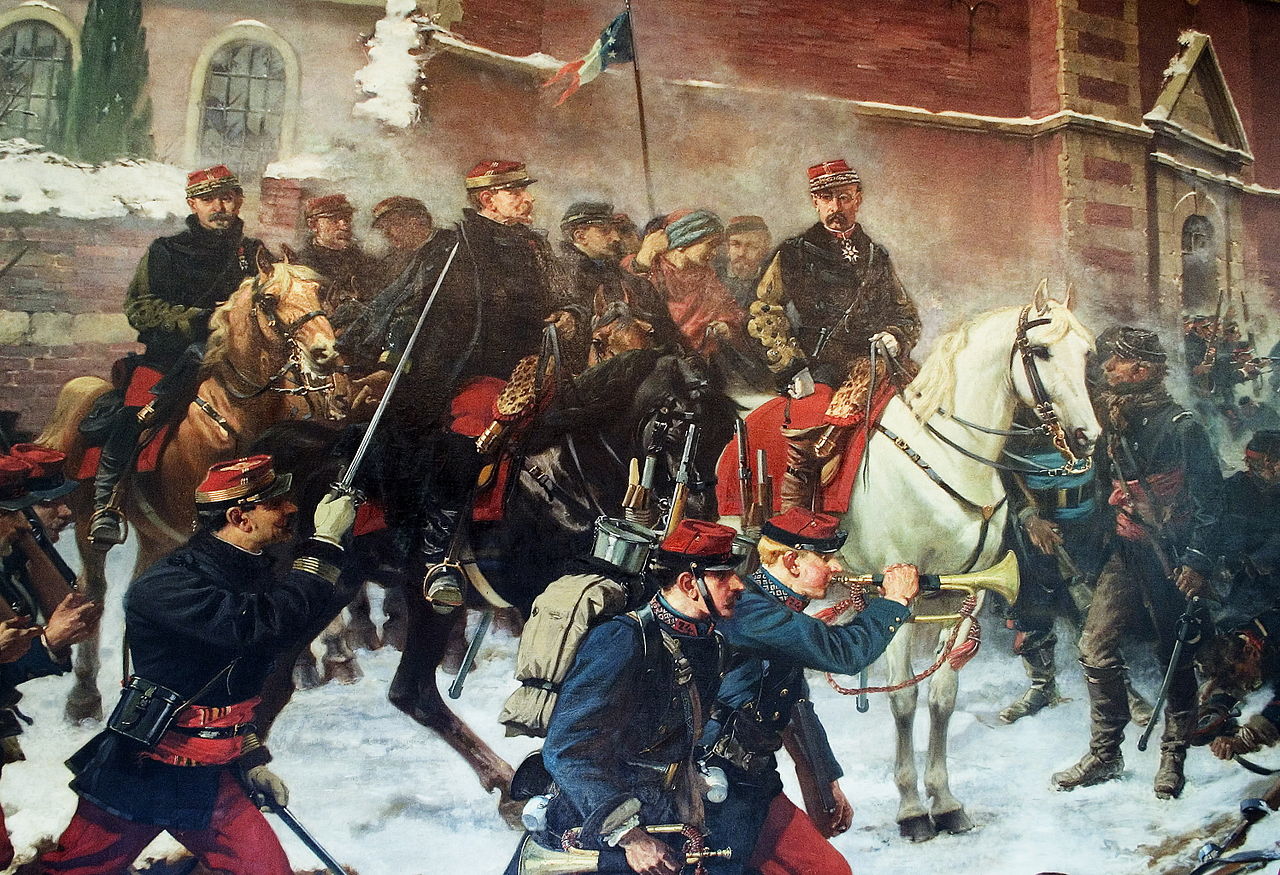
Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)

The War at Sea
Blockade
When the war began, the French government ordered a blockade of the North German coasts, which the small North German navy (Norddeutsche Bundesmarine) with only five ironclads and various minor vessels could do little to oppose. For most of the war, the three largest German ironclads were out of service with engine troubles; only the turret ship SMS Arminius was available to conduct operations. By the time engine repairs had been completed, the French fleet had already departed. The blockade proved only partially successful due to crucial oversights by the planners in Paris. Reservists that were supposed to be at the ready in case of war, were working in the Newfoundland fisheries or in Scotland. Only part of the 470-ship French Navy put to sea on 24 July. Before long, the French navy ran short of coal, needing 200 short tons (180 t) per day and having a bunker capacity in the fleet of only 250 short tons (230 t). A blockade of Wilhelmshaven failed and conflicting orders about operations in the Baltic Sea or a return to France Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe., made the French naval efforts futile. Spotting a blockade-runner became unwelcome because of the question du charbon; pursuit of Prussian ships quickly depleted the coal reserves of the French ships.
Second French Empire was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Paris with broad boulevards, striking public buildings, and elegant residential districts for upscale Parisians. In international policy, Napoleon III tried to emulate his uncle Napoleon I, engaging in numerous imperial ventures around the world as well as several wars in Europe., made the French naval efforts futile. Spotting a blockade-runner became unwelcome because of the question du charbon; pursuit of Prussian ships quickly depleted the coal reserves of the French ships.

French warships at sea in 1870
To relieve pressure from the expected German attack into Alsace-Lorraine, Napoleon III and the French high command planned a seaborne invasion of northern Germany as soon as war began. The French expected the invasion to divert German troops and to encourage Denmark to join in the war, with its 50,000-strong army and the Royal Danish Navy. It was discovered that Prussia The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. had recently built defences around the big North German ports, including coastal artillery batteries with Krupp heavy artillery, which with a range of 4,000 yards (3,700 m), had double the range of French naval guns. The French Navy lacked the heavy guns to engage the coastal defences and the topography of the Prussian coast made a seaborne invasion of northern Germany impossible.
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1871 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. had recently built defences around the big North German ports, including coastal artillery batteries with Krupp heavy artillery, which with a range of 4,000 yards (3,700 m), had double the range of French naval guns. The French Navy lacked the heavy guns to engage the coastal defences and the topography of the Prussian coast made a seaborne invasion of northern Germany impossible.
The French Marines and naval infantry intended for the invasion of northern Germany were dispatched to reinforce the French Army of Châlons and fell into captivity at Sedan along with Napoleon III. A shortage of officers, following the capture of most of the professional French army at the Siege of Metz and at the Battle of Sedan, led naval officers to be sent from their ships to command hastily assembled reservists of the Garde Mobile. As the autumn storms of the North Sea forced the return of more of the French ships, the blockade of the north German ports diminished and in September 1870 the French navy abandoned the blockade for the winter. The rest of the navy retired to ports along the English Channel and remained in port for the rest of the war.
HISTORY

RESOURCES
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Franco-Prussian War (1870 to 1871)", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0.
© Stories Preschool. All Rights Reserved.