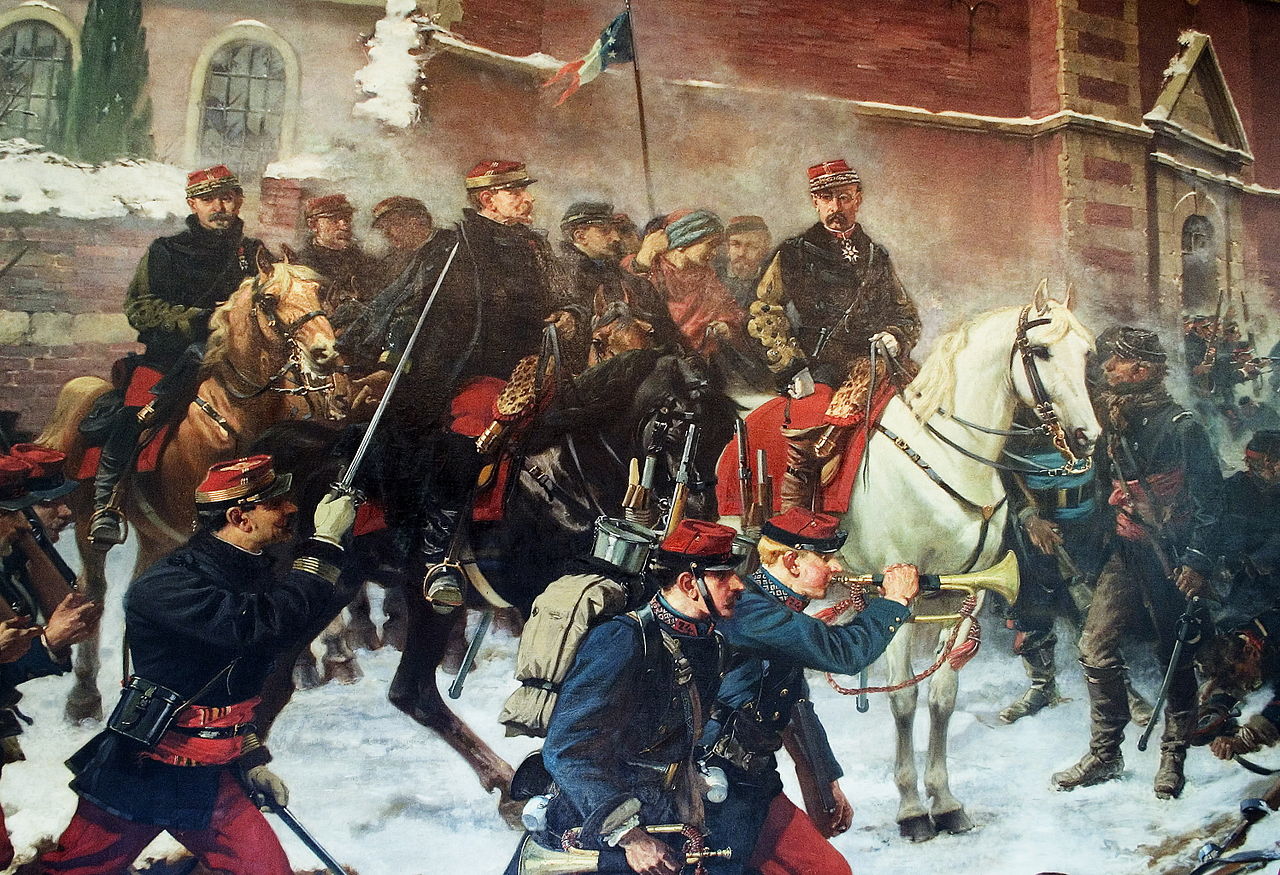
Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)

Causes of War
The causes of the Franco-Prussian War are deeply rooted in the events surrounding the unification of Germany. In the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, Prussia had annexed numerous territories and formed the North German Confederation. This new power destabilized the European balance of power established by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 after the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon III, then the emperor of France Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe., demanded compensations in Belgium
Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe., demanded compensations in Belgium Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country as it exists today was established following the 1830 Belgian Revolution. Belgium has also been the battleground of European powers, earning the moniker the "Battlefield of Europe", a reputation reinforced in the 20th century by both world wars. and on the left bank of the Rhine to secure France's strategic position, which the Prussian chancellor, Otto von Bismarck, flatly refused. Prussia
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country as it exists today was established following the 1830 Belgian Revolution. Belgium has also been the battleground of European powers, earning the moniker the "Battlefield of Europe", a reputation reinforced in the 20th century by both world wars. and on the left bank of the Rhine to secure France's strategic position, which the Prussian chancellor, Otto von Bismarck, flatly refused. Prussia The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. then turned its attention towards the south of Germany, where it sought to incorporate the southern German kingdoms, Bavaria, Württemberg, Baden and Hesse-Darmstadt, into a unified Prussia-dominated Germany. France was strongly opposed to any further alliance of German states, which would have significantly strengthened the Prussian military.
