Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)

Battle of Wörth
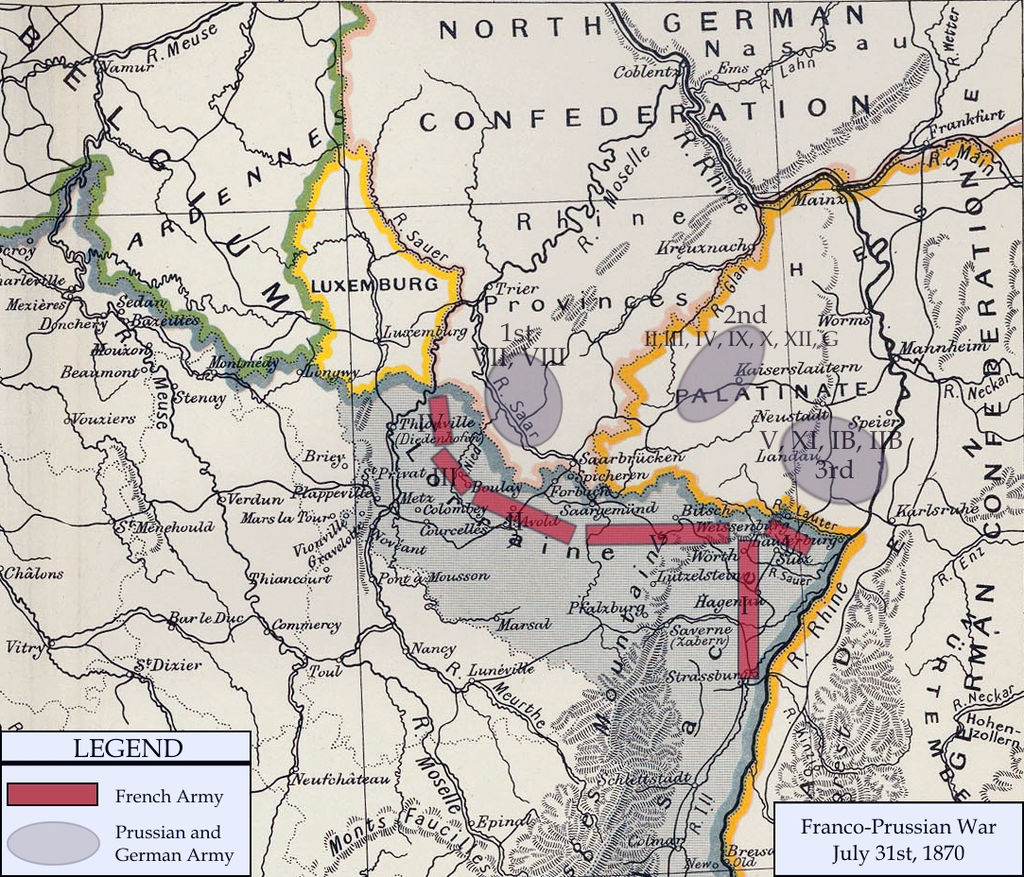
The Battle of Wörth (also known as Fröschwiller or Reichshoffen) began when the two armies clashed again on 6 August near Wörth in the town of Fröschwiller, about 10 miles (16 km) from Wissembourg. The Crown Prince of Prussia's 3rd army had, on the quick reaction of his Chief of Staff General von Blumenthal, drawn reinforcements which brought its strength up to 140,000 troops.
The French Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe. had been slowly reinforced and their force numbered only 35,000. Although badly outnumbered, the French defended their position just outside Fröschwiller. By afternoon, the Germans had suffered c. 10,500 killed or wounded and the French had lost a similar number of casualties and another c. 9,200 men taken prisoner, a loss of about 50%.
Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe. had been slowly reinforced and their force numbered only 35,000. Although badly outnumbered, the French defended their position just outside Fröschwiller. By afternoon, the Germans had suffered c. 10,500 killed or wounded and the French had lost a similar number of casualties and another c. 9,200 men taken prisoner, a loss of about 50%.
The Germans captured Fröschwiller which sat on a hilltop in the centre of the French line. Having lost any hope for victory and facing a massacre, the French army disengaged and retreated in a westerly direction towards Bitche and Saverne, hoping to join French forces on the other side of the Vosges mountains. The German 3rd army did not pursue the French but remained in Alsace and moved slowly south, attacking and destroying the French garrisons in the vicinity.

