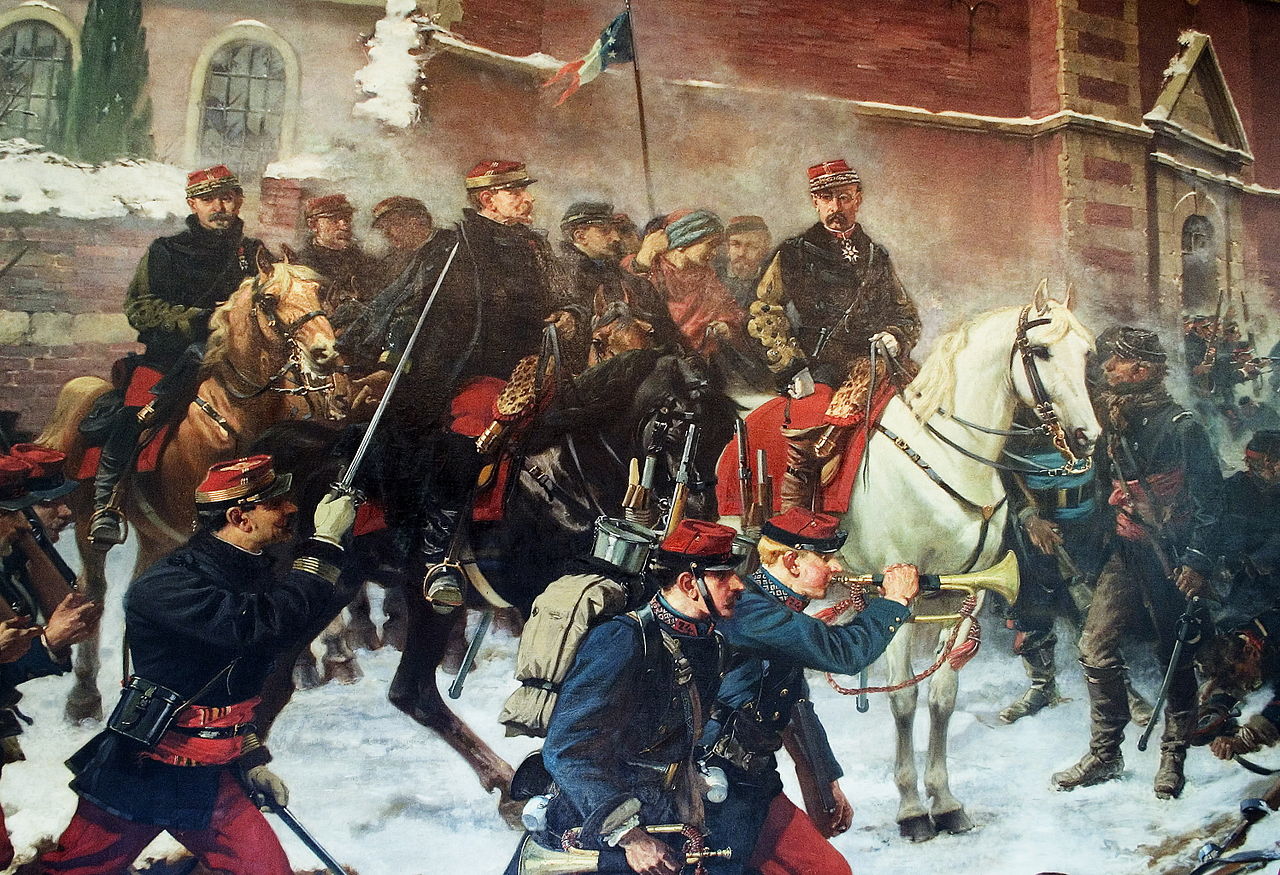
Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)

Battle of Wissembourg
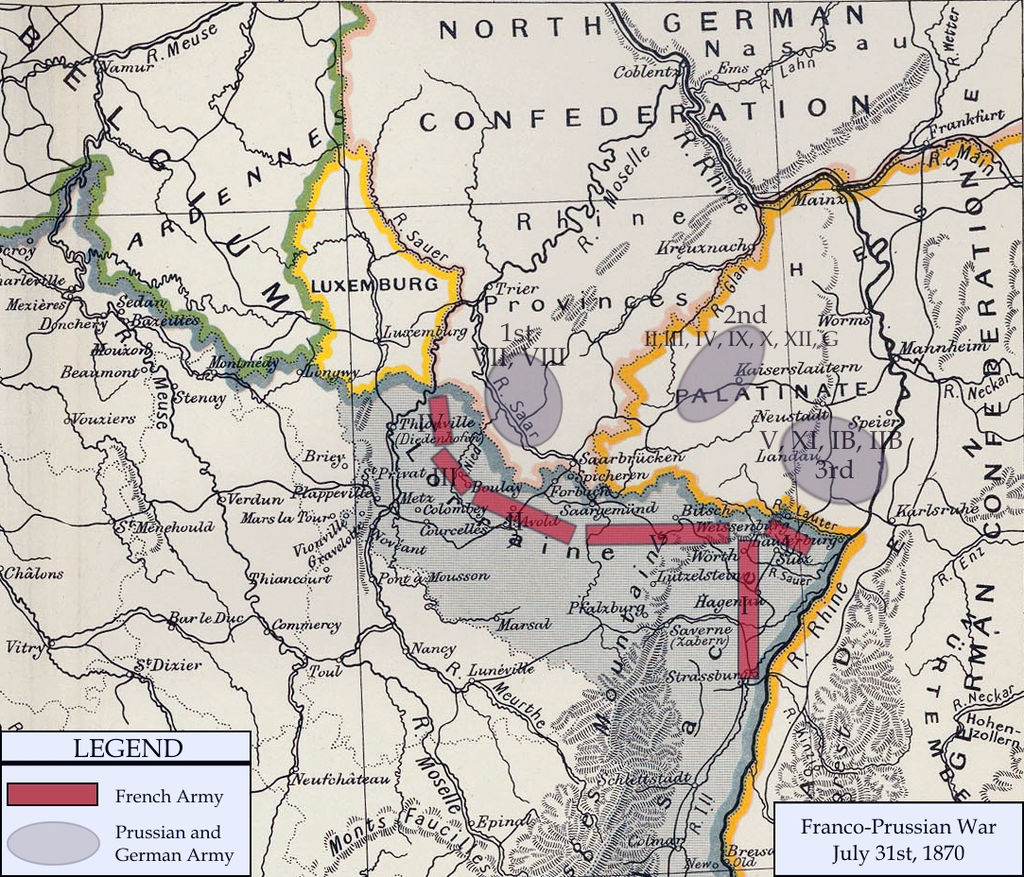
Prussian Army Advance
Upon learning from captured Prussian soldiers and a local area police chief, that the Prussian Crown Prince's Third Army was just 30 miles (48 km) from Saarbrücken near the town of Wissembourg, General Le Bœuf and Napoleon III decided to retreat to defensive positions. General Frossard, without instructions, hastily withdrew the elements of the Army of the Rhine in Saarbrücken back to Spicheren and Forbach.
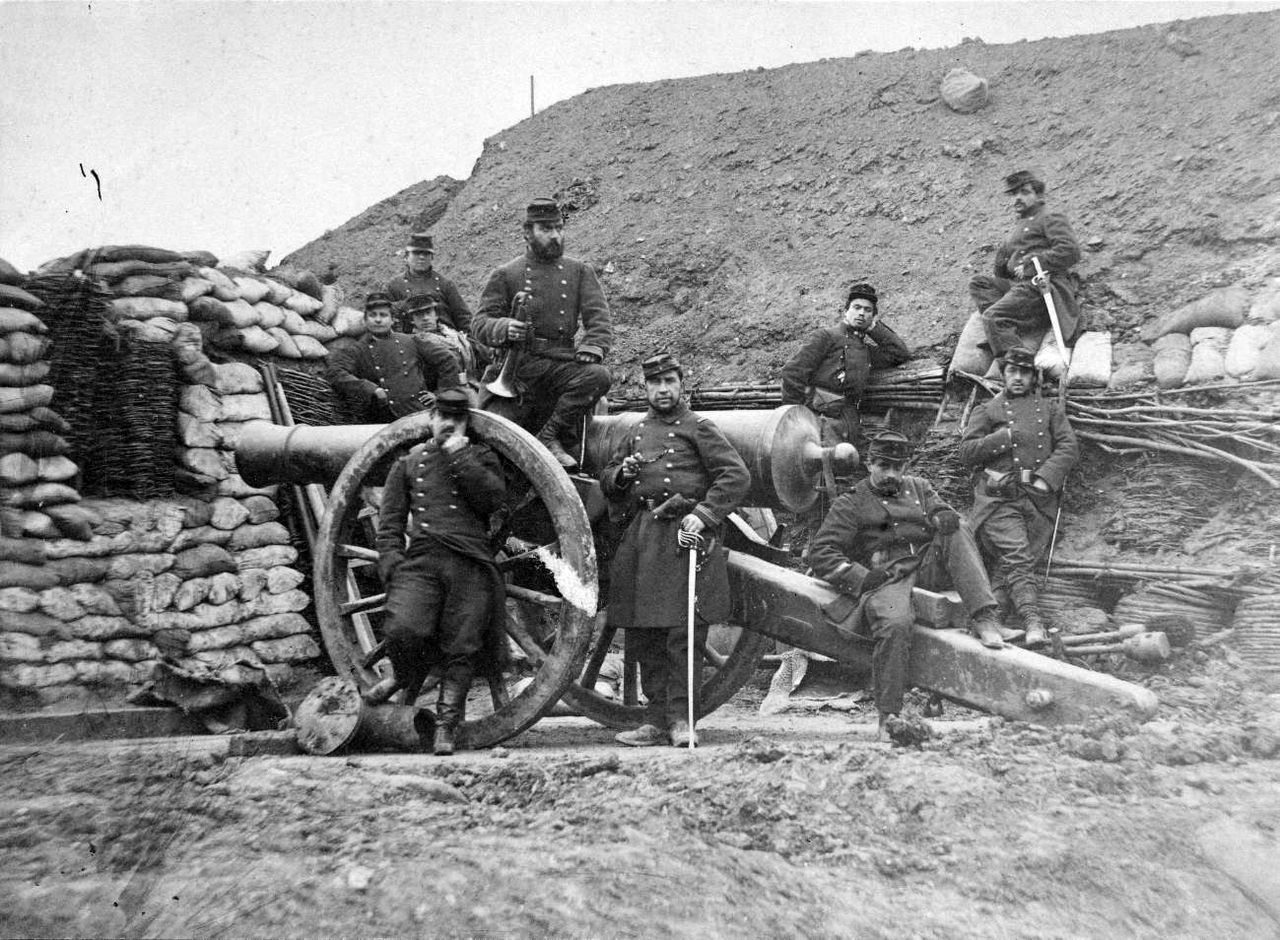

French muzzle-loading artillery in position during the Franco-Prussian War

French muzzle-loading artillery in position during the Franco-Prussian War
( Click image to enlarge)
