 October, to which the French immediately acceded. Italy was neutralised and the Nine Years' War in the peninsula came to an end. Savoy had emerged as an independent sovereign House and a key second-rank power: the Alps, rather than the River Po, would be the boundary of France in the south-east.
The Treaty of Turin started a scramble for peace. With the continual disruption of trade and commerce politicians from England and the Dutch Republic were desirous for an end to the war. France was also facing economic exhaustion, but above all Louis XIV was becoming convinced that Charles II of Spain The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. was near death and he knew that the break-up of the coalition would be essential if France was to benefit from the dynastic battle ahead. The contending parties agreed to meet at Ryswick (Rijswijk) and come to a negotiated settlement. But as talks continued through 1697, so did the fighting. The main French goal that year in the Spanish Netherlands was Ath. Vauban and Catinat (now with troops freed from the Italian font) invested the town on 15 May while Marshals Boufflers and Villeroi covered the siege; after an assault on 5 June the Count of Roeux surrendered and the garrison marched out two days later. The Rhineland theatre in 1697 was again quiet: the French commander, Marshal Choiseul (who had replaced the sick de Lorge the previous year), was content to remain behind his fortified lines. Although Baden took Ebernberg on 27 September, news of the peace brought an end to the desultory campaign, and both armies drew back from one another. In Catalonia, however, French forces (now also reinforced with troops from Italy) achieved considerable success when Vendôme, commanding some 32,000 troops, besieged and captured Barcelona. The garrison, under Prince George of Hesse-Darmstadt, capitulated on 10 August. Yet it had been a hard fought contest: French casualties amounted to about 9,000, and the Spanish had suffered some 12,000 killed, wounded or lost.
The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. was near death and he knew that the break-up of the coalition would be essential if France was to benefit from the dynastic battle ahead. The contending parties agreed to meet at Ryswick (Rijswijk) and come to a negotiated settlement. But as talks continued through 1697, so did the fighting. The main French goal that year in the Spanish Netherlands was Ath. Vauban and Catinat (now with troops freed from the Italian font) invested the town on 15 May while Marshals Boufflers and Villeroi covered the siege; after an assault on 5 June the Count of Roeux surrendered and the garrison marched out two days later. The Rhineland theatre in 1697 was again quiet: the French commander, Marshal Choiseul (who had replaced the sick de Lorge the previous year), was content to remain behind his fortified lines. Although Baden took Ebernberg on 27 September, news of the peace brought an end to the desultory campaign, and both armies drew back from one another. In Catalonia, however, French forces (now also reinforced with troops from Italy) achieved considerable success when Vendôme, commanding some 32,000 troops, besieged and captured Barcelona. The garrison, under Prince George of Hesse-Darmstadt, capitulated on 10 August. Yet it had been a hard fought contest: French casualties amounted to about 9,000, and the Spanish had suffered some 12,000 killed, wounded or lost.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Nine Years' War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.