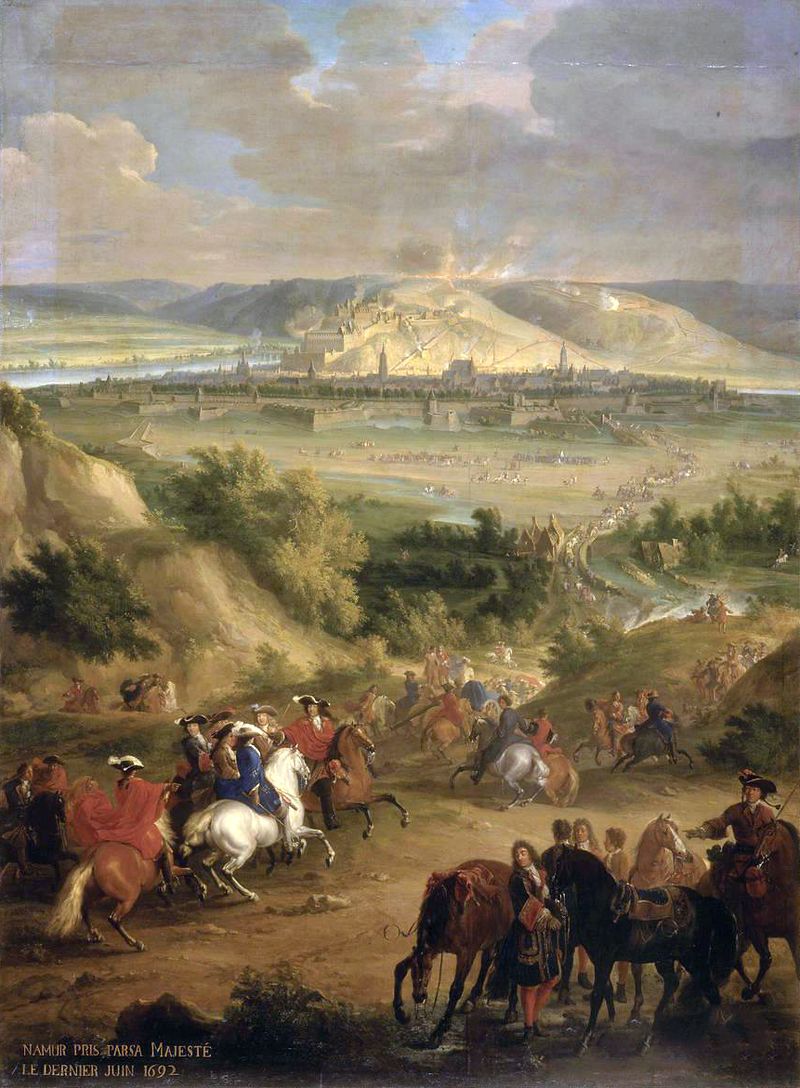
Nine Years' War (1688–97)

Expanding War: 1690–91
The main fighting of the Nine Years' War took place around France's borders: in the Spanish Netherlands; the Rhineland; Catalonia; and Piedmont-Savoy. The importance of the Spanish Netherlands was the result of its geographic position, sandwiched between France The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. and the Dutch Republic
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. and the Dutch Republic The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined.. Initially Marshal Humières commanded French forces in this theatre but in 1689, while the French concentrated on the Rhine, it produced little more than a stand-off – the most significant engagement occurred when William's second-in-command, the Prince of Waldeck, defeated Humières in a skirmish at the Battle of Walcourt on 25 August. However, by 1690 the Spanish Netherlands had become the main seat of the war where the French formed two armies: Boufflers' army on the Moselle, and a larger force to the west under Humières' successor – and Louis XIV's greatest general of the period – Marshal Luxembourg. On 1 July Luxembourg secured a clear tactical victory over Waldeck at the Battle of Fleurus; but his success produced little benefit – Louis XIV's concerns for the dauphin on the Rhine (where Marshal de Lorge now held actual command) overrode strategic necessity in the other theatres and forestalled a plan to besiege Namur or Charleroi. For the Emperor and the German princes, though, the most serious fact of 1690 was that the Turks had been victorious on the Danube, requiring them to send reinforcements to the east. The Elector of Bavaria – now Imperial commander-in-chief following Lorraine's death in April – could offer nothing on the lower or upper Rhine, and the campaign failed to produce a single major battle or siege.