Marshal MacMahon, now closest to Wissembourg, spread his four divisions over 20 miles (32 km) to react to any Prussian The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. invasion. This organization of forces was due to a lack of supplies, forcing each division to seek out basic provisions along with the representatives of the army supply arm that was supposed to aid them. What made a bad situation much worse was the conduct of General Auguste-Alexandre Ducrot, commander of the 1st Division. He told General Abel Douay, commander of the 2nd Division, on 1 August that "The information I have received makes me suppose that the enemy has no considerable forces very near his advance posts, and has no desire to take the offensive". Two days later, he told MacMahon that he had not found "a single enemy post ... it looks to me as if the menace of the Bavarians is simply bluff". Even though Ducrot shrugged off the possibility of an attack by the Germans, MacMahon tried to warn the other divisions of his army, without success.
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. invasion. This organization of forces was due to a lack of supplies, forcing each division to seek out basic provisions along with the representatives of the army supply arm that was supposed to aid them. What made a bad situation much worse was the conduct of General Auguste-Alexandre Ducrot, commander of the 1st Division. He told General Abel Douay, commander of the 2nd Division, on 1 August that "The information I have received makes me suppose that the enemy has no considerable forces very near his advance posts, and has no desire to take the offensive". Two days later, he told MacMahon that he had not found "a single enemy post ... it looks to me as if the menace of the Bavarians is simply bluff". Even though Ducrot shrugged off the possibility of an attack by the Germans, MacMahon tried to warn the other divisions of his army, without success.
