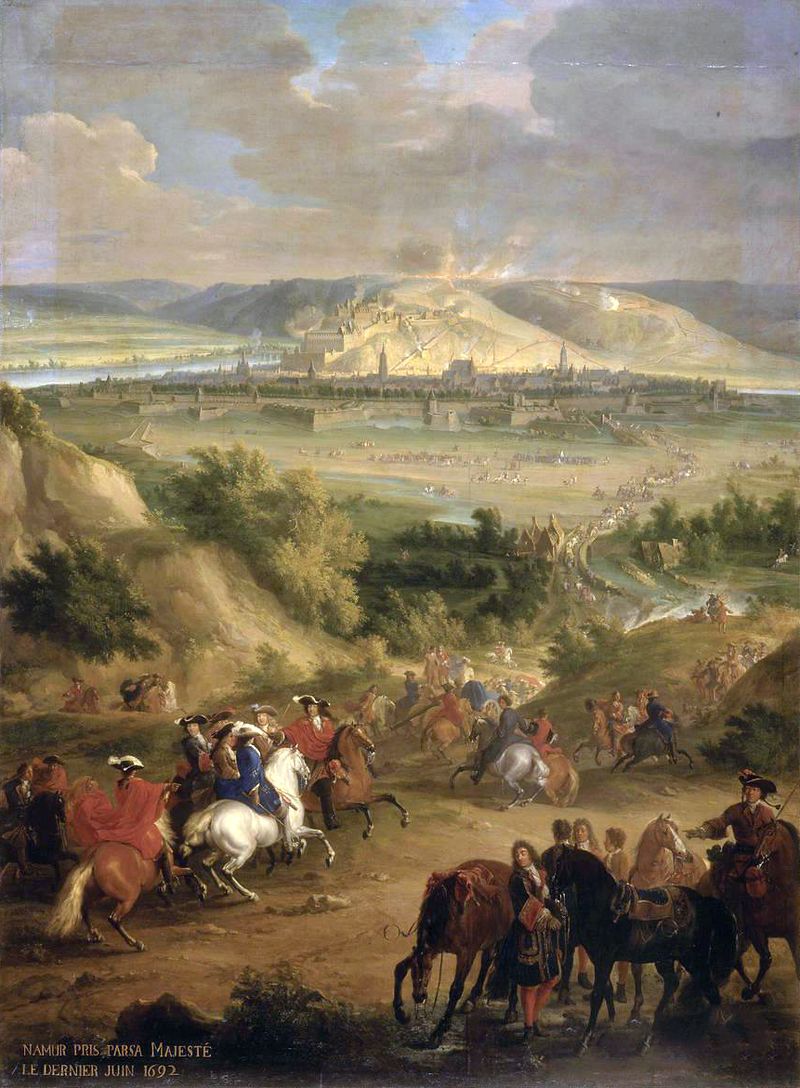
Nine Years' War (1688–97)

Treaty of Ryswick
The peace conference opened in May 1697 in William III's palace at Ryswick near The Hague. The Swedes were the official mediators, but it was through the private efforts of Boufflers and William Bentinck, the Earl of Portland that the major issues were resolved. William III had no intention of continuing the war or pressing for Leopold I's claims in the Rhineland or for the Spanish succession: it seemed more important for Dutch The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined. and British security to obtain Louis XIV's recognition of the 1688 revolution.
The Dutch Republic was a confederation that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795. It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. The income from this trade allowed the Dutch Republic to compete militarily against much larger countries. It amassed a huge fleet of 2,000 ships, initially larger than the fleets of England and France combined. and British security to obtain Louis XIV's recognition of the 1688 revolution.
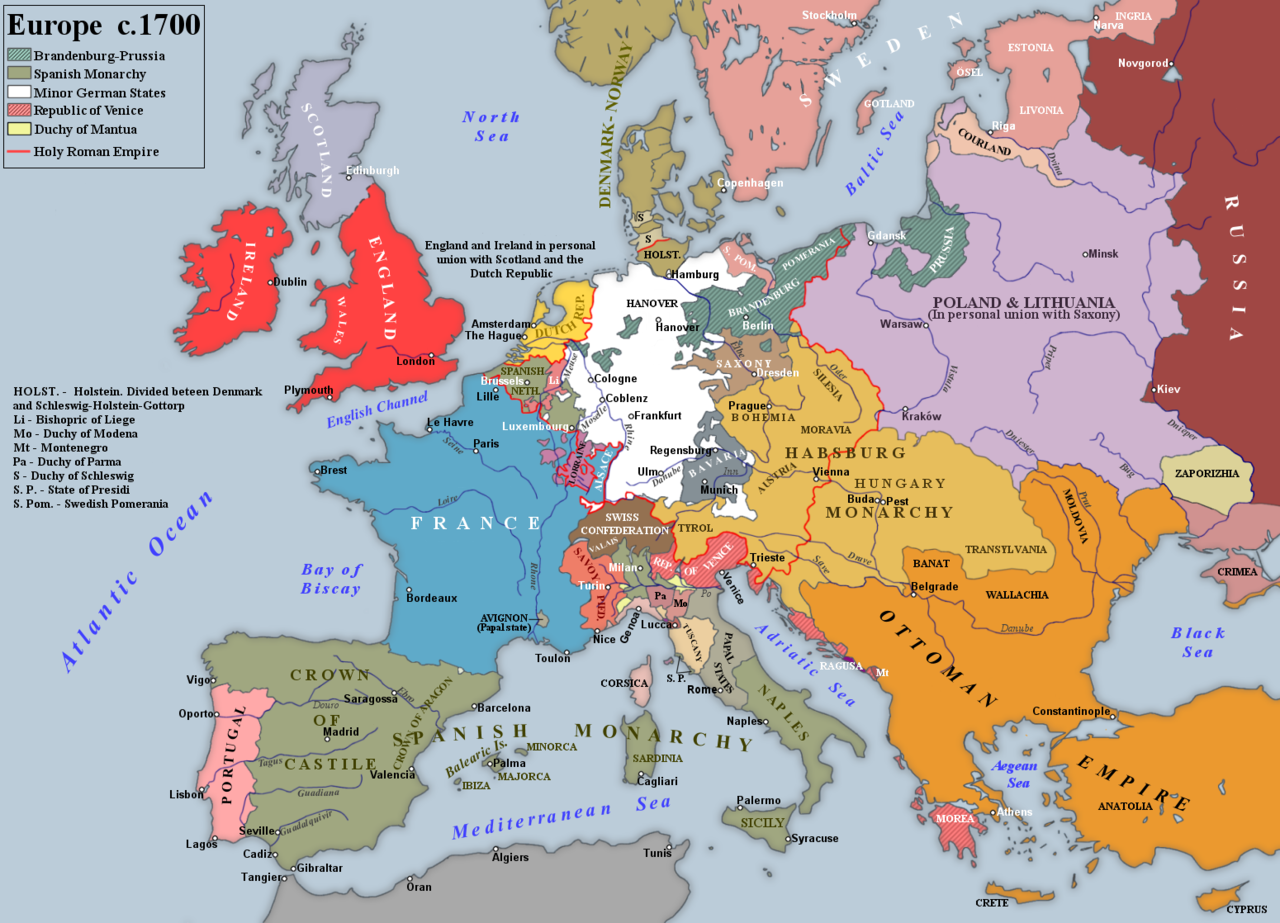
Map of European borders as they stood after the Treaty of Ryswick and just prior to Louis XIV's last great war, the War of the Spanish Succession

Map of European borders as they stood after the Treaty of Ryswick and just prior to Louis XIV's last great war, the War of the Spanish Succession
( Click image to enlarge)
By the terms of the Treaty of Ryswick, Louis XIV kept the whole of Alsace, including Strasbourg. Lorraine returned to its duke (although France The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. retained rights to march troops through the territory), and the French abandoned all gains on the right bank of the Rhine – Philppsburg, Breisach, Freiburg and Kehl. Additionally, the new French fortresses of La Pile, Mont Royal and Fort Louis were to be demolished. To win favour with Madrid over the Spanish succession question, Louis XIV evacuated Catalonia in Spain and Luxembourg, Chimay, Mons, Coutrai, Charleroi and Ath in the Low Countries. The Maritime Powers asked for no territory, but the Dutch were given a favourable commercial treaty, of which the most important provision was to relax regulations to favour Dutch trade and return to the French tariff of 1664. Although Louis XIV continued to shelter James II he now recognised William III as King of Protestant England, and undertook not to actively support the candidature of James II's son. He also gave way over the Palatinate and Cologne issues. Beyond this, the French gained recognition of their ownership of the western half of the island of Hispaniola.
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe since the High Middle Ages. It was also an early colonial power, with possessions around the world. Colonial conflicts with Great Britain led to the loss of much of its North American holdings by 1763. The Kingdom of France adopted a written constitution in 1791, but the Kingdom was abolished a year later and replaced with the First French Republic. retained rights to march troops through the territory), and the French abandoned all gains on the right bank of the Rhine – Philppsburg, Breisach, Freiburg and Kehl. Additionally, the new French fortresses of La Pile, Mont Royal and Fort Louis were to be demolished. To win favour with Madrid over the Spanish succession question, Louis XIV evacuated Catalonia in Spain and Luxembourg, Chimay, Mons, Coutrai, Charleroi and Ath in the Low Countries. The Maritime Powers asked for no territory, but the Dutch were given a favourable commercial treaty, of which the most important provision was to relax regulations to favour Dutch trade and return to the French tariff of 1664. Although Louis XIV continued to shelter James II he now recognised William III as King of Protestant England, and undertook not to actively support the candidature of James II's son. He also gave way over the Palatinate and Cologne issues. Beyond this, the French gained recognition of their ownership of the western half of the island of Hispaniola.
The representatives of the Dutch Republic, England The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927., and Spain
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from about 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Viking invasions of the 9th century upset the balance of power between the English kingdoms, and native Anglo-Saxon life in general. The English lands were unified in the 10th century in a reconquest completed by King Æthelstan in 927., and Spain The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. signed the treaty on 20 September 1697. Emperor Leopold I, desperate for a continuation of the war so as to strengthen his own claims to the Spanish succession, initially resisted the treaty, but because he was still at war with the Turks, and could not face fighting France alone, he also sought terms and signed on 30 October. The Emperor's finances were in a bad state, and the dissatisfaction aroused by the raising of Hanover to electoral rank had impaired Leopold I's influence in Germany. The Protestant princes had also blamed him for the religious clause in the treaty, which stipulated that the lands of the Reunions that France was to surrender would remain Catholic, even those that had been forcibly converted—a clear defiance of the Westphalia settlement. However, the Emperor had netted an enormous accretion of power: Leopold I's son, Joseph, had been named King of the Romans (1690), and the Emperor's candidate for the Polish throne, August of Saxony, had carried the day over Louis XIV's candidate, the Prince of Conti. Additionally, Prince Eugene of Savoy's decisive victory over the Ottoman Turks
The Spanish Empire was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast territory. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, reaching its maximum extent in the 18th century. signed the treaty on 20 September 1697. Emperor Leopold I, desperate for a continuation of the war so as to strengthen his own claims to the Spanish succession, initially resisted the treaty, but because he was still at war with the Turks, and could not face fighting France alone, he also sought terms and signed on 30 October. The Emperor's finances were in a bad state, and the dissatisfaction aroused by the raising of Hanover to electoral rank had impaired Leopold I's influence in Germany. The Protestant princes had also blamed him for the religious clause in the treaty, which stipulated that the lands of the Reunions that France was to surrender would remain Catholic, even those that had been forcibly converted—a clear defiance of the Westphalia settlement. However, the Emperor had netted an enormous accretion of power: Leopold I's son, Joseph, had been named King of the Romans (1690), and the Emperor's candidate for the Polish throne, August of Saxony, had carried the day over Louis XIV's candidate, the Prince of Conti. Additionally, Prince Eugene of Savoy's decisive victory over the Ottoman Turks The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. at the Battle of Zenta – leading to the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699 – consolidated the Austrian Habsburgs
The Ottoman Empire, also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453. The Ottoman Empire's defeat and the occupation of part of its territory by the Allied Powers in the aftermath of World War I resulted in its partitioning and the loss of its Middle Eastern territories. at the Battle of Zenta – leading to the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699 – consolidated the Austrian Habsburgs The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. and tipped the European balance of power in favour of the Emperor.
The Archduchy of Austria was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire and the nucleus of the Habsburg monarchy. With its capital at Vienna, the archduchy was centered at the Empire's southeastern periphery. The archduchy's history as an imperial state ended with the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806. It was replaced with the Lower and Upper Austria crown lands of the Austrian Empire. and tipped the European balance of power in favour of the Emperor.
The war had allowed William III to destroy militant Jacobitism and helped bring Scotland and Ireland under more direct control. England emerged as a great economic and naval power and became an important player in European affairs, allowing her to use her wealth and energy in world politics to the fullest advantage. William III also continued to prioritise the security of the Dutch Republic, and in 1698 the Dutch garrisoned a series of fortresses in the Spanish Netherlands as a barrier to French attack – future foreign policy would centre on the maintenance and extension of these barrier fortresses. However, the question of the Spanish inheritance was not discussed at Ryswick, and it remained the most important unsolved question of European politics. Within three years Charles II of Spain would be dead, and Louis XIV and the Grand Alliance would again plunge Europe into conflict – the War of the Spanish Succession.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Nine Years' War", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.














