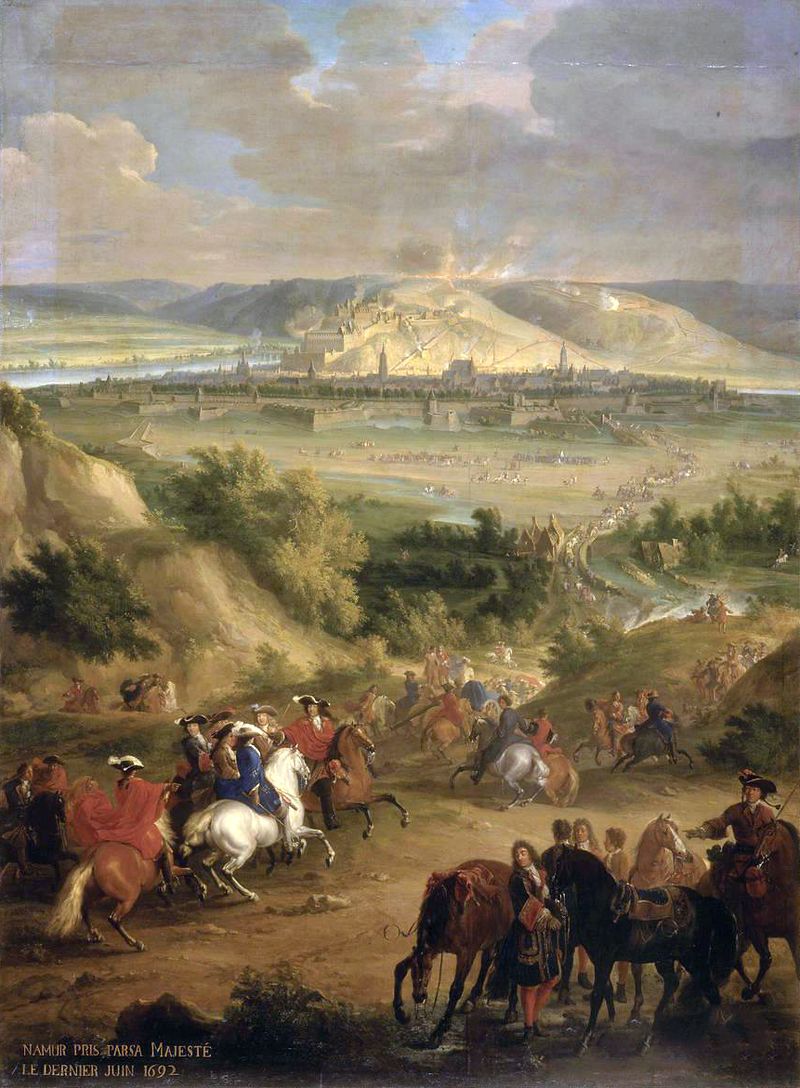
Nine Years' War (1688–97)

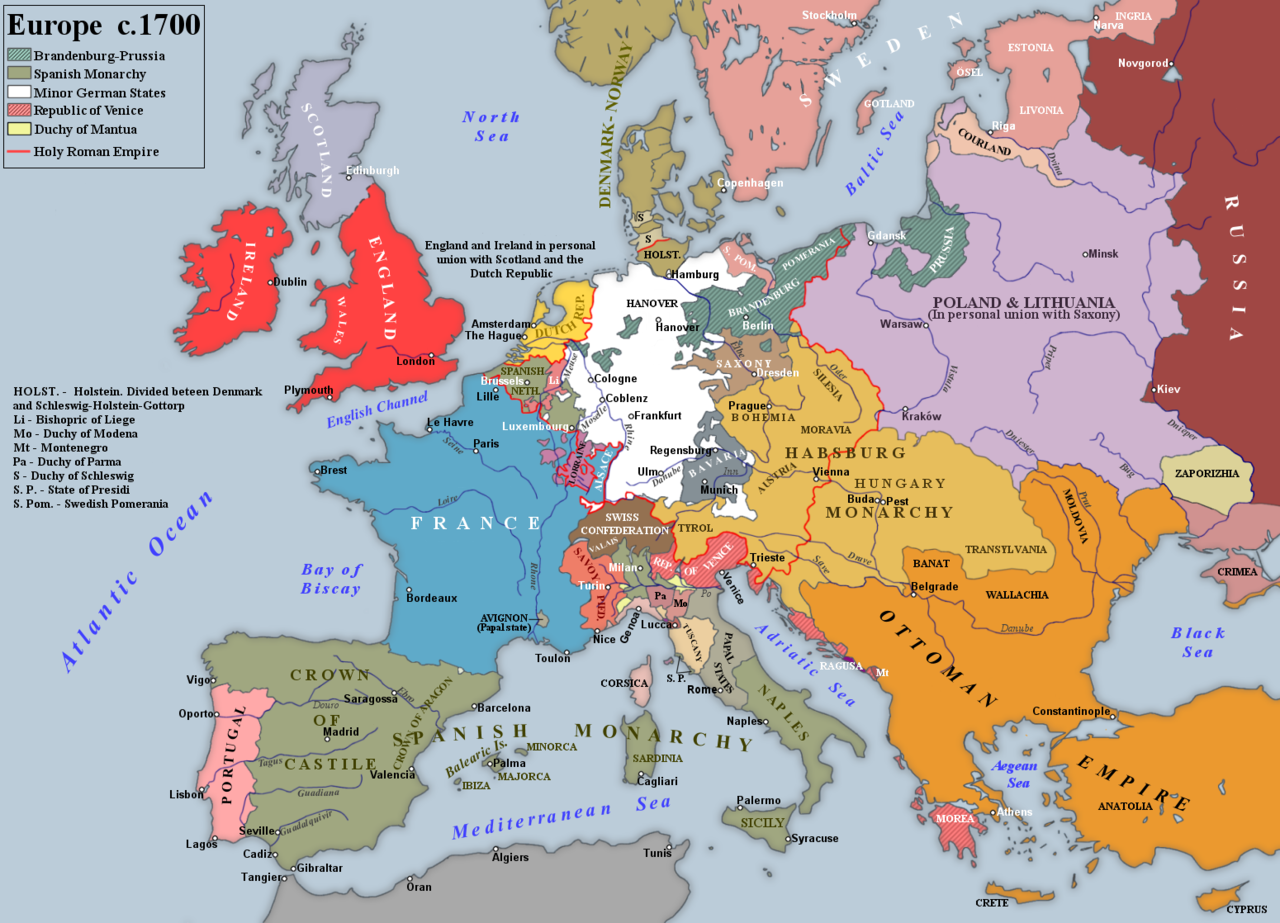
War Aims and the Grand Alliance
The success of William's invasion of England rapidly led to the coalition he had long desired. On 12 May 1689 the Dutch and the Holy Roman The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. Emperor had signed an offensive compact in Vienna, the aims of which were no less than to force France
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. From the accession of Otto I in 962 until the twelfth century, the Empire was the most powerful monarchy in Europe. The empire reached the apex of territorial expansion and power in the mid-thirteenth century, but overextending led to partial collapse. Emperor had signed an offensive compact in Vienna, the aims of which were no less than to force France The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. back to her borders as they were at the end of the Franco-Spanish War (1659), thus depriving Louis XIV of all his gains since his assumption of power. This meant for the Emperor and the German princes the reconquest of Lorraine, Strasbourg, parts of Alsace, and some Rhineland fortresses. Leopold I had tried to disentangle himself from the Turkish war to concentrate on the coming struggle, but the French invasion of the Rhineland had encouraged the Turks to stiffen their terms for peace and make demands the Emperor could not conceivably accept. Leopold I's decision to side with the coalition (against the opposition of many of his advisers) was, therefore, a decision to intervene in the west while continuing to fight the Ottomans
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. back to her borders as they were at the end of the Franco-Spanish War (1659), thus depriving Louis XIV of all his gains since his assumption of power. This meant for the Emperor and the German princes the reconquest of Lorraine, Strasbourg, parts of Alsace, and some Rhineland fortresses. Leopold I had tried to disentangle himself from the Turkish war to concentrate on the coming struggle, but the French invasion of the Rhineland had encouraged the Turks to stiffen their terms for peace and make demands the Emperor could not conceivably accept. Leopold I's decision to side with the coalition (against the opposition of many of his advisers) was, therefore, a decision to intervene in the west while continuing to fight the Ottomans The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. in the Balkans. Although the Emperor's immediate concerns were for the Rhineland, the most important parts of the treaty were the secret articles pledging England
The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. in the Balkans. Although the Emperor's immediate concerns were for the Rhineland, the most important parts of the treaty were the secret articles pledging England The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927. and the States-General to assist him in securing the Spanish succession should Charles II die without an heir, and to use their influence to secure his son's election to succeed him as Emperor.
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927. and the States-General to assist him in securing the Spanish succession should Charles II die without an heir, and to use their influence to secure his son's election to succeed him as Emperor.

