Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)

French Army Incursion
Preparations for the Offensive
On 28 July 1870 Napoleon III left Paris for Metz and assumed command of the newly titled Army of the Rhine, some 202,448 strong and expected to grow as the French mobilization progressed. Marshal MacMahon took command of I Corps (4 infantry divisions) near Wissembourg, Marshal François Canrobert brought VI Corps (four infantry divisions) to Châlons-sur-Marne in northern France as a reserve and to guard against a Prussian advance through Belgium Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country as it exists today was established following the 1830 Belgian Revolution. Belgium has also been the battleground of European powers, earning the moniker the "Battlefield of Europe", a reputation reinforced in the 20th century by both world wars..
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country as it exists today was established following the 1830 Belgian Revolution. Belgium has also been the battleground of European powers, earning the moniker the "Battlefield of Europe", a reputation reinforced in the 20th century by both world wars..
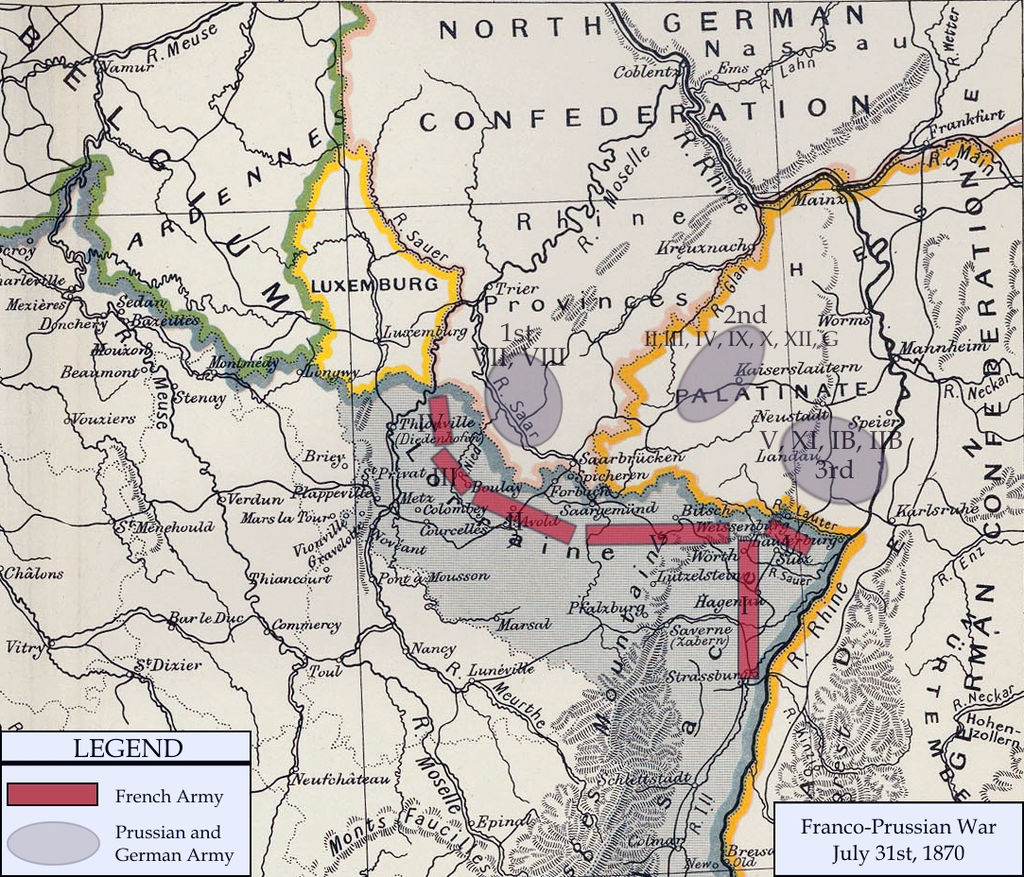
Map of German and French armies near their common border on 31 July 1870

Map of German and French armies near their common border on 31 July 1870
( Click image to enlarge)
A pre-war plan laid out by the late Marshal Niel called for a strong French Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe. offensive from Thionville towards Trier and into the Prussian Rhineland. This plan was discarded in favour of a defensive plan by Generals Charles Frossard and Bartélemy Lebrun, which called for the Army of the Rhine to remain in a defensive posture near the German border and repel any Prussian offensive. As Austria along with Bavaria, Württemberg and Baden were expected to join in a revenge war against Prussia
Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe. offensive from Thionville towards Trier and into the Prussian Rhineland. This plan was discarded in favour of a defensive plan by Generals Charles Frossard and Bartélemy Lebrun, which called for the Army of the Rhine to remain in a defensive posture near the German border and repel any Prussian offensive. As Austria along with Bavaria, Württemberg and Baden were expected to join in a revenge war against Prussia The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin., I Corps would invade the Bavarian Palatinate and proceed to "free" the South German states in concert with Austro-Hungarian forces. VI Corps would reinforce either army as needed.
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin., I Corps would invade the Bavarian Palatinate and proceed to "free" the South German states in concert with Austro-Hungarian forces. VI Corps would reinforce either army as needed.
Unfortunately for Frossard's plan, the Prussian army was mobilizing far more rapidly than expected. The Austro-Hungarians Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. Austria-Hungary was one of the Central Powers in World War I, which began with an Austro-Hungarian war declaration on the Kingdom of Serbia on 28 July 1914., still smarting after their defeat by Prussia in the Austro-Prussian War, were treading carefully before stating that they would only commit to France's cause if the southern Germans viewed the French positively. This did not materialize as the South German states had come to Prussia's aid and were mobilizing their armies against France.
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. Austria-Hungary was one of the Central Powers in World War I, which began with an Austro-Hungarian war declaration on the Kingdom of Serbia on 28 July 1914., still smarting after their defeat by Prussia in the Austro-Prussian War, were treading carefully before stating that they would only commit to France's cause if the southern Germans viewed the French positively. This did not materialize as the South German states had come to Prussia's aid and were mobilizing their armies against France.

These books are available for download with Apple Books on your Mac or iOS device
Occupation of Saarbrücken
Napoleon III was under immense domestic pressure to launch an offensive before the full might of Moltke's forces was mobilized and deployed. Reconnaissance by Frossard's forces had identified only the Prussian 16th Infantry Division guarding the border town of Saarbrücken, right before the entire Army of the Rhine. Accordingly, on 31 July the Army marched forward toward the Saar River to seize Saarbrücken.

French Lancers and Cuirassiers guarding captured Bavarian soldiers
General Frossard's II Corps and Marshal Bazaine's III Corps crossed the German border on 2 August, and began to force the Prussian 40th Regiment of the 16th Infantry Division from the town of Saarbrücken with a series of direct attacks. The Chassepot rifle proved its worth against the Dreyse rifle, with French riflemen regularly outdistancing their Prussian counterparts in the skirmishing around Saarbrücken. However the Prussians resisted strongly, and the French suffered 86 casualties to the Prussian 83 casualties. Saarbrücken also proved to be a major obstacle in terms of logistics. Only one railway there led to the German hinterland but could be easily defended by a single force, and the only river systems in the region ran along the border instead of inland. While the French hailed the invasion as the first step towards the Rhineland and later Berlin, General Le Bœuf and Napoleon III were receiving alarming reports from foreign news sources of Prussian and Bavarian armies massing to the southeast in addition to the forces to the north and northeast.
Moltke had indeed massed three armies in the area—the Prussian First Army with 50,000 men, commanded by General Karl von Steinmetz opposite Saarlouis, the Prussian Second Army with 134,000 men commanded by Prince Friedrich Karl opposite the line Forbach-Spicheren, and the Prussian Third Army with 120,000 men commanded by Crown Prince Friedrich Wilhelm, poised to cross the border at Wissembourg.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.