The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined.. Initially Marshal Humières commanded French forces in this theatre but in 1689, while the French concentrated on the Rhine, it produced little more than a stand-off – the most significant engagement occurred when William's second-in-command, the Prince of Waldeck, defeated Humières in a skirmish at the Battle of Walcourt on 25 August. However, by 1690 the Spanish Netherlands had become the main seat of the war where the French formed two armies: Boufflers' army on the Moselle, and a larger force to the west under Humières' successor – and Louis XIV's greatest general of the period – Marshal Luxembourg. On 1 July Luxembourg secured a clear tactical victory over Waldeck at the Battle of Fleurus; but his success produced little benefit – Louis XIV's concerns for the dauphin on the Rhine (where Marshal de Lorge now held actual command) overrode strategic necessity in the other theatres and forestalled a plan to besiege Namur or Charleroi. For the Emperor and the German princes, though, the most serious fact of 1690 was that the Turks had been victorious on the Danube, requiring them to send reinforcements to the east. The Elector of Bavaria – now Imperial commander-in-chief following Lorraine's death in April – could offer nothing on the lower or upper Rhine, and the campaign failed to produce a single major battle or siege.

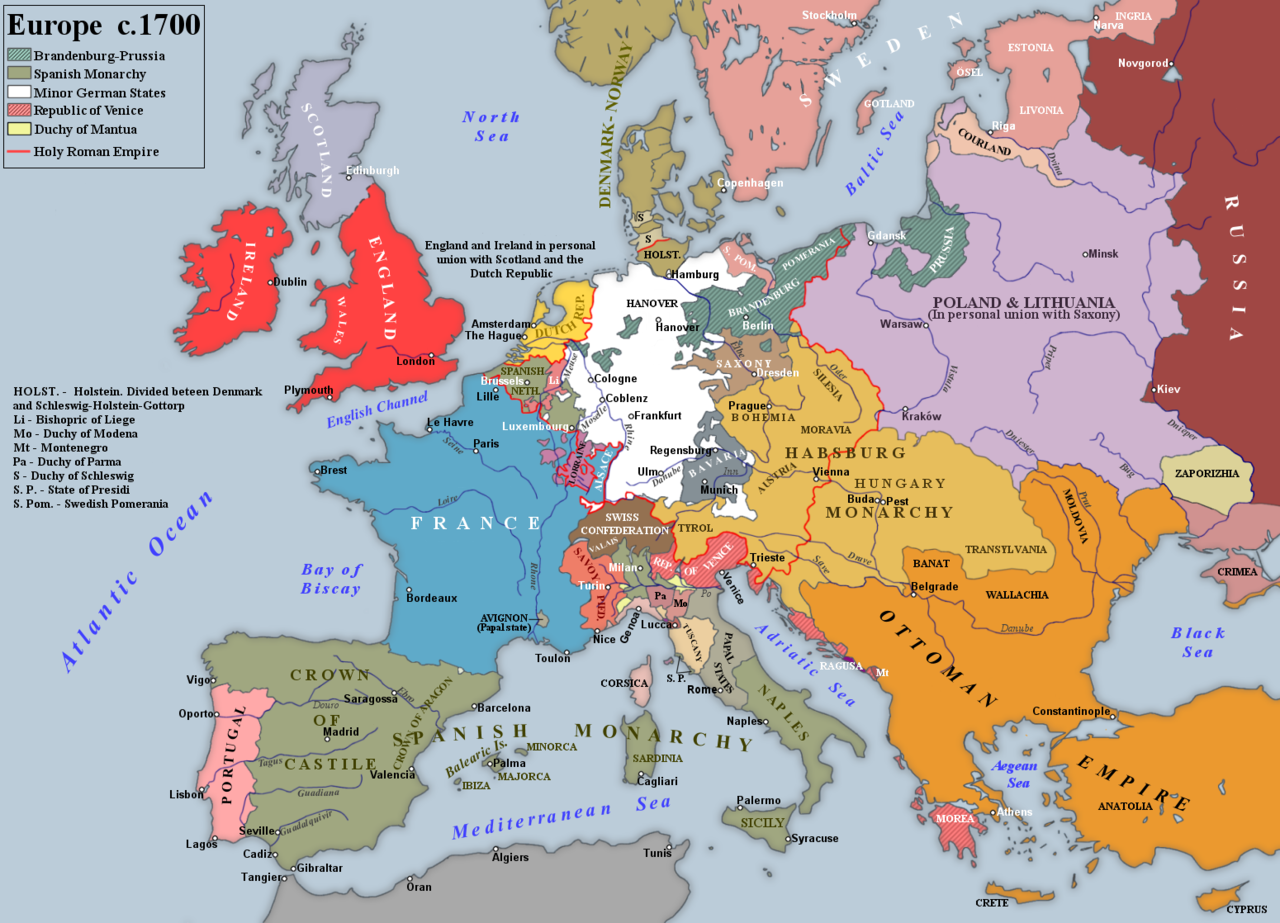
The Low Countries c. 1700: the principal theatre during the Nine Years' War

The Low Countries c. 1700: the principal theatre during the Nine Years' War
( Click image to enlarge)
The smallest front of the war was in Catalonia. In 1689 the Duke of Noailles had led French forces there aimed at bringing further pressure to bear on the Spanish by re-igniting a peasant rising against Charles II, which initially broke out in 1687. Exploiting the situation, Noailles captured Camprodon on 22 May, but a larger Spanish The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. army under the Duke of Villahermosa forced him to withdraw back to Roussillon in August. The Catalan campaign settled down in 1690, but a new front in Piedmont-Savoy proved more eventful. A ferment of religious animosities and Savoyard hatred of the French produced a theatre characterised by massacres and atrocities: constant guerrilla attacks by the armed populace were met by draconian reprisals. In 1690 Saint-Ruth took most of the Victor Amadeus II's exposed Duchy of Savoy, routing the Savoyard army in the process until only the great fortress of Montmélian remained in ducal hands; while to the south in Piedmont, Nicolas Catinat led 12,000 men and soundly defeated Victor Amadeus at the Battle of Staffarda on 18 August. Catinat immediately took Saluzzo, followed by Savigliano, Fossano, and Susa, but lacking sufficient troops, and with sickness rife within his army, Catinat was obliged to withdraw back across the Alps for the winter.