Marshal Vauban (1633–1707). Louis XIV's greatest military engineer and one of his most trusted advisers
William III regarded the war as an opportunity to reduce the power of France and protect the Dutch Republic The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined., while providing conditions that would encourage trade and commerce. Although there remained territorial anomalies, Dutch war aims did not involve substantial alterations to the frontier; but William did aim to secure his new position in Britain. By seeking refuge in France and subsequently invading Ireland, James II had given William III the ideal instrument to convince the English parliament that entry into a major European war was unavoidable. With the support of Parliament, William III and Mary II declared war on 17 May 1689 (O.S.). This Anglo-Dutch alignment was the basis for the Grand Alliance, ratified on 20 December by William III representing England, Anthonie Heinsius and Treasurer Jacob Hop representing the Dutch Republic, and Königsegg and Stratman representing Emperor Leopold I. Like the Dutch the English were not preoccupied with territorial gains on the Continent, but were deeply concerned with limiting the power of France to defend against a Jacobite restoration (Louis XIV threatened to overthrow the Glorious Revolution and the precarious political settlement by supporting the old king over the new one). William III had secured his goal of mobilising Britain's resources for the anti-French coalition, but the Jacobite threat in Scotland and Ireland meant only a small English expeditionary force could be committed to assist the Dutch States Army in the coalition in the Spanish Netherlands for the first three years of the war.
The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined., while providing conditions that would encourage trade and commerce. Although there remained territorial anomalies, Dutch war aims did not involve substantial alterations to the frontier; but William did aim to secure his new position in Britain. By seeking refuge in France and subsequently invading Ireland, James II had given William III the ideal instrument to convince the English parliament that entry into a major European war was unavoidable. With the support of Parliament, William III and Mary II declared war on 17 May 1689 (O.S.). This Anglo-Dutch alignment was the basis for the Grand Alliance, ratified on 20 December by William III representing England, Anthonie Heinsius and Treasurer Jacob Hop representing the Dutch Republic, and Königsegg and Stratman representing Emperor Leopold I. Like the Dutch the English were not preoccupied with territorial gains on the Continent, but were deeply concerned with limiting the power of France to defend against a Jacobite restoration (Louis XIV threatened to overthrow the Glorious Revolution and the precarious political settlement by supporting the old king over the new one). William III had secured his goal of mobilising Britain's resources for the anti-French coalition, but the Jacobite threat in Scotland and Ireland meant only a small English expeditionary force could be committed to assist the Dutch States Army in the coalition in the Spanish Netherlands for the first three years of the war.
The Duke of Lorraine also joined the Alliance at the same time as England, while the King of Spain The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. (who had been at war with France since April 1689) and the Duke of Savoy signed in June 1690. The Allies had offered Victor Amadeus handsome terms to join the Grand Alliance, including the return of Casale to Mantua (he hoped it would revert to him upon the death of the childless Duke of Mantua) and of Pinerolo to himself. His adhesion to the Allied cause would facilitate the invasion of France through Dauphiné and Provence, where the naval base of Toulon lay. In contrast Louis XIV had embarked on a policy of overt military intimidation to retain Savoy in the French orbit, and had envisaged the military occupation of parts of Piedmont (including the citadel of Turin) to guarantee communications between Pinerolo and Casale. French demands on Victor Amadeus, and their determination to prevent the Duke from achieving his dynastic aims, were nothing less than an attack on Savoyard independence, convincing the Duke that he had to stand up to French aggression.
The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. (who had been at war with France since April 1689) and the Duke of Savoy signed in June 1690. The Allies had offered Victor Amadeus handsome terms to join the Grand Alliance, including the return of Casale to Mantua (he hoped it would revert to him upon the death of the childless Duke of Mantua) and of Pinerolo to himself. His adhesion to the Allied cause would facilitate the invasion of France through Dauphiné and Provence, where the naval base of Toulon lay. In contrast Louis XIV had embarked on a policy of overt military intimidation to retain Savoy in the French orbit, and had envisaged the military occupation of parts of Piedmont (including the citadel of Turin) to guarantee communications between Pinerolo and Casale. French demands on Victor Amadeus, and their determination to prevent the Duke from achieving his dynastic aims, were nothing less than an attack on Savoyard independence, convincing the Duke that he had to stand up to French aggression.
The Elector of Bavaria consented to add his name to the Grand Alliance on 4 May 1690, while the Elector of Brandenburg joined the anti-French coalition on 6 September. However, few of the minor powers were as devoted to the common cause, and all protected their own interests; some never hesitated to exact a high price for continuing their support. Charles XI of Sweden supplied the contingents due from his German possessions to the Allied cause (6,000 men and 12 warships), while in August 1689 Christian V of Denmark agreed to a treaty to supply William III with 7,000 troops in return for a subsidy. However, in March 1691 Sweden and Denmark put aside their mutual distrust and made a treaty of armed neutrality for the protection of their commerce and to prevent the war spreading north. To the annoyance of the Maritime Powers the Swedes now saw their rôle outside the great power-struggle of the Nine Years' War, exploiting opportunities to increase their own maritime trade. Nevertheless, Louis XIV at last faced a powerful coalition aimed at forcing France to recognise Europe's rights and interests.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Nine Years' War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.