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. then turned its attention towards the south of Germany, where it sought to incorporate the southern German kingdoms, Bavaria, Württemberg, Baden and Hesse-Darmstadt, into a unified Prussia-dominated Germany. France was strongly opposed to any further alliance of German states, which would have significantly strengthened the Prussian military.
In Prussia, some officials considered a war against France both inevitable and necessary to arouse German nationalism in those states that would allow the unification of a great German empire. This aim was epitomized by Prussian Chancellor Otto von Bismarck's later statement: "I did not doubt that a Franco-German war must take place before the construction of a United Germany could be realised." Bismarck also knew that France should be the aggressor in the conflict to bring the southern German states to side with Prussia, hence giving Germans numerical superiority. Many Germans also viewed the French as the traditional destabilizer of Europe, and sought to weaken France to prevent further breaches of the peace.
The immediate cause of the war resided in the candidacy of Leopold of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, a Prussian prince, to the throne of Spain Spain or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country primarily located in southwestern Europe with parts of territory in the Atlantic Ocean and across the Mediterranean Sea. A major country of the Age of Discovery, Spain began the colonization of the New World in 1492 developing one of the largest empires in history and underpinned the emergence of a global trading system primarily fuelled by precious metals.. France feared encirclement by an alliance between Prussia and Spain. The Hohenzollern prince's candidacy was withdrawn under French diplomatic pressure, but Otto von Bismarck goaded the French into declaring war by altering a telegram sent by William I. Releasing the Ems Dispatch to the public, Bismarck made it sound as if the king had treated the French envoy in a demeaning fashion, which inflamed public opinion in France.
Spain or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country primarily located in southwestern Europe with parts of territory in the Atlantic Ocean and across the Mediterranean Sea. A major country of the Age of Discovery, Spain began the colonization of the New World in 1492 developing one of the largest empires in history and underpinned the emergence of a global trading system primarily fuelled by precious metals.. France feared encirclement by an alliance between Prussia and Spain. The Hohenzollern prince's candidacy was withdrawn under French diplomatic pressure, but Otto von Bismarck goaded the French into declaring war by altering a telegram sent by William I. Releasing the Ems Dispatch to the public, Bismarck made it sound as if the king had treated the French envoy in a demeaning fashion, which inflamed public opinion in France.
Some historians argue that Napoleon III also sought war, particularly as a result of the diplomatic failure, in 1866, to obtain any concessions following the Austro-Prussian War, and he believed he would win a conflict with Prussia. They also argue that he wanted a war to resolve growing domestic political problems. Other historians, notably French historian Pierre Milza, dispute this. On 8 May 1870, shortly before the war, French voters had overwhelmingly supported Napoleon III's program in a national plebiscite, with 7,358,000 votes yes against 1,582,000 votes no, an increase of support of two million votes since the legislative elections in 1869. According to Milza, the Emperor had no need for a war to increase his popularity.
The Ems telegram had exactly the effect on French public opinion that Bismarck had intended. "This text produced the effect of a red flag on the Gallic bull", Bismarck later wrote. Gramont, the French foreign minister, declared that he felt "he had just received a slap". The leader of the monarchists in Parliament, Adolphe Thiers, spoke for moderation, arguing that France had won the diplomatic battle and there was no reason for war, but he was drowned out by cries that he was a traitor and a Prussian. Napoleon's new prime minister, Emile Ollivier, declared that France had done all that it could humanly and honorably do to prevent the war, and that he accepted the responsibility "with a light heart." A crowd of 15–20,000 people, carrying flags and patriotic banners, marched through the streets of Paris, demanding war. On 19 July 1870 a declaration of war was sent to the Prussian government. The southern German states immediately sided with Prussia.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.