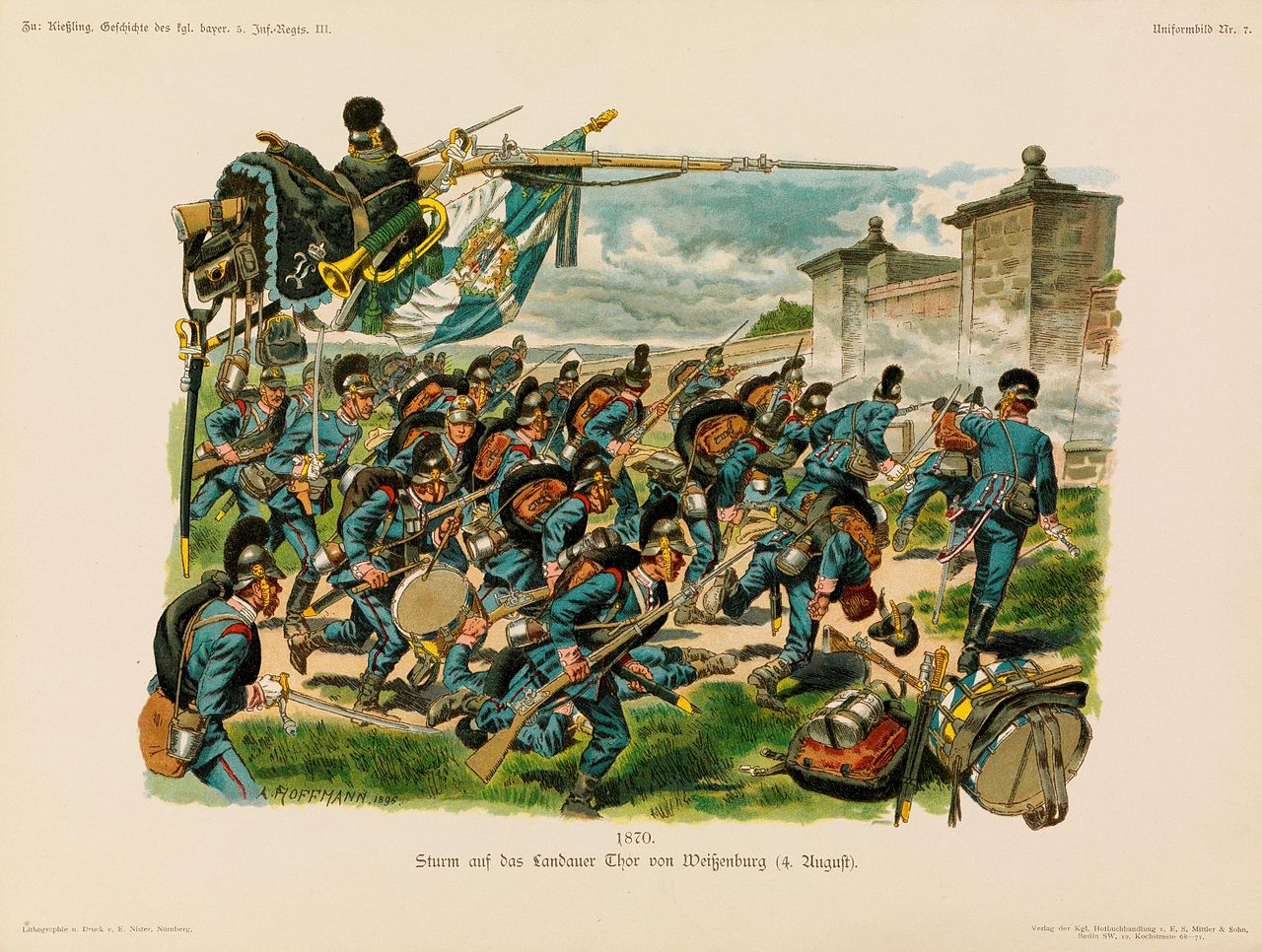

Bavarian infantry at the battle of Wissembourg, 1870

Bavarian infantry at the battle of Wissembourg, 1870
( Click image to enlarge)
The first action of the Franco-Prussian War took place on 4 August 1870. This battle saw the unsupported division of General Douay of I Corps, with some attached cavalry, which was posted to watch the border, attacked in overwhelming but uncoordinated fashion by the German 3rd Army. During the day, elements of a Bavarian and two Prussian corps became engaged and were aided by Prussian artillery, which blasted holes in the defenses of the town. Douay held a very strong position initially, thanks to the accurate long-range fire of the Chassepots but his force was too thinly stretched to hold it. Douay was killed in the late morning when a caisson of the divisional mitrailleuse battery exploded near him; the encirclement of the town by the Prussians threatened the French avenue of retreat.
The fighting within the town had become extremely intense, becoming a door to door battle of survival. Despite a never-ending attack of Prussian infantry, the soldiers of the 2nd Division kept to their positions. The people of the town of Wissembourg finally surrendered to the Germans. The French Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe. troops who did not surrender retreated westward, leaving behind 1,000 dead and wounded and another 1,000 prisoners and all of their remaining ammunition. The final attack by the Prussian troops also cost c. 1,000 casualties. The German cavalry then failed to pursue the French and lost touch with them. The attackers had an initial superiority of numbers, a broad deployment which made envelopment highly likely but the effectiveness of French Chassepot rifle-fire inflicted costly repulses on infantry attacks, until the French infantry had been extensively bombarded by the Prussian artillery.
Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe. troops who did not surrender retreated westward, leaving behind 1,000 dead and wounded and another 1,000 prisoners and all of their remaining ammunition. The final attack by the Prussian troops also cost c. 1,000 casualties. The German cavalry then failed to pursue the French and lost touch with them. The attackers had an initial superiority of numbers, a broad deployment which made envelopment highly likely but the effectiveness of French Chassepot rifle-fire inflicted costly repulses on infantry attacks, until the French infantry had been extensively bombarded by the Prussian artillery.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.