The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. army under the Duke of Villahermosa forced him to withdraw back to Roussillon in August. The Catalan campaign settled down in 1690, but a new front in Piedmont-Savoy proved more eventful. A ferment of religious animosities and Savoyard hatred of the French produced a theatre characterised by massacres and atrocities: constant guerrilla attacks by the armed populace were met by draconian reprisals. In 1690 Saint-Ruth took most of the Victor Amadeus II's exposed Duchy of Savoy, routing the Savoyard army in the process until only the great fortress of Montmélian remained in ducal hands; while to the south in Piedmont, Nicolas Catinat led 12,000 men and soundly defeated Victor Amadeus at the Battle of Staffarda on 18 August. Catinat immediately took Saluzzo, followed by Savigliano, Fossano, and Susa, but lacking sufficient troops, and with sickness rife within his army, Catinat was obliged to withdraw back across the Alps for the winter.

These books are available for download with Apple Books on your Mac or iOS device
French successes in 1690 had checked the Allies on most of the mainland fronts, yet their victories had not broken the Grand Alliance. With the hope of unhinging the coalition French commanders in 1691 prepared for an early double-blow: the capture of Mons in the Spanish Netherlands, and Nice in northern Italy. Boufflers invested Mons on 15 March with some 46,000 men, while Luxembourg commanded a similar force of observation. After some of the most intense fighting of all of Louis XIV's wars the town inevitably capitulated on 8 April. Luxembourg proceeded to take Halle at the end of May, while Boufflers bombarded Liège; but these acts proved to have no political nor strategic consequence. The final action of note in the Low Countries came on 19 September when Luxembourg's cavalry surprised and defeated the rear of the Allied forces in a minor action near Leuze. Now that the defence of the Spanish Netherlands depended almost wholly on the Allies William III insisted on replacing its Spanish governor, the Marquis of Gastañaga, with the Elector of Bavaria, thus overcoming delays in getting decisions from Madrid.
In 1691 there was little significant fighting in the Catalan and Rhineland fronts. In contrast, the northern Italian theatre was very active. Villefranche fell to French forces on 20 March, followed by Nice on 1 April, forestalling any chance of an Allied invasion of France along the coast. Meanwhile, to the north, in the Duchy of Savoy, the Marquis of La Hoguette took Montmélian (the region's last remaining stronghold) on 22 December – a major loss for the Grand Alliance. However, by comparison the French campaign on the Piedmontese plain was far from successful. Although Carmagnola fell in June, the Marquis of Feuquières, on learning of the approach of Prince Eugene of Savoy's relief force, precipitously abandoned the Siege of Cuneo with the loss of some 800 men and all his heavy guns. With Louis XIV concentrating his resources in Alsace and the Low Countries, Catinat was forced onto the defensive. The initiative in northern Italy now passed to the Allies who, as early as August, had 45,000 men (on paper) in the region, enabling them to regain Carmagnola in October. Louis XIV offered peace terms in December, but anticipating military superiority for the following campaign Amadeus was not prepared to negotiate seriously.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Nine Years' War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.