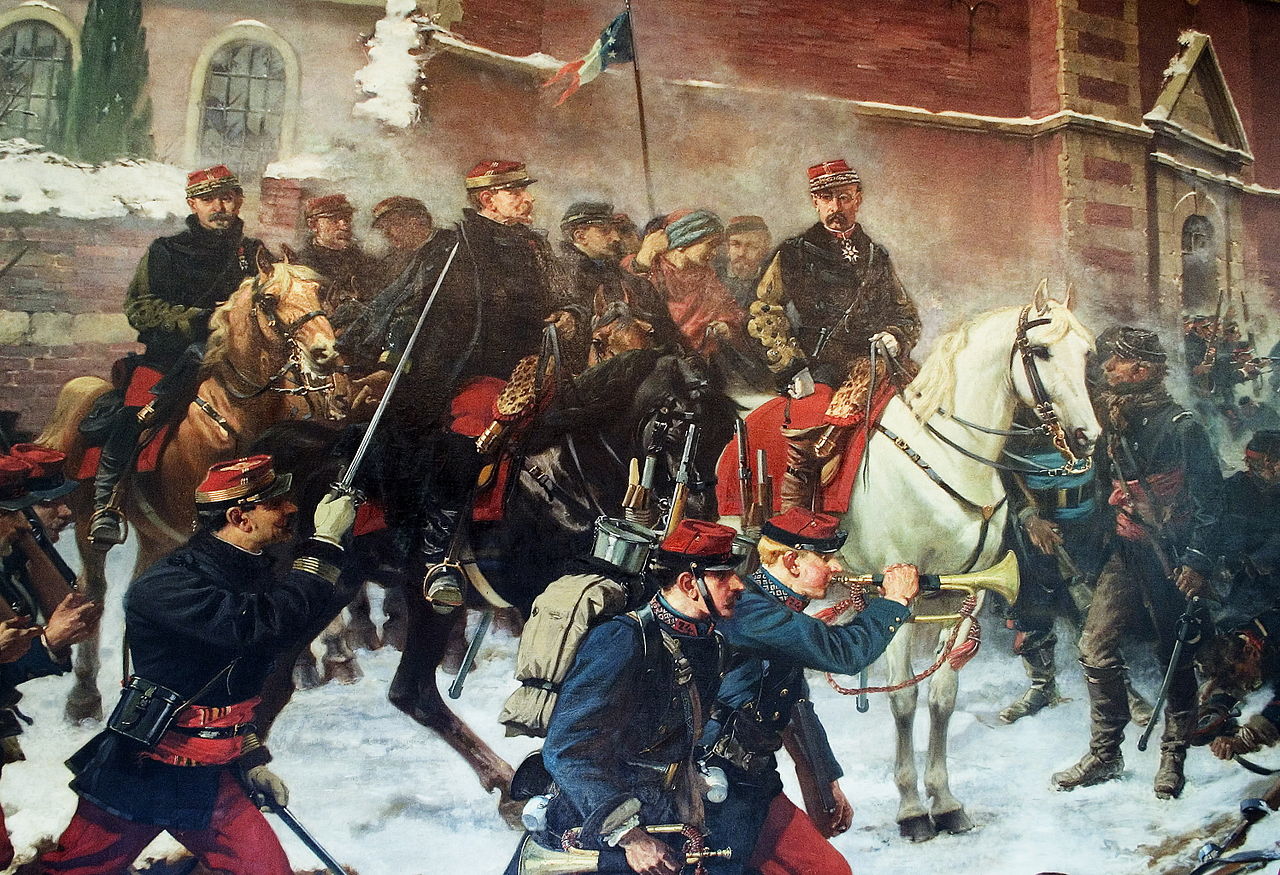
Aimé Morot's La bataille de Reichshoffen, 1887

Aimé Morot's La bataille de Reichshoffen, 1887
( Click image to enlarge